The Plasma Membrane
... • To act as a barrier between a cell and its environment • To maintain homeostasis in a cell (a balance of conditions suitable for life) ...
... • To act as a barrier between a cell and its environment • To maintain homeostasis in a cell (a balance of conditions suitable for life) ...
Cell Membrane Notes
... Slide one: cell membrane vs. cell wall Cell Membranes _________________ what comes into and out of cells Cell Walls provide _____________________________________ for the cell ...
... Slide one: cell membrane vs. cell wall Cell Membranes _________________ what comes into and out of cells Cell Walls provide _____________________________________ for the cell ...
BIOLOGY BINGO BOARD
... like a transportation system within the cell, like a intracellular highway system Nucleus – not found in prokaryotes (bacteria), only found in eukaryotes, contains the DNA and controls ALL of the functions of the cell, surrounded by a membrane Homeostasis – maintaining a balance, ex: temperature, ch ...
... like a transportation system within the cell, like a intracellular highway system Nucleus – not found in prokaryotes (bacteria), only found in eukaryotes, contains the DNA and controls ALL of the functions of the cell, surrounded by a membrane Homeostasis – maintaining a balance, ex: temperature, ch ...
Chapter 3 Cell Structure - Shelbyville Central Schools
... • Phospholipid made of phosphate group and 2 fatty acids ...
... • Phospholipid made of phosphate group and 2 fatty acids ...
Contents: The Journal of Cell Biology
... accumulates in the jump muscles of Drosophila melanogaster adults. Each of the cells in this muscle show pink-colored nuclei surrounded by two mRNA-containing lumens which stain blue. There are four columns of myofibrils (white areas) per cell which separate the lumens from each other and from the c ...
... accumulates in the jump muscles of Drosophila melanogaster adults. Each of the cells in this muscle show pink-colored nuclei surrounded by two mRNA-containing lumens which stain blue. There are four columns of myofibrils (white areas) per cell which separate the lumens from each other and from the c ...
Homework Questions – Unit 1 – Biochemistry
... 3. Compare and contrast endocytosis to active transport. ...
... 3. Compare and contrast endocytosis to active transport. ...
Name Period ______ Section 3: Eukaryotic Cells: The Inside Story
... The Cell’s Delivery System 8. What are the functions of the endoplasmic reticulum? (Circle all that apply.) a. It stores DNA. b. It makes lipids. c. It moves substances to different places in the cell. d. It breaks down harmful chemicals. 9. __________________cause the surface of some ER to look rou ...
... The Cell’s Delivery System 8. What are the functions of the endoplasmic reticulum? (Circle all that apply.) a. It stores DNA. b. It makes lipids. c. It moves substances to different places in the cell. d. It breaks down harmful chemicals. 9. __________________cause the surface of some ER to look rou ...
Cell Structure
... molecules can pass others act like small pumps, actively pushing molecules from one side of the membrane to the other ...
... molecules can pass others act like small pumps, actively pushing molecules from one side of the membrane to the other ...
H 3 - Absorption of digested foods - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... surface facing the lumen of the gut, greatly increase the surface area in contact with material to be absorbed mitochondria – these organelles are present in large numbers, suggesting a significant demand for ATP in these cells for active transport pinocytotic vesicles – these are the site of pi ...
... surface facing the lumen of the gut, greatly increase the surface area in contact with material to be absorbed mitochondria – these organelles are present in large numbers, suggesting a significant demand for ATP in these cells for active transport pinocytotic vesicles – these are the site of pi ...
Cell Test
... Circle in the correct letter on your scantron sheet (2 pts.) Pick the correct letter from the table for questions 1-5. a. Nucleolus ...
... Circle in the correct letter on your scantron sheet (2 pts.) Pick the correct letter from the table for questions 1-5. a. Nucleolus ...
Mid-Term Review
... Budding: a new organism grows from the body of the parent organism Binary Fission: one-celled bacterium without a nucleus copies its genetic information and then divides into 2 identical cells Regeneration: if an organism breaks into pieces, a whole new organism can grow ...
... Budding: a new organism grows from the body of the parent organism Binary Fission: one-celled bacterium without a nucleus copies its genetic information and then divides into 2 identical cells Regeneration: if an organism breaks into pieces, a whole new organism can grow ...
Nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Membrane Lysosome Vacuole
... is the location where many important molecules are created and metabolized. The is where proteins are translated. It is the ribosomes that give the rough ER its bumpy appearance. The is where lipids and steroids are synthesized. The endoplasmic reticulum also these new molecules throughout the cell. ...
... is the location where many important molecules are created and metabolized. The is where proteins are translated. It is the ribosomes that give the rough ER its bumpy appearance. The is where lipids and steroids are synthesized. The endoplasmic reticulum also these new molecules throughout the cell. ...
Passive Transport in the Cell
... Animal cells that have a lot of water move in will burst. Plant cells that have a lot of water move in will press against the cell wall and become very firm. ...
... Animal cells that have a lot of water move in will burst. Plant cells that have a lot of water move in will press against the cell wall and become very firm. ...
The basic unit of life is the CELL. This is the smallest entity that is
... information necessary to sustain and propagate life. The nucleic acids (DNA & RNA) and associated enzymes and proteins are found in the nucleus. 4. The ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM. Closely associated with the nucleus is a system of membrane bound tubules, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The membrane surro ...
... information necessary to sustain and propagate life. The nucleic acids (DNA & RNA) and associated enzymes and proteins are found in the nucleus. 4. The ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM. Closely associated with the nucleus is a system of membrane bound tubules, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The membrane surro ...
Functions of Cell Parts
... for future use Directs cell activities and passes on hereditary traits of the cell Controls what enters and leaves the cell ...
... for future use Directs cell activities and passes on hereditary traits of the cell Controls what enters and leaves the cell ...
Label the organelles in the animal cell (see page 175
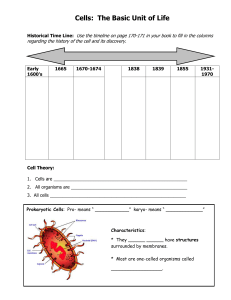
... 1. Cells are ______________________________________________________ 2. All organisms are _______________________________________________ 3. All cells _______________________________________________________ Prokaryotic Cells: Pro- means “ ____________” karyo- means “ _____________” ...
... 1. Cells are ______________________________________________________ 2. All organisms are _______________________________________________ 3. All cells _______________________________________________________ Prokaryotic Cells: Pro- means “ ____________” karyo- means “ _____________” ...
Cheek Cell Lab
... like nearly clear purplish blobs. If you are looking at something dark dark purple, it is probably not a cell. 7. Once you think you have located a cell, switch to high power and refocus. (Remember, do NOT use the coarse adjustment knob at this point) ...
... like nearly clear purplish blobs. If you are looking at something dark dark purple, it is probably not a cell. 7. Once you think you have located a cell, switch to high power and refocus. (Remember, do NOT use the coarse adjustment knob at this point) ...
The Cell
... Structure: Membrane covered spheres Function: Transport particles, including proteins, around and out of cell. Released from the ER and Golgi bodies ...
... Structure: Membrane covered spheres Function: Transport particles, including proteins, around and out of cell. Released from the ER and Golgi bodies ...
Cells Alive Worksheet
... button) - For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. 1. What do mitochondria do? ...
... button) - For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. 1. What do mitochondria do? ...