Cell Organelles Worksheet
... all shapes and sizes and any citizen of Grant can get the instructions and begin making their own widgets. Widgets are generally produced in small shops around the city, these small shops can be built by the carpenter's union (whose headquarters are in town hall). After the widget is constructed, th ...
... all shapes and sizes and any citizen of Grant can get the instructions and begin making their own widgets. Widgets are generally produced in small shops around the city, these small shops can be built by the carpenter's union (whose headquarters are in town hall). After the widget is constructed, th ...
The cell - Emilangues
... Here is a footage of a real cell. These thread-like structures are the chromosomes. As we said, these chromosomes contain all of your genetic information in the form of genes and, more importantly, DNA. Chromosomes are only visible when a cell is about to split during mitosis, as you see here. We’ll ...
... Here is a footage of a real cell. These thread-like structures are the chromosomes. As we said, these chromosomes contain all of your genetic information in the form of genes and, more importantly, DNA. Chromosomes are only visible when a cell is about to split during mitosis, as you see here. We’ll ...
Document
... transparent body allows view of digestive and circulatory vessels, have photoreceptors in their tails, use corkscrew motions/reflex to escape predators. Duckweed (Lemna) small green plant that floats on the top of the water, purple ventral surface, food for many ...
... transparent body allows view of digestive and circulatory vessels, have photoreceptors in their tails, use corkscrew motions/reflex to escape predators. Duckweed (Lemna) small green plant that floats on the top of the water, purple ventral surface, food for many ...
Cells Ch1.1 Notes The Cell is the Basic Unit of Life All Living Things
... Cells & Heredity Chapter 1 Vocabulary 1. Unicellular – organisms made of a single cell 2. Multicellular – organisms made of two or more cells 3. Prokaryotic – cells with no nucleus 4. Eukaryotic – cells with a nucleus 5. Cell membrane – a protective covering enclosing a cell 6. Cell wall – a rigid p ...
... Cells & Heredity Chapter 1 Vocabulary 1. Unicellular – organisms made of a single cell 2. Multicellular – organisms made of two or more cells 3. Prokaryotic – cells with no nucleus 4. Eukaryotic – cells with a nucleus 5. Cell membrane – a protective covering enclosing a cell 6. Cell wall – a rigid p ...
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Biology 100
... synthesis of proteins from DNA to RNA. The nucleolus is a dense area within the nucleus with DNA fragments, ribosomal RNA, and proteins. The nucleolus organizes the RNA and proteins into the ribosomal subunits. ...
... synthesis of proteins from DNA to RNA. The nucleolus is a dense area within the nucleus with DNA fragments, ribosomal RNA, and proteins. The nucleolus organizes the RNA and proteins into the ribosomal subunits. ...
Ch.8- Cellular basis of Reproduction and Inheritance
... lining up in the middle of the cell and separating When did the sister chromatids get made? Interphase (S phase) ...
... lining up in the middle of the cell and separating When did the sister chromatids get made? Interphase (S phase) ...
Looking Inside Cells 3.2 Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus
... 9. Watch the video. Answer the questions. a. How long ago were tiny organs found in the cytoplasm of a cell? _________ b. What was the name given to these tiny organs? ______________________ 10. What are the 3 basic functions of the organelles inside the cytoplasm? a. Produce _______________ b. ____ ...
... 9. Watch the video. Answer the questions. a. How long ago were tiny organs found in the cytoplasm of a cell? _________ b. What was the name given to these tiny organs? ______________________ 10. What are the 3 basic functions of the organelles inside the cytoplasm? a. Produce _______________ b. ____ ...
Slide ()
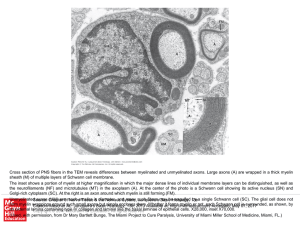
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
Document
... 2. What is the difference between a nucleotide and a nucleic acid? What are the 3 components of a nucleotide? Nucleic acids are molecules that contain our genetic information – more specifically, the code for protein synthesis. DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nu ...
... 2. What is the difference between a nucleotide and a nucleic acid? What are the 3 components of a nucleotide? Nucleic acids are molecules that contain our genetic information – more specifically, the code for protein synthesis. DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nu ...
Cell Structure Practice: Nucleus
... F. Ribosome releases the unfinished protein 3 G. Protein is shipped out of the cell 8 H. Folded protein enters the Golgi apparatus 6 ...
... F. Ribosome releases the unfinished protein 3 G. Protein is shipped out of the cell 8 H. Folded protein enters the Golgi apparatus 6 ...
THE CELL - MacsScienceSpace
... Cell unit objectives OBJECTIVES 1) EXPLAIN WHAT GENERAL TOPIC(S) BIOLOGY DEALS WITH. 2) LIST AND EXPLAIN THE CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVINGS THINGS AND GIVE EXAMPLES OF EACH. 3) DEFINE METABOLISM AND THE PROCESSES THAT MAKE IT UP. 4) EXPLAIN HOW RESPONDING TO A STIMULUS EFFECTS A LIVING ORGANISM. 5) LIST ...
... Cell unit objectives OBJECTIVES 1) EXPLAIN WHAT GENERAL TOPIC(S) BIOLOGY DEALS WITH. 2) LIST AND EXPLAIN THE CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVINGS THINGS AND GIVE EXAMPLES OF EACH. 3) DEFINE METABOLISM AND THE PROCESSES THAT MAKE IT UP. 4) EXPLAIN HOW RESPONDING TO A STIMULUS EFFECTS A LIVING ORGANISM. 5) LIST ...
Cells
... 4. Rudolf Virchow – hypothesized that new cells don’t form on their own. Cells divide to form new cells 5. Anton van Leeuwenhoek – used simple microscopes to observe tiny animalcules “beasties”later named bacteria ...
... 4. Rudolf Virchow – hypothesized that new cells don’t form on their own. Cells divide to form new cells 5. Anton van Leeuwenhoek – used simple microscopes to observe tiny animalcules “beasties”later named bacteria ...
Cell Structure
... 1. Membranes retain the cell contents. 2. Membranes control what enters and leaves the cell. 3. Membranes recognise molecules that touch them. ...
... 1. Membranes retain the cell contents. 2. Membranes control what enters and leaves the cell. 3. Membranes recognise molecules that touch them. ...
Cell Organelle Web Quest
... Hover over all of the different organelles of the plant and animal cell to find out their names and functions. Put a check for each structure that you find in a plant or animal cell. Leave it blank if it is absent. One is done for you because it is missing from the diagram. ...
... Hover over all of the different organelles of the plant and animal cell to find out their names and functions. Put a check for each structure that you find in a plant or animal cell. Leave it blank if it is absent. One is done for you because it is missing from the diagram. ...
Understand: All living things are made of cell that complete jobs
... Do: Draw the 6 phases, label the phases, and label the parts in each phase (spindle fibers, ...
... Do: Draw the 6 phases, label the phases, and label the parts in each phase (spindle fibers, ...
Document
... 3. Draw a red blood cell in an isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solution. Draw dots to show the solute concentration and draw arrows to show which way the water would move. (Osmosis) ...
... 3. Draw a red blood cell in an isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solution. Draw dots to show the solute concentration and draw arrows to show which way the water would move. (Osmosis) ...
L3.b Spiral Review
... a. Animals do not use water. b. Animals breathe in oxygen. c. Animals need extra energy to survive. d. Animal cells do not contain chloroplasts. Tuesday 5. The nucleus is located in the center of the cell and is known as the cell’s ___________. a. b. c. d. ...
... a. Animals do not use water. b. Animals breathe in oxygen. c. Animals need extra energy to survive. d. Animal cells do not contain chloroplasts. Tuesday 5. The nucleus is located in the center of the cell and is known as the cell’s ___________. a. b. c. d. ...
Topic 2 revision notes - Mr Cartlidge`s Saigon Science Blog
... Helps keep plant cells turgid (firm) Chlorophyll taps light energy for photosynthesis ...
... Helps keep plant cells turgid (firm) Chlorophyll taps light energy for photosynthesis ...
5.1 The Cell Cycle - Science With Ms. Ortiz
... • The main stages of the cell cycle are gap 1, synthesis, gap 2, and mitosis. – Gap 1 (G1): cell growth and normal functions – DNA synthesis (S): copies DNA – Gap 2 (G2): additional growth – Mitosis (M): includes division of the cell nucleus (mitosis) and division of the cell cytoplasm (cytokinesis) ...
... • The main stages of the cell cycle are gap 1, synthesis, gap 2, and mitosis. – Gap 1 (G1): cell growth and normal functions – DNA synthesis (S): copies DNA – Gap 2 (G2): additional growth – Mitosis (M): includes division of the cell nucleus (mitosis) and division of the cell cytoplasm (cytokinesis) ...
3) Cellular Aging - Cal State LA
... Sites of protein synthesis (aa assemble to protein) in response to the instructions from DNA Ribosome travels along an mRNA molecule and “reads” its message tRNA delivers the aa, and ribosome assembles them in the sequence directed by mRNA ...
... Sites of protein synthesis (aa assemble to protein) in response to the instructions from DNA Ribosome travels along an mRNA molecule and “reads” its message tRNA delivers the aa, and ribosome assembles them in the sequence directed by mRNA ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.