Measuring the Size of Elementary Particle Collisions
... Bosons are integer spin particles. Identical Bosons have a symmetric two particle wave function -any number may occupy a given quantum state... Photons and pions are examples of Bosons Fermions are half-integer spin particles. Identical Fermions have an antisymmetric wave function -only one particle ...
... Bosons are integer spin particles. Identical Bosons have a symmetric two particle wave function -any number may occupy a given quantum state... Photons and pions are examples of Bosons Fermions are half-integer spin particles. Identical Fermions have an antisymmetric wave function -only one particle ...
Teaching the Standard Model in IB Physics by Debra Blake
... describe interaction of quarks, leptons and the mediator of these interactions. They are used to compute lifetimes and cross section for particle interaction events. The time (ct) and space (x) axes are normally not drawn but time (ct) is positive upward and generally drawn with time flowing horizon ...
... describe interaction of quarks, leptons and the mediator of these interactions. They are used to compute lifetimes and cross section for particle interaction events. The time (ct) and space (x) axes are normally not drawn but time (ct) is positive upward and generally drawn with time flowing horizon ...
Possible differences among codes for CT* and CBOP2T*
... How to avoid spurious repeated collisions ...
... How to avoid spurious repeated collisions ...
Mysteries of Mass Article in Scientific American
... A practical problem with performing such tests is that we do not yet understand the theories well enough to calcu late what masses the Riggs bosons themselves should have, which makes searching for them more difficult because one must examine a range of masses. A cornbination of theoretical reasonin ...
... A practical problem with performing such tests is that we do not yet understand the theories well enough to calcu late what masses the Riggs bosons themselves should have, which makes searching for them more difficult because one must examine a range of masses. A cornbination of theoretical reasonin ...
RelativityWorkbook-Student
... of how this is set up and how it runs, and you will be given real data sets from this apparatus. From this you may make your own graphs and see how the predictions of relativity “stack up”. ...
... of how this is set up and how it runs, and you will be given real data sets from this apparatus. From this you may make your own graphs and see how the predictions of relativity “stack up”. ...
feofilov-cern-15-Oct-09
... rapidity windows). In a case of smaller windows of 0.2 units of rapidity the minimal required statistics will be 1 - 2 x 10^6 . ...
... rapidity windows). In a case of smaller windows of 0.2 units of rapidity the minimal required statistics will be 1 - 2 x 10^6 . ...
ppt - Desy
... • A small asymmetry in the momentum carried by s-s could have a large effect They claim to have measured this asymmetry from dimuons. But a LO analysis of s-s makes no sense and cannot be directly transplanted here (as*valence corrections are large and process dependent) ...
... • A small asymmetry in the momentum carried by s-s could have a large effect They claim to have measured this asymmetry from dimuons. But a LO analysis of s-s makes no sense and cannot be directly transplanted here (as*valence corrections are large and process dependent) ...
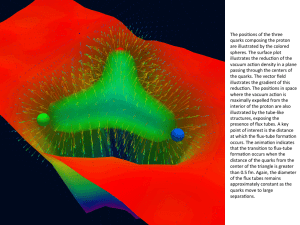
The positons of the three quarks composing the proton are
... quark. The vast bulk of the constituent-mass of a light quark is contained in a cloud of gluons, which are dragged along by the quark as it propagates. In this way, a quark that appears to be absolutely massless at high energies acquires a large constituent mass at low energies. ...
... quark. The vast bulk of the constituent-mass of a light quark is contained in a cloud of gluons, which are dragged along by the quark as it propagates. In this way, a quark that appears to be absolutely massless at high energies acquires a large constituent mass at low energies. ...
On-Shell Methods in Quantum Field Theory
... understanding of theoretical uncertainties will be required for <5% predictions for future precision measurements ...
... understanding of theoretical uncertainties will be required for <5% predictions for future precision measurements ...
Introduction to Particle Physics
... larger for massive s) be reduced? Why is the electric charge of electron and proton equal? Should the gauge couplings unify at high energies? In the SM they do not! Why are ~17 orders of magnitude between EW and Planck scale? How can the fine tuning problem be solved ? What is the nature of dark ma ...
... larger for massive s) be reduced? Why is the electric charge of electron and proton equal? Should the gauge couplings unify at high energies? In the SM they do not! Why are ~17 orders of magnitude between EW and Planck scale? How can the fine tuning problem be solved ? What is the nature of dark ma ...
PARTICLE PHYSICS BEYOND THE STANDARD MODEL
... Over the last decades experiments and theory in particle physics and astrophysics have been extraordinarily successful in developing Standard Models of particle physics and cosmology. They describe a wealth of measurements based on first principles of field theory. The discovery of a Higgs boson can ...
... Over the last decades experiments and theory in particle physics and astrophysics have been extraordinarily successful in developing Standard Models of particle physics and cosmology. They describe a wealth of measurements based on first principles of field theory. The discovery of a Higgs boson can ...
Hughes - INFN Bologna
... that we could use it to do an experiment on near-threshold pion photoproduction using the Glasgow 300 MeV electron synchrotron. We designed a tube running through the chamber, which could be filled with pressurized hydrogen or deuterium as a target for the gammas. The challenge of course was to make ...
... that we could use it to do an experiment on near-threshold pion photoproduction using the Glasgow 300 MeV electron synchrotron. We designed a tube running through the chamber, which could be filled with pressurized hydrogen or deuterium as a target for the gammas. The challenge of course was to make ...
The Nobel Prize in Physics 2004
... in spite of the very large difference in strength between the two interactions there are several similarities. The interaction strength decreases with the square of the distance and has a long range. Both the electromagnetic interaction and the gravitational interaction are mediated by force carrie ...
... in spite of the very large difference in strength between the two interactions there are several similarities. The interaction strength decreases with the square of the distance and has a long range. Both the electromagnetic interaction and the gravitational interaction are mediated by force carrie ...
pptx file - Northwestern University
... • Four force carriers for three forces (electromagnetic, weak & strong – not gravity). • The Higgs field is special – it gives mass. 7 - November - 2012 ...
... • Four force carriers for three forces (electromagnetic, weak & strong – not gravity). • The Higgs field is special – it gives mass. 7 - November - 2012 ...
128 KB
... which the muons were deflected by the protons… Armed with the EMC results, theorists were able to calculate the total spin content of the proton carried by the quarks. To everyone’s amazement, they came up with an answer that was close to zero… Was there a problem with the theory, the experiment or ...
... which the muons were deflected by the protons… Armed with the EMC results, theorists were able to calculate the total spin content of the proton carried by the quarks. To everyone’s amazement, they came up with an answer that was close to zero… Was there a problem with the theory, the experiment or ...
Large Hadron Collider

The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world's largest and most powerful particle collider, the largest, most complex experimental facility ever built, and the largest single machine in the world. It was built by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) between 1998 and 2008 in collaboration with over 10,000 scientists and engineers from over 100 countries, as well as hundreds of universities and laboratories. It lies in a tunnel 27 kilometres (17 mi) in circumference, as deep as 175 metres (574 ft) beneath the France–Switzerland border near Geneva, Switzerland. Its first research run took place from 30 March 2010 to 13 February 2013 at an initial energy of 3.5 teraelectronvolts (TeV) per beam (7 TeV total), almost 4 times more than the previous world record for a collider, rising to 4 TeV per beam (8 TeV total) from 2012. On 13 February 2013 the LHC's first run officially ended, and it was shut down for planned upgrades. 'Test' collisions restarted in the upgraded collider on 5 April 2015, reaching 6.5 TeV per beam on 20 May 2015 (13 TeV total, the current world record for particle collisions). Its second research run commenced on schedule, on 3 June 2015.The LHC's aim is to allow physicists to test the predictions of different theories of particle physics, high-energy physics and in particular, to prove or disprove the existence of the theorized Higgs boson and the large family of new particles predicted by supersymmetric theories, and other unsolved questions of physics, advancing human understanding of physical laws. It contains seven detectors, each designed for certain kinds of research. The proton-proton collision is the primary operation method, but the LHC has also collided protons with lead nuclei for two months in 2013 and used lead–lead collisions for about one month each in 2010, 2011, and 2013 for other investigations. The LHC's computing grid was (and currently is) a world record holder. Data from collisions was anticipated to be produced at an unprecedented rate for the time, of tens of petabytes per year, a major challenge at the time, to be analysed by a grid-based computer network infrastructure connecting 140 computing centers in 35 countries – by 2012 the Worldwide LHC Computing Grid was also the world's largest distributed computing grid, comprising over 170 computing facilities in a worldwide network across 36 countries.