Standard model of particle physics
... and physicists detected new particles in the higher atmosphere, e.g. muons and pions. These new particles initiated new conservation laws and quantities, like the strangeness. These was discovered as secondary radiation in pictures of Figure 1: First picture of anticloud chambers. matter: the track ...
... and physicists detected new particles in the higher atmosphere, e.g. muons and pions. These new particles initiated new conservation laws and quantities, like the strangeness. These was discovered as secondary radiation in pictures of Figure 1: First picture of anticloud chambers. matter: the track ...
Classically conformal BL extended Standard Model
... The minimal B-L model naturally realized at TeV scale Yuta Orikasa(SOKENDAI) Satoshi Iso(KEK,SOKENDAI) Nobuchika Okada(University of Alabama) Phys.Lett.B676(2009)81 Phys.Rev.D80(2009)115007 ...
... The minimal B-L model naturally realized at TeV scale Yuta Orikasa(SOKENDAI) Satoshi Iso(KEK,SOKENDAI) Nobuchika Okada(University of Alabama) Phys.Lett.B676(2009)81 Phys.Rev.D80(2009)115007 ...
Topic 7 Collision Dynamics
... In the systems we are interested in there will be six knowns: the masses m1, m2 and the initial speeds v1ix, v1iy , v2ix, v2iy . However, that leaves four unknowns and three equations. ...
... In the systems we are interested in there will be six knowns: the masses m1, m2 and the initial speeds v1ix, v1iy , v2ix, v2iy . However, that leaves four unknowns and three equations. ...
Glossary File
... Charm (c) is the fourth quark (in order of increasing mass), with an electric charge +2/3. ...
... Charm (c) is the fourth quark (in order of increasing mass), with an electric charge +2/3. ...
Slides
... – If supersymmetry is correct, they would also have new, but much more massive relatives called superpartners Theoretically this is very nice – eliminates mathematical problems in standard model – allows unification of forces at much higher energies – provides a path to the incorporation of gravity ...
... – If supersymmetry is correct, they would also have new, but much more massive relatives called superpartners Theoretically this is very nice – eliminates mathematical problems in standard model – allows unification of forces at much higher energies – provides a path to the incorporation of gravity ...
AQA A Physics - Particle Physics
... classification system which he called The Eight-fold Way. In this scheme, the quark arrangements are elements of special unity group SU(3). This is a mathematical group of unitary matrices and the octets and other diagrams may be seen as different representations of this group. Note that an introduc ...
... classification system which he called The Eight-fold Way. In this scheme, the quark arrangements are elements of special unity group SU(3). This is a mathematical group of unitary matrices and the octets and other diagrams may be seen as different representations of this group. Note that an introduc ...
Document
... compared to size of system; Number of gluons is large New: Can only be made and probed in high energy collsions Universal: Independent of hadron, renormalization group equations have a universal solution. Universality <=> Fundamental It is a theory of: Origin of glue and sea quarks in hadrons Cross ...
... compared to size of system; Number of gluons is large New: Can only be made and probed in high energy collsions Universal: Independent of hadron, renormalization group equations have a universal solution. Universality <=> Fundamental It is a theory of: Origin of glue and sea quarks in hadrons Cross ...
Development of a Time Projection Chamber Using Gas Electron
... Double track resolution was evaluated by the distribution of distance between two hits in drift direction Multiple hits in one event (6.4ms) were generated by high beam rate (~4000cps/cm2) and a lead block (1X0) Since distance between scattered secondary particles is generally less than 20mm, those ...
... Double track resolution was evaluated by the distribution of distance between two hits in drift direction Multiple hits in one event (6.4ms) were generated by high beam rate (~4000cps/cm2) and a lead block (1X0) Since distance between scattered secondary particles is generally less than 20mm, those ...
Document
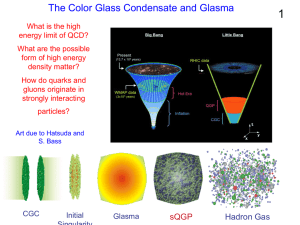
... Why is the Color Glass Condensate Important? It is a new universal form of matter: Matter: Carries energy; Separation of gluons is small compared to size of system; Number of gluons is large New: Can only be made and probed in high energy collsions Universal: Independent of hadron, renormalization ...
... Why is the Color Glass Condensate Important? It is a new universal form of matter: Matter: Carries energy; Separation of gluons is small compared to size of system; Number of gluons is large New: Can only be made and probed in high energy collsions Universal: Independent of hadron, renormalization ...
The Higgs Boson and Electroweak Symmetry Breaking
... In this lecture, I have described 4 possible models of EWSB. We do not know whether the Higgs boson is elementary or composite; I have presented models of both types. In each model, the Higgs boson is part of a larger superstructure that will be revealed when we experiment at multi-100 GeV eneriges ...
... In this lecture, I have described 4 possible models of EWSB. We do not know whether the Higgs boson is elementary or composite; I have presented models of both types. In each model, the Higgs boson is part of a larger superstructure that will be revealed when we experiment at multi-100 GeV eneriges ...
Slide 1
... › Lattice QCD: from first principle › Perturbation theory: interpretation › AdS/CFT correspondence: bound ...
... › Lattice QCD: from first principle › Perturbation theory: interpretation › AdS/CFT correspondence: bound ...
CMS
... May allow discovery of heavy SUSY Higgs bosons in LHC wedge region CP quantum numbers & CP violation in Higgs sector directly measurable from azimuthal asymmetry of protons ...
... May allow discovery of heavy SUSY Higgs bosons in LHC wedge region CP quantum numbers & CP violation in Higgs sector directly measurable from azimuthal asymmetry of protons ...
Large Hadron Collider

The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world's largest and most powerful particle collider, the largest, most complex experimental facility ever built, and the largest single machine in the world. It was built by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) between 1998 and 2008 in collaboration with over 10,000 scientists and engineers from over 100 countries, as well as hundreds of universities and laboratories. It lies in a tunnel 27 kilometres (17 mi) in circumference, as deep as 175 metres (574 ft) beneath the France–Switzerland border near Geneva, Switzerland. Its first research run took place from 30 March 2010 to 13 February 2013 at an initial energy of 3.5 teraelectronvolts (TeV) per beam (7 TeV total), almost 4 times more than the previous world record for a collider, rising to 4 TeV per beam (8 TeV total) from 2012. On 13 February 2013 the LHC's first run officially ended, and it was shut down for planned upgrades. 'Test' collisions restarted in the upgraded collider on 5 April 2015, reaching 6.5 TeV per beam on 20 May 2015 (13 TeV total, the current world record for particle collisions). Its second research run commenced on schedule, on 3 June 2015.The LHC's aim is to allow physicists to test the predictions of different theories of particle physics, high-energy physics and in particular, to prove or disprove the existence of the theorized Higgs boson and the large family of new particles predicted by supersymmetric theories, and other unsolved questions of physics, advancing human understanding of physical laws. It contains seven detectors, each designed for certain kinds of research. The proton-proton collision is the primary operation method, but the LHC has also collided protons with lead nuclei for two months in 2013 and used lead–lead collisions for about one month each in 2010, 2011, and 2013 for other investigations. The LHC's computing grid was (and currently is) a world record holder. Data from collisions was anticipated to be produced at an unprecedented rate for the time, of tens of petabytes per year, a major challenge at the time, to be analysed by a grid-based computer network infrastructure connecting 140 computing centers in 35 countries – by 2012 the Worldwide LHC Computing Grid was also the world's largest distributed computing grid, comprising over 170 computing facilities in a worldwide network across 36 countries.