ExamView Pro - Midterm review sheet #3.tst
... a. Prokaryotic cells are the world's smallest cells and probably were the first cells on Earth. b. Eukaryotic cells have many membrane-covered organelles, allowing many different chemical processes to occur at the same time. c. All plants, animals, fungi, and protists are made up of eukaryotic cells ...
... a. Prokaryotic cells are the world's smallest cells and probably were the first cells on Earth. b. Eukaryotic cells have many membrane-covered organelles, allowing many different chemical processes to occur at the same time. c. All plants, animals, fungi, and protists are made up of eukaryotic cells ...
$doc.title
... C. viral DNA takes over and causes the cell to make viral parts (lytic cycle) or it can remain dormant (lysogenic cycle) ...
... C. viral DNA takes over and causes the cell to make viral parts (lytic cycle) or it can remain dormant (lysogenic cycle) ...
Semester Study Guide
... What is an energy pyramid and what is each level of an energy pyramid called? ...
... What is an energy pyramid and what is each level of an energy pyramid called? ...
We are going to take a tour of the cell. and open your “Cel
... 7. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) description and function: ...
... 7. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) description and function: ...
Direct Nuclear Transport of Aptamer-RNA Chimeras to
... of therapeutics rivaling antibodies in binding specificity and affinity at a fraction of their size and with minimal immunogenic activity. Furthermore, aptamer-chimeras (ACs) are developing into potent cell-type specific vectors for delivering RNA or DNA cargoes. However, current methods have limite ...
... of therapeutics rivaling antibodies in binding specificity and affinity at a fraction of their size and with minimal immunogenic activity. Furthermore, aptamer-chimeras (ACs) are developing into potent cell-type specific vectors for delivering RNA or DNA cargoes. However, current methods have limite ...
Life Is Cellular
... 1665- Robert Hooke looked at slices of cork and saw something similar to image H- called them “cells” Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first to observe living microorganisms. -observed living organisms in his mouth ...
... 1665- Robert Hooke looked at slices of cork and saw something similar to image H- called them “cells” Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first to observe living microorganisms. -observed living organisms in his mouth ...
Specialised Cells
... They contain many different types of cells. Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. This is known as cell specialism Not all cells look the same. Some cells have a special shape and features to help them do a certain job. ...
... They contain many different types of cells. Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. This is known as cell specialism Not all cells look the same. Some cells have a special shape and features to help them do a certain job. ...
Cell Structure and Function (Chapter 7)
... Some prokaryotes have them, but most do not Use the energy from sunlight to make energy-rich food ...
... Some prokaryotes have them, but most do not Use the energy from sunlight to make energy-rich food ...
Cell Structure Notes
... Therefore, as a cell grows, its need for oxygen increases faster than its ability to get oxygen. So the cell must divide into smaller cells or suffocate! ...
... Therefore, as a cell grows, its need for oxygen increases faster than its ability to get oxygen. So the cell must divide into smaller cells or suffocate! ...
The cell cycle - U of L Class Index
... gametes (reproductive cells) have only 23 chromosomes (n). ...
... gametes (reproductive cells) have only 23 chromosomes (n). ...
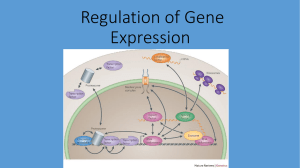
Regulation of Gene Expression
... • Transcriptional Control: the cell can speed up or slow down the transcription of mRNA from the gene that codes for the polypeptide • Post-transcriptional Control: the cell may transcribe the mRNA but break it down before translation. It can also modify the poly-A tail. ...
... • Transcriptional Control: the cell can speed up or slow down the transcription of mRNA from the gene that codes for the polypeptide • Post-transcriptional Control: the cell may transcribe the mRNA but break it down before translation. It can also modify the poly-A tail. ...
Structure: strong, stiff, nonliving layer outside of the cell membrane
... Structure: One of a set of structures found in the nucleus; made of DNA, plus some protein Function: contains DNA which carries hereditary/genetic information Found: Plant & Animal Cells ...
... Structure: One of a set of structures found in the nucleus; made of DNA, plus some protein Function: contains DNA which carries hereditary/genetic information Found: Plant & Animal Cells ...
Chp. 7 PP cells
... in the cell or secretion outside the cell. Lysosomes: small organelles filled with __________ that function in the digestion of lipids, carbs, and proteins. “Cleanup Crew” ...
... in the cell or secretion outside the cell. Lysosomes: small organelles filled with __________ that function in the digestion of lipids, carbs, and proteins. “Cleanup Crew” ...
Randolph-Henry Biology Benchmark Test Six Weeks #1
... Do not write on this test booklet!!!! Multiple Choice: Select the best answer and mark on your answer sheet. _____1. Which of the sciences is the study of Plants? a. zoology b. botany c. mycology d. ecology _____2. Which scientist is considered to be the father of modern genetics? a. Darwin b. Paste ...
... Do not write on this test booklet!!!! Multiple Choice: Select the best answer and mark on your answer sheet. _____1. Which of the sciences is the study of Plants? a. zoology b. botany c. mycology d. ecology _____2. Which scientist is considered to be the father of modern genetics? a. Darwin b. Paste ...
7th Grade Geography Assessment Task 1
... centriole, golgi apparatus, cytoskeleton, & lysosome. The plant cell must include: lysosome, mitochondrion, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum (smooth & rough) chloroplast (grana, stroma, thylakoid), free ribosomes, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cytoskeleton, cell wall plasma membrane, vacuole with cell ...
... centriole, golgi apparatus, cytoskeleton, & lysosome. The plant cell must include: lysosome, mitochondrion, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum (smooth & rough) chloroplast (grana, stroma, thylakoid), free ribosomes, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cytoskeleton, cell wall plasma membrane, vacuole with cell ...
The Organelles of Cells
... d) What would you consider to be the “POWER PLANT” of the cell? _______________________ e) What would you consider to be the “STORAGE BIN” of the cell? _______________________ f) What would you consider to be the “SOLAR PANNEL” of the cell? ______________________ ...
... d) What would you consider to be the “POWER PLANT” of the cell? _______________________ e) What would you consider to be the “STORAGE BIN” of the cell? _______________________ f) What would you consider to be the “SOLAR PANNEL” of the cell? ______________________ ...
1. Most viruses consist of genetic material and which of the following
... 6. Which cycle is demonstrated by a virus that has infected a host cell but is not being replicated? a) lysogenic cycle b) lytic cycle c) citric acid cycle d) cell cycle 7. Which illness is not caused by a virus? a) cholera b) flu c) HIV d) common cold 8. Which term applies to the specific type of v ...
... 6. Which cycle is demonstrated by a virus that has infected a host cell but is not being replicated? a) lysogenic cycle b) lytic cycle c) citric acid cycle d) cell cycle 7. Which illness is not caused by a virus? a) cholera b) flu c) HIV d) common cold 8. Which term applies to the specific type of v ...
3-D Cell Model Evaluation Rubric
... This rubric is used to verify specific tasks performed when constructing this model. If the task has been successfully completed with quality, all points are awarded; poor quality work will reduce the scores at instructor’s discretion. No points are awar ded if the task is not complete. ...
... This rubric is used to verify specific tasks performed when constructing this model. If the task has been successfully completed with quality, all points are awarded; poor quality work will reduce the scores at instructor’s discretion. No points are awar ded if the task is not complete. ...
Bell Ringer – October 10th – 14th, Chapter 10 Cell Structure
... 1. In what way could two eukaryotic cells be different from each other? a. Two eukaryotic cells could differ in the number and types of prokaryotes they contain. b. Two eukaryotic cells could differ in the number and types of organelles they contain. c. One eukaryotic cell could have a cell membrane ...
... 1. In what way could two eukaryotic cells be different from each other? a. Two eukaryotic cells could differ in the number and types of prokaryotes they contain. b. Two eukaryotic cells could differ in the number and types of organelles they contain. c. One eukaryotic cell could have a cell membrane ...
Chapter 6 Part A I. The Importance of Cells
... – Nucleoplasm = entire region within the nucleus. – Cytoplasm = Entire region between the nucleus and plasma membrane. – Cytosol = viscous liquid found in the cytoplasm. ...
... – Nucleoplasm = entire region within the nucleus. – Cytoplasm = Entire region between the nucleus and plasma membrane. – Cytosol = viscous liquid found in the cytoplasm. ...
Section: 2.3 Name: Question of the Day
... Within the cell but outside the nucleus lies the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the “fluid” within the cell and contains the __________________, which is a gelatin-like aqueous fluid. The cytoplasm contains multiple cell parts known as ____________________________. Organelle means “little organ”, and s ...
... Within the cell but outside the nucleus lies the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the “fluid” within the cell and contains the __________________, which is a gelatin-like aqueous fluid. The cytoplasm contains multiple cell parts known as ____________________________. Organelle means “little organ”, and s ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.