Handou
... 3. Six of the organelles (other than the plasma membrane) contain one or more membranes. List these organelles. 4. Different cells contain different amounts of each organelle. a) What type of organelle would be found in high amounts in a leaf cell? b) What type of organelle would be found in high am ...
... 3. Six of the organelles (other than the plasma membrane) contain one or more membranes. List these organelles. 4. Different cells contain different amounts of each organelle. a) What type of organelle would be found in high amounts in a leaf cell? b) What type of organelle would be found in high am ...
Cell Organelles and Functions Powerpoint
... a hollow tube, the other two are long, stringy fibers ...
... a hollow tube, the other two are long, stringy fibers ...
Name
... need to include the proper organelles and other cell parts in each drawing. The drawing should be colored, neat, and the parts labeled properly. You will be comparing the cell to a school (just like we did with a city similes on our index cards.) Just as all of the organelles are found inside of a c ...
... need to include the proper organelles and other cell parts in each drawing. The drawing should be colored, neat, and the parts labeled properly. You will be comparing the cell to a school (just like we did with a city similes on our index cards.) Just as all of the organelles are found inside of a c ...
Ch. 7 - Crestwood Local Schools
... cell. The signal is received at the membrane and passed on. Exception - intracellular receptors ...
... cell. The signal is received at the membrane and passed on. Exception - intracellular receptors ...
Unit 6
... • The cell is the smallest unit having the properties of life • The continuity of life arises directly from the growth and division of single cells ...
... • The cell is the smallest unit having the properties of life • The continuity of life arises directly from the growth and division of single cells ...
LEARNING GOALS - Cell Membranes
... environments, while the hydrophobic fatty acid portions face each other within the interior of the membrane itself. Embedded proteins can be hydrophilic, with charged and polar side groups, or hydrophobic, with nonpolar side groups. Small, uncharged polar molecules and small nonpolar molecules, such ...
... environments, while the hydrophobic fatty acid portions face each other within the interior of the membrane itself. Embedded proteins can be hydrophilic, with charged and polar side groups, or hydrophobic, with nonpolar side groups. Small, uncharged polar molecules and small nonpolar molecules, such ...
cell
... cell (sel) The smallest unit of living matter that can carry out the basic processes of life. organelle (ôr´gə nel´) Organelles are cell structures that work together to carry out life processes. ...
... cell (sel) The smallest unit of living matter that can carry out the basic processes of life. organelle (ôr´gə nel´) Organelles are cell structures that work together to carry out life processes. ...
AP Biology Cell Poster
... 1. Choose an animal or plant cell to do your poster on. Select 15 cell organelles or cell structures from the list at the bottom of this page that pertain to this type of cell. You can ONLY use those that belong to that type of cell. 2. (15 pts) On one side of your poster, you must draw your chosen ...
... 1. Choose an animal or plant cell to do your poster on. Select 15 cell organelles or cell structures from the list at the bottom of this page that pertain to this type of cell. You can ONLY use those that belong to that type of cell. 2. (15 pts) On one side of your poster, you must draw your chosen ...
Cell Boundaries - Deans Community High School
... Explain: how the cell wall helps to form a continuous water conducting pathway in a plant. ...
... Explain: how the cell wall helps to form a continuous water conducting pathway in a plant. ...
A Cell is like a Factory - Sterlingmontessoriscience
... controls all of the activity inside the cell • The nucleus does the same thing for plant and animal cells ...
... controls all of the activity inside the cell • The nucleus does the same thing for plant and animal cells ...
Cells: Organelles, Membranes and Communication Test Review
... Know what each of the organelles covered in your class and book does and why the cell needs it - why would it have more than average number of them? What would happen if you got rid of them? Be able to recognize and explain where and how each of the organelles formed (endosymbiosis or invaginati ...
... Know what each of the organelles covered in your class and book does and why the cell needs it - why would it have more than average number of them? What would happen if you got rid of them? Be able to recognize and explain where and how each of the organelles formed (endosymbiosis or invaginati ...
Transcription Translation Molecular Structure of Ion Channels
... -each has an amino group -each has an acid group ...
... -each has an amino group -each has an acid group ...
The Cell - oteroteacher
... the carotenoids into the pink and orange pigment molecules deposited in the feathers, bill, and legs of the ...
... the carotenoids into the pink and orange pigment molecules deposited in the feathers, bill, and legs of the ...
Keystone Biology Cram Sheet: MODULE 1 1. Because carbon has 4
... 15. The ER is like a protein assembly line. The workers along it are ribosomes, which actually line up the amino acids in the right order (according to the DNA code) 16. The proteins are finished, tweaked, modified, packaged and shipped by Golgi. 17. Vesicles carry the final protein products through ...
... 15. The ER is like a protein assembly line. The workers along it are ribosomes, which actually line up the amino acids in the right order (according to the DNA code) 16. The proteins are finished, tweaked, modified, packaged and shipped by Golgi. 17. Vesicles carry the final protein products through ...
Name: Date: Test Review Unit V: Cell membrane and cellular
... 14. By which process do plants (their roots) absorb nutrients/minerals from the surrounding soil? 15. Which organelle is responsible for water balance, gas exchange and excretion in a single celled organism? 16. What are the 3 characteristics of active transport? a. b. c. 17. What is ATP? 18. Draw a ...
... 14. By which process do plants (their roots) absorb nutrients/minerals from the surrounding soil? 15. Which organelle is responsible for water balance, gas exchange and excretion in a single celled organism? 16. What are the 3 characteristics of active transport? a. b. c. 17. What is ATP? 18. Draw a ...
notes
... Molecules are always on the move They bump into each other As the bump they begin to spread out What do you think the goal of diffusion is? ...
... Molecules are always on the move They bump into each other As the bump they begin to spread out What do you think the goal of diffusion is? ...
Cell Parts and Functions
... 2. provides protection and support for the cell Other: it is flexible so it can change shape under pressure; by allowing things to move in and out, it helps maintain homeostasis B. nucleus Type of cell: both plant and animal (only in eukaryotic cells) Location: found within the cytoplasm; separated ...
... 2. provides protection and support for the cell Other: it is flexible so it can change shape under pressure; by allowing things to move in and out, it helps maintain homeostasis B. nucleus Type of cell: both plant and animal (only in eukaryotic cells) Location: found within the cytoplasm; separated ...
organization - Catawba County Schools
... What are the 3 domains, and what type of cells do the organisms in each domain have? Define specialization in your own words. Describe the levels of organization in a tree. In what way does a specialized cell in a multicellular organism differ from the cell of a unicellular organism? How is a model ...
... What are the 3 domains, and what type of cells do the organisms in each domain have? Define specialization in your own words. Describe the levels of organization in a tree. In what way does a specialized cell in a multicellular organism differ from the cell of a unicellular organism? How is a model ...
Worksheet
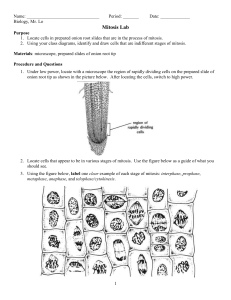
... a. Is the DNA in the form of chromatin or chromosomes? b. Is the nuclear membrane present? c. In what sub-stage is the DNA replicated? 4. At the end of prophase… a. Is the DNA in the form of chromatin or chromosomes? b. Is the nuclear membrane present? 5. At the end of metaphase… a. Where is the DNA ...
... a. Is the DNA in the form of chromatin or chromosomes? b. Is the nuclear membrane present? c. In what sub-stage is the DNA replicated? 4. At the end of prophase… a. Is the DNA in the form of chromatin or chromosomes? b. Is the nuclear membrane present? 5. At the end of metaphase… a. Where is the DNA ...
Parts of a Cell - susanpittinaro
... • Also called the Cell Membrane • Separates cell from its environment ...
... • Also called the Cell Membrane • Separates cell from its environment ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.