Cell story book project
... Cell Story Book Project due January 14, 2010 Imagine that you work for the Shaps Book Company. Your editor wants you to develop a children’s book about cells and their parts. The book should be something that a 2nd-4th grader would be able to understand. The editor gives you a list of the book requi ...
... Cell Story Book Project due January 14, 2010 Imagine that you work for the Shaps Book Company. Your editor wants you to develop a children’s book about cells and their parts. The book should be something that a 2nd-4th grader would be able to understand. The editor gives you a list of the book requi ...
Cell Structure
... Cytoplasm – gelatin-like substance between the cell membrane and nucleus (cytosol) Mitochondria – site of energy production (ATP); two layers • Outer layer – barrier • Inner layer – called christae • Has its own DNA ...
... Cytoplasm – gelatin-like substance between the cell membrane and nucleus (cytosol) Mitochondria – site of energy production (ATP); two layers • Outer layer – barrier • Inner layer – called christae • Has its own DNA ...
Mitosis PPT
... as chromosomes • Nuclear membrane dissolves • Centrioles migrate to opposite poles • Spindle fibers form Easy to remember- Prophase- proceeding into mitosis ...
... as chromosomes • Nuclear membrane dissolves • Centrioles migrate to opposite poles • Spindle fibers form Easy to remember- Prophase- proceeding into mitosis ...
HW 11/3 Mitosis
... At the end of interphase, the cell has made duplicates of everything in preparation for dividing. As the cell begins to divide, it goes through a process called mitosis. In mitosis, the nucleus divides followed by the cytoplasm dividing, resulting in two cells. After the cytoplasm divides, cell divi ...
... At the end of interphase, the cell has made duplicates of everything in preparation for dividing. As the cell begins to divide, it goes through a process called mitosis. In mitosis, the nucleus divides followed by the cytoplasm dividing, resulting in two cells. After the cytoplasm divides, cell divi ...
Animal cells
... 7-Mitochondria - power producers and the sites of cellular respiration. 8-Nucleus - membrane bound structure that contains the cell's hereditary information. 9-Nucleolus - structure within the nucleus that helps in the synthesis of ribosomes. ...
... 7-Mitochondria - power producers and the sites of cellular respiration. 8-Nucleus - membrane bound structure that contains the cell's hereditary information. 9-Nucleolus - structure within the nucleus that helps in the synthesis of ribosomes. ...
The Cell Notes
... nucleus. It is made of DNA bound to protein, and carries the hereditary information in the cell Chromosomes- chromatin condenses to form chromosomes during cell division Nucleolus- Small dense region inside the nucleus that is responsible for the assembly of ribosomes, which make proteins Nuclear me ...
... nucleus. It is made of DNA bound to protein, and carries the hereditary information in the cell Chromosomes- chromatin condenses to form chromosomes during cell division Nucleolus- Small dense region inside the nucleus that is responsible for the assembly of ribosomes, which make proteins Nuclear me ...
Cells
... protects the cell and gives it shape. • Plants, bacteria, fungi and some protists have Cell Walls. ...
... protects the cell and gives it shape. • Plants, bacteria, fungi and some protists have Cell Walls. ...
Biology Cell Test
... 7. Which of the following orgamsms are prokaryotes? a. plants c. bacteria b. animals d. all of the above 8. Which of the following is NOT found in the nucleus? a. cytoplasm c. chromatin b. nucleolus d. DNA 9. Which organelle breaks down food into molecules the cell can use? a. Golgi apparatus c. end ...
... 7. Which of the following orgamsms are prokaryotes? a. plants c. bacteria b. animals d. all of the above 8. Which of the following is NOT found in the nucleus? a. cytoplasm c. chromatin b. nucleolus d. DNA 9. Which organelle breaks down food into molecules the cell can use? a. Golgi apparatus c. end ...
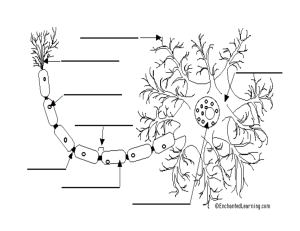
axon diagram
... myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers ...
... myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers ...
Bio07_TR_U03_CH10.QXD
... 7. Sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes. 8. Two new nuclear envelopes form. 9. The nucleolus disappears and the nuclear envelope breaks down. 10. Each chromosome is connected to a spindle fiber. 11. The individual chromosomes move apart. ...
... 7. Sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes. 8. Two new nuclear envelopes form. 9. The nucleolus disappears and the nuclear envelope breaks down. 10. Each chromosome is connected to a spindle fiber. 11. The individual chromosomes move apart. ...
document
... 5. Where in the body would you find ciliated cells (cells with cilia attached)? 6. The cells of the retina have few mitochondria – why do you think this is? ...
... 5. Where in the body would you find ciliated cells (cells with cilia attached)? 6. The cells of the retina have few mitochondria – why do you think this is? ...
Biology Benchmark Study Guide
... 13. What part of a plant cell provides support because it is very rigid? Cell wall 14. What property of the cell membrane describes its ability to move certain materials in and out of the cell? Selective permeability to allow only certain materials to pass through 15. What organelle stores water and ...
... 13. What part of a plant cell provides support because it is very rigid? Cell wall 14. What property of the cell membrane describes its ability to move certain materials in and out of the cell? Selective permeability to allow only certain materials to pass through 15. What organelle stores water and ...
Six Kingdoms of Life
... reproduction, circulation, excretion, movement, control, and coordination, and for protection from disease). Organ system skeletal muscular cardiovascular digestive respiratory nervous excretory ...
... reproduction, circulation, excretion, movement, control, and coordination, and for protection from disease). Organ system skeletal muscular cardiovascular digestive respiratory nervous excretory ...
Cell Transport Notes Learning Targets 8. Explain the significance of
... 10 Explain the terms: hypotonic, hypertonic or isotonic in relationship to the internal environments of cells. ...
... 10 Explain the terms: hypotonic, hypertonic or isotonic in relationship to the internal environments of cells. ...
Review_Cells_ANSWERS_MOD
... hand. They are not to be considered suitable as test answers, for example. 1. What are the three principles of Cell Theory? - All cells come from pre-existing cells, the cell is the smallest living organizational unit, and the organisms are made of one or more cells. 2. List some difference between ...
... hand. They are not to be considered suitable as test answers, for example. 1. What are the three principles of Cell Theory? - All cells come from pre-existing cells, the cell is the smallest living organizational unit, and the organisms are made of one or more cells. 2. List some difference between ...
Anatomy Memorization: Chapter 1
... Organelle = membrane enclose structures with specific functions Cytoskeleton = microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules Microvilli, cilia, flagella = organelle for movement Ribosome = manufactures proteins can be free (floating in cytoplasm) or fixed (on RER) Centrioles = direct movement ...
... Organelle = membrane enclose structures with specific functions Cytoskeleton = microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules Microvilli, cilia, flagella = organelle for movement Ribosome = manufactures proteins can be free (floating in cytoplasm) or fixed (on RER) Centrioles = direct movement ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.