What is the difference in the functioning between rough ER and
... The ER can attach itself to the cell membrane to move proteins out of the cell. ...
... The ER can attach itself to the cell membrane to move proteins out of the cell. ...
Cell culture on high-extension surfaces
... Cell culture on high-extension surfaces: Novel technology in support of regenerative medicine Thomas M. Quinn and Derek H. Rosenzweig While seeking ways for improved culture of chondrocytes for cartilage tissue engineering, we have developed novel technology for cell culture on extendable surfaces. ...
... Cell culture on high-extension surfaces: Novel technology in support of regenerative medicine Thomas M. Quinn and Derek H. Rosenzweig While seeking ways for improved culture of chondrocytes for cartilage tissue engineering, we have developed novel technology for cell culture on extendable surfaces. ...
Plant Cells and Tissues
... Only ~16 of 92 naturally occurring elements are essential to most plants ...
... Only ~16 of 92 naturally occurring elements are essential to most plants ...
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
... – Mitochondria and Chloroplasts have their own DNA!? American biologist Lynn Margulis has suggested that these organelles are descendants of ancient, independent prokaryotes. The ancestors of modern-day eukaryotes may have developed symbiotic relationships with such prokaryotes millions of years ago ...
... – Mitochondria and Chloroplasts have their own DNA!? American biologist Lynn Margulis has suggested that these organelles are descendants of ancient, independent prokaryotes. The ancestors of modern-day eukaryotes may have developed symbiotic relationships with such prokaryotes millions of years ago ...
THINK ABOUT IT
... It was not until the mid-1600s that scientists began to use microscopes to observe living things. The research of a few famous scientists led to the development of The Cell Theory. Robert Hooke (England-1665) • Used an early compound microscope to look at a nonliving thin slice of cork (plant materi ...
... It was not until the mid-1600s that scientists began to use microscopes to observe living things. The research of a few famous scientists led to the development of The Cell Theory. Robert Hooke (England-1665) • Used an early compound microscope to look at a nonliving thin slice of cork (plant materi ...
Cells and Cell Organelles
... (1) More advanced, larger, and contain organelles. These cells have a nucleus. Organisms made of these cells include protists, fungi, plants, and animals (including humans). 2.Organelles allow many activities to take place within the same cell other reactions take place on membrane surfaces and euka ...
... (1) More advanced, larger, and contain organelles. These cells have a nucleus. Organisms made of these cells include protists, fungi, plants, and animals (including humans). 2.Organelles allow many activities to take place within the same cell other reactions take place on membrane surfaces and euka ...
cell structure location description function
... Breaks down larger food molecules into smaller molecules Digests old cell parts ...
... Breaks down larger food molecules into smaller molecules Digests old cell parts ...
cells final - educ399portfolioedwinawilson
... influence the activity of other cells that may be far from where the hormone was produced. For a hormone to affect a target cell, it must attach to a receptor protein on the target cell membrane or inside the cell. Hormone binding to a receptor triggers an intricate set of biochemical interactions t ...
... influence the activity of other cells that may be far from where the hormone was produced. For a hormone to affect a target cell, it must attach to a receptor protein on the target cell membrane or inside the cell. Hormone binding to a receptor triggers an intricate set of biochemical interactions t ...
1. Miller Urey experiment (30 minutes)
... Control group: The group of specimens that are placed in the “normal” conditions for comparison to the experimental group to determine if there was an effect based on the independent variable. Covalent bond: An intramolecular bond where atoms are sharing electrons equally. Cytokinesis: After mitosis ...
... Control group: The group of specimens that are placed in the “normal” conditions for comparison to the experimental group to determine if there was an effect based on the independent variable. Covalent bond: An intramolecular bond where atoms are sharing electrons equally. Cytokinesis: After mitosis ...
Cells and Cell Theory
... Example: We maintain our body temperature by shivering to get warm and sweating to cool off. ...
... Example: We maintain our body temperature by shivering to get warm and sweating to cool off. ...
cell membrane
... The protist Vorticelli feeding with cilia Movement of substances like mucus ...
... The protist Vorticelli feeding with cilia Movement of substances like mucus ...
Patch Clamp Technique
... allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in cells. This discovery made it possible to record the currents of single ion channels for the first time, proving their involvement in fundamental cell processes such as action potential conduction. Erwin Neher and Bert Sakmann developed the patc ...
... allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in cells. This discovery made it possible to record the currents of single ion channels for the first time, proving their involvement in fundamental cell processes such as action potential conduction. Erwin Neher and Bert Sakmann developed the patc ...
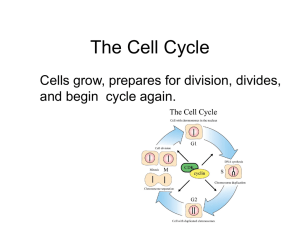
Ch. 10 Flip Book
... processes have occurred inside the cell Ex: doesn’t let the cell enter mitosis until all chromosomes have been replicated ...
... processes have occurred inside the cell Ex: doesn’t let the cell enter mitosis until all chromosomes have been replicated ...
Biology Formative Week 20 2007
... Usually connected to other cells, with a membrane surrounding its genetic material Usually connected to other cells, with no membrane surrounding its genetic material ...
... Usually connected to other cells, with a membrane surrounding its genetic material Usually connected to other cells, with no membrane surrounding its genetic material ...
Cell Theory Rap
... It gives orders kinda like the brain It’s protected by the nuclear membrane Around the cell you’ll find another skin The cell membrane holds the whole cell in Its job isn’t simple there’s no doubt It lets some things go in and some things go out Now please don’t lose your science enthusiasm Listen t ...
... It gives orders kinda like the brain It’s protected by the nuclear membrane Around the cell you’ll find another skin The cell membrane holds the whole cell in Its job isn’t simple there’s no doubt It lets some things go in and some things go out Now please don’t lose your science enthusiasm Listen t ...
Passive vs Active Transport
... • Channels (are specific) help molecule or ions enter or leave the cell • Channels usually are transport proteins (aquaporins facilitate the movement of water) • No energy is used ...
... • Channels (are specific) help molecule or ions enter or leave the cell • Channels usually are transport proteins (aquaporins facilitate the movement of water) • No energy is used ...
Looking Inside Cells 3.2 Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus
... 9. Watch the video. Answer the questions. a. How long ago were tiny organs found in the cytoplasm of a cell? _________ b. What was the name given to these tiny organs? ______________________ 10. What are the 3 basic functions of the organelles inside the cytoplasm? a. Produce _______________ b. ____ ...
... 9. Watch the video. Answer the questions. a. How long ago were tiny organs found in the cytoplasm of a cell? _________ b. What was the name given to these tiny organs? ______________________ 10. What are the 3 basic functions of the organelles inside the cytoplasm? a. Produce _______________ b. ____ ...
TheHumanCheekCellANSWERKEY
... All living things are made of cells Cells can only come from other cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function 2. Describe or define each of the following: Cell membrane: Outer boundary of the cell Cytoplasm: Fluid within the cell Nucleus: Control center of the cell Organelle: Cell stru ...
... All living things are made of cells Cells can only come from other cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function 2. Describe or define each of the following: Cell membrane: Outer boundary of the cell Cytoplasm: Fluid within the cell Nucleus: Control center of the cell Organelle: Cell stru ...
Participating Laboratory: Stem Cell Research Center
... mouse antiserum raised against human skin fibroblast cells. Guinea pig complement was used. ...
... mouse antiserum raised against human skin fibroblast cells. Guinea pig complement was used. ...
BIOLOGY 1 TEST REVIEW SHEET
... 18. What is facilitated diffusion? Is this passive or active transport? What does facilitated diffusion help move across the membrane? How? 19. What is a concentration gradient? What does dynamic equilibrium mean? 20. What is the difference between passive and active transport? 21. What is an isoton ...
... 18. What is facilitated diffusion? Is this passive or active transport? What does facilitated diffusion help move across the membrane? How? 19. What is a concentration gradient? What does dynamic equilibrium mean? 20. What is the difference between passive and active transport? 21. What is an isoton ...
cell specialization
... • probably evolved many times • provides opportunity of specialization of cells • a step above colonial organization • cells perform special functions • differentiation of cells • stem cells (pluripotent) • defined by pattern of regulated gene expression ...
... • probably evolved many times • provides opportunity of specialization of cells • a step above colonial organization • cells perform special functions • differentiation of cells • stem cells (pluripotent) • defined by pattern of regulated gene expression ...