The Cell
... material is not surrounded by a(n) (2.) membrane. Another characteristic of prokaryotic cells is that they do not have all the (3.) cell parts found in eukaryotic cells. Most prokaryotic cells are one-celled, or (4.) unicellular organisms and are called (5.) prokaryotes. Another word for prokaryotes ...
... material is not surrounded by a(n) (2.) membrane. Another characteristic of prokaryotic cells is that they do not have all the (3.) cell parts found in eukaryotic cells. Most prokaryotic cells are one-celled, or (4.) unicellular organisms and are called (5.) prokaryotes. Another word for prokaryotes ...
The Cell - juan
... • In animal cells, Golgi complex also manufactures lysosomes (sacs which contain enzymes that breakdown materials) • Golgi Complex modifies carbohydrates and lipids and packages into vesicles, which are then transported out of the cell. ...
... • In animal cells, Golgi complex also manufactures lysosomes (sacs which contain enzymes that breakdown materials) • Golgi Complex modifies carbohydrates and lipids and packages into vesicles, which are then transported out of the cell. ...
SBI 3CI
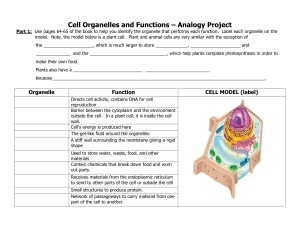
... Fill in the table with the cell part that best matches the definition. (9) Name of Cell Part Description/Function of Cell Part It has phospholipid molecules & controls access to & from the cell It has a porous double membrane & controls the cell activities It is attached or unattached in the cytopla ...
... Fill in the table with the cell part that best matches the definition. (9) Name of Cell Part Description/Function of Cell Part It has phospholipid molecules & controls access to & from the cell It has a porous double membrane & controls the cell activities It is attached or unattached in the cytopla ...
Course Outline
... Interpret results to form conclusion Conclusion support hypothesis or not? Determine experimental reliability Extend to further experiments/analyses Infer/generalize from various data sources (diagrams, micrographs, graphs) Present conclusions with most appropriate means of communication (graph, dia ...
... Interpret results to form conclusion Conclusion support hypothesis or not? Determine experimental reliability Extend to further experiments/analyses Infer/generalize from various data sources (diagrams, micrographs, graphs) Present conclusions with most appropriate means of communication (graph, dia ...
Cells & Microscopes Quick Quiz 3
... 3. iodine would show it's cell structures up better 4. It contains chloroplasts ...
... 3. iodine would show it's cell structures up better 4. It contains chloroplasts ...
DAW Lecture 3 PPT
... Carrier-mediated introduction of the DNA Positively charged carrier molecules are mixed with the DNA and added to ...
... Carrier-mediated introduction of the DNA Positively charged carrier molecules are mixed with the DNA and added to ...
Unit Title / Grade Level Unit 3: The Basis of Life (Covering Chapters
... LS.3.2 Interactions of Living Systems: Students understand that organisms in all ecosystems interact with and depend on each other, and that organisms with similar needs compete for limited resources. What are the characteristics of a living organism? How are living things classified and why is it i ...
... LS.3.2 Interactions of Living Systems: Students understand that organisms in all ecosystems interact with and depend on each other, and that organisms with similar needs compete for limited resources. What are the characteristics of a living organism? How are living things classified and why is it i ...
Name
... Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. _____ 7. Which of the following is a function of the cell membrane? a. breaks down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins from foods b. stores water, salt, proteins, and carbohydrates c. keeps the cell wall ...
... Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. _____ 7. Which of the following is a function of the cell membrane? a. breaks down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins from foods b. stores water, salt, proteins, and carbohydrates c. keeps the cell wall ...
Welcome to Mrs. Thompson`s 5th Grade Class
... Vacuoles are storage bubbles found in cells. Vacuoles might store food or any variety of nutrients a cell might need to survive. They also store waste products so the rest of the cell is protected from contamination. Eventually, those waste products are sent out of the cell. ...
... Vacuoles are storage bubbles found in cells. Vacuoles might store food or any variety of nutrients a cell might need to survive. They also store waste products so the rest of the cell is protected from contamination. Eventually, those waste products are sent out of the cell. ...
New Data, Research and Tools at genome.ucsc.edu
... blood cells) share the same DNA, which parts of the DNA are used by cells varies. • As cells divide they differentiate into different cell types based on signals from other cells, the environment, a bit of randomness, and the cell’s internal state. • Most of the differentiation decisions ...
... blood cells) share the same DNA, which parts of the DNA are used by cells varies. • As cells divide they differentiate into different cell types based on signals from other cells, the environment, a bit of randomness, and the cell’s internal state. • Most of the differentiation decisions ...
Mitosis and Meiosis
... All new cells come from previously existing cells. New cells are formed by the process of cell division which involves both replication of the cell's nucleus (karyokinesis) and division of the cytoplasm( cytokinesis). There are two types of nuclear division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis typically re ...
... All new cells come from previously existing cells. New cells are formed by the process of cell division which involves both replication of the cell's nucleus (karyokinesis) and division of the cytoplasm( cytokinesis). There are two types of nuclear division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis typically re ...
Cells -ATP, RNA, DNA notes
... Cells store and use information The _________________________________ of plant and animal cells is the control center The nucleus contains _________________________________. DNA has the instructions, _________________________________, for the entire cell DNA and RNA work together to ________________ ...
... Cells store and use information The _________________________________ of plant and animal cells is the control center The nucleus contains _________________________________. DNA has the instructions, _________________________________, for the entire cell DNA and RNA work together to ________________ ...
What part of the cell controls what goes in and out of the cell
... proteins and other things • In the cell membrane • That move around the surface of cells (fluid) ...
... proteins and other things • In the cell membrane • That move around the surface of cells (fluid) ...
The NIMA-related kinase NEK1 cycles through the nucleus
... characterization, little is known of the cellular functions of NEK1. NEK1 is found associated with centrosomes, where it remains throughout the cell cycle [6–8]. It has recently been implicated in the maintenance of centrosomes and in the formation of the primary cilium [7–9]. It remains unknown, ho ...
... characterization, little is known of the cellular functions of NEK1. NEK1 is found associated with centrosomes, where it remains throughout the cell cycle [6–8]. It has recently been implicated in the maintenance of centrosomes and in the formation of the primary cilium [7–9]. It remains unknown, ho ...
File - Mrs. Weber`s Science Classroom
... Organelles: structure in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell that can act as a storage site, process energy, move materials or manufacture substances. Tissues: a group of similar cells that work together to do one job. Each cell in a tissue does its part to keep the tissue alive. Organ: a structure m ...
... Organelles: structure in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell that can act as a storage site, process energy, move materials or manufacture substances. Tissues: a group of similar cells that work together to do one job. Each cell in a tissue does its part to keep the tissue alive. Organ: a structure m ...
Common Assessment #3 Review Sheet Why is the plasma
... If a plasma membrane was twice as thick as normal, would it be easier or more difficult for the molecules to move across the membrane of a cell? ...
... If a plasma membrane was twice as thick as normal, would it be easier or more difficult for the molecules to move across the membrane of a cell? ...
7.3 ANIMAL and PLANT CELL STRUCTURE HO
... cytoplasm of the cell and carry out the activities that keep the cell alive. Plant and animal cells have many of the same organelles, but they also have some major differences. These different cellular structures have a huge impact on how these different living things go about the business of life. ...
... cytoplasm of the cell and carry out the activities that keep the cell alive. Plant and animal cells have many of the same organelles, but they also have some major differences. These different cellular structures have a huge impact on how these different living things go about the business of life. ...
Bacterial Cell Structure Internal Structures Nucleoid DNA
... Internal Structure: Bacteria have a very simple internal structure, and no membrane-bound organelles. nucleoid DNA in the bacterial cell is generally confined to this central region. Though it isn't bounded by a membrane, it is visibly distinct (by transmission microscopy) from the rest of the cell ...
... Internal Structure: Bacteria have a very simple internal structure, and no membrane-bound organelles. nucleoid DNA in the bacterial cell is generally confined to this central region. Though it isn't bounded by a membrane, it is visibly distinct (by transmission microscopy) from the rest of the cell ...
Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle
... gradient (from high to low concentration) through a protein ...
... gradient (from high to low concentration) through a protein ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.