Topic 8 Checkpoint Answers File
... Antibiotic resistance genes may be transferred to bacteria in the gut which could build up resistance to certain antibiotics used in medical treatments. There are health concerns related to the formation of harmful products in the GMO by new genes, and the products are then eaten. Transfer of genes ...
... Antibiotic resistance genes may be transferred to bacteria in the gut which could build up resistance to certain antibiotics used in medical treatments. There are health concerns related to the formation of harmful products in the GMO by new genes, and the products are then eaten. Transfer of genes ...
Lecture 2 - Cell assembly
... • Cell wall structure • Two distinct groups of bacteria with very different cell walls – Gram negative has an outer lipid membrane (different from the inner, or plasma membrane) – Gram positive lacks the outer membrane but has a thicker peptidogycan layer ...
... • Cell wall structure • Two distinct groups of bacteria with very different cell walls – Gram negative has an outer lipid membrane (different from the inner, or plasma membrane) – Gram positive lacks the outer membrane but has a thicker peptidogycan layer ...
Cell Organelles Graphic Organizer - Liberty Union High School District
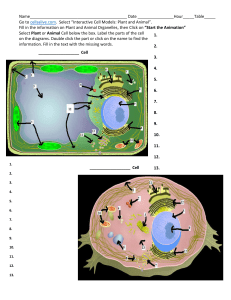
... Name:__________________________ Per:________ Date:_________ ...
... Name:__________________________ Per:________ Date:_________ ...
The Cell in Action
... Cell Energy • Photosynthesis is the process that plants use to take energy from the sun, carbon dioxide and water to create glucose (sugar) and Oxygen. • Cellular respiration is a way that animals break down glucose into water, carbon dioxide and energy. • Most cellular respiration takes place in t ...
... Cell Energy • Photosynthesis is the process that plants use to take energy from the sun, carbon dioxide and water to create glucose (sugar) and Oxygen. • Cellular respiration is a way that animals break down glucose into water, carbon dioxide and energy. • Most cellular respiration takes place in t ...
The Cell
... ► Small, they contain chemicals and enzymes for digestion ► Involved in cleaning up cell parts, molecules, etc. that have died or outlived their usefulness ► Formed by the Golgi Apparatus ► Also called the “Suicide Sac” ...
... ► Small, they contain chemicals and enzymes for digestion ► Involved in cleaning up cell parts, molecules, etc. that have died or outlived their usefulness ► Formed by the Golgi Apparatus ► Also called the “Suicide Sac” ...
DW#4 CellsAlive Websearch
... convoluted, forming 34. ____________________________ (cristae) when viewed in cross-section. The cristae greatly increase the inner membrane's surface area. It is on these cristae that food (sugar) is combined with oxygen to produce ATP - the primary energy source for the cell. Vacuole: A vacuole is ...
... convoluted, forming 34. ____________________________ (cristae) when viewed in cross-section. The cristae greatly increase the inner membrane's surface area. It is on these cristae that food (sugar) is combined with oxygen to produce ATP - the primary energy source for the cell. Vacuole: A vacuole is ...
3-cell-cycle-and-division-mitosis-16-17
... Remember the two reasons why cells divide rather than continue to grow larger: DNA Overload 1. __________________________________ Exchanging Materials 2. _________________________________ DNA overload is when the DNA has too many tasks to do (such as making proteins) and not enough DNA to get the j ...
... Remember the two reasons why cells divide rather than continue to grow larger: DNA Overload 1. __________________________________ Exchanging Materials 2. _________________________________ DNA overload is when the DNA has too many tasks to do (such as making proteins) and not enough DNA to get the j ...
Skills Worksheet
... 1. What is the cytoskeleton, and what is its function? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. What are three types of cytoskeleton fibers, and what does each do? ______________________________________________ ...
... 1. What is the cytoskeleton, and what is its function? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. What are three types of cytoskeleton fibers, and what does each do? ______________________________________________ ...
Homeostasis and Biochemistry
... What are they Chemical Messengers Where do the messengers go to Cells What on the cells do they interact with Receptors Why are only certain cells affected by hormones Cells have specific receptors ...
... What are they Chemical Messengers Where do the messengers go to Cells What on the cells do they interact with Receptors Why are only certain cells affected by hormones Cells have specific receptors ...
IB Biology Summer Assignment WHS
... gradient until equilibrium is reached. Molecules continue to move back and forth in equilibrium without change in concentration. In cells only hydro ...
... gradient until equilibrium is reached. Molecules continue to move back and forth in equilibrium without change in concentration. In cells only hydro ...
microbes cause disease!!
... Toxins are the waste products from bacteria Bacterial infections fever, swelling, rash Treat with ANTIBIOTICS! ...
... Toxins are the waste products from bacteria Bacterial infections fever, swelling, rash Treat with ANTIBIOTICS! ...
chapter 7
... Ribosome- where protein synthesis formation of) occurs. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) – a system of membranes that moves proteins and other substances through the cell. (Transports). Rough ER has ribosomes attached to it. Smooth ER has no ribosomes. Golgi apparatus (Golgi body) – a set of flattened mem ...
... Ribosome- where protein synthesis formation of) occurs. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) – a system of membranes that moves proteins and other substances through the cell. (Transports). Rough ER has ribosomes attached to it. Smooth ER has no ribosomes. Golgi apparatus (Golgi body) – a set of flattened mem ...
cell membrane
... – Are composed of RNA and protein. – Produced by the nucleolus within the nucleus. ...
... – Are composed of RNA and protein. – Produced by the nucleolus within the nucleus. ...
Structure of the Cell Membrane
... bulky material into a cell • Uses energy • Cell membrane in-folds around food particle • “cell eating” • forms food vacuole & digests food • This is how white blood cells eat bacteria! ...
... bulky material into a cell • Uses energy • Cell membrane in-folds around food particle • “cell eating” • forms food vacuole & digests food • This is how white blood cells eat bacteria! ...
Diffusion & Osmosis
... The movement of molecules from an area in which they are highly concentrated to an area in which they are less Concentrated. requires ...
... The movement of molecules from an area in which they are highly concentrated to an area in which they are less Concentrated. requires ...
The Origin of Eukaryotic Cells
... The eukaryotic cell might have evolved when a large anaerobic amoeboid prokaryote ingested small aerobic bacteria and stabilized them instead of digesting them. This idea is known as the endosymbiont hypothesis and was first proposed by Lynn Margulis, a biologist at Boston University. (Symbiosis is ...
... The eukaryotic cell might have evolved when a large anaerobic amoeboid prokaryote ingested small aerobic bacteria and stabilized them instead of digesting them. This idea is known as the endosymbiont hypothesis and was first proposed by Lynn Margulis, a biologist at Boston University. (Symbiosis is ...
Presentation on Cells
... Why are cells different? Some animal and plant cells are made of just one cell, or just few cells. All of their cells have to carry out all the processes of life. However, large organisms are more complicated and they have different organs to do different jobs. The shape and structure of each cell ...
... Why are cells different? Some animal and plant cells are made of just one cell, or just few cells. All of their cells have to carry out all the processes of life. However, large organisms are more complicated and they have different organs to do different jobs. The shape and structure of each cell ...
Cell Structure & Function - Woodcliff Lake Public Schools
... • Both cells have organelles in them. • Each organelle has a special job to do to help the cell function. • We will only be learning about some of the organelles. ...
... • Both cells have organelles in them. • Each organelle has a special job to do to help the cell function. • We will only be learning about some of the organelles. ...
Plant Structure and Types of Cells Notes
... Found in parts of the plant that are no longer growing. Skeletal support for water-conducting tissues and the plant itself. These cell fibers are used to make linen and rope. Form a major part of fruit pits and hard outer shells of nuts. ...
... Found in parts of the plant that are no longer growing. Skeletal support for water-conducting tissues and the plant itself. These cell fibers are used to make linen and rope. Form a major part of fruit pits and hard outer shells of nuts. ...
CELL
... In the CYTOPLASM of some plant cells, there are many SMALL, GREEN structures called CHLOROPLASTS. ...
... In the CYTOPLASM of some plant cells, there are many SMALL, GREEN structures called CHLOROPLASTS. ...
Introduction Resources Answers to questions
... 2. Add the size of a virus, animal cell and bacterium to the scale above to show their relative size. 3. Antibiotic drugs interfere with the chemical reactions of bacterial or fungal cells. For example, penicillin prevents the bacteria making the material for their cell wall. Use the diagrams of str ...
... 2. Add the size of a virus, animal cell and bacterium to the scale above to show their relative size. 3. Antibiotic drugs interfere with the chemical reactions of bacterial or fungal cells. For example, penicillin prevents the bacteria making the material for their cell wall. Use the diagrams of str ...
Topic: What I KNOW What I WANT to know HOW I can learn more
... What do cells look like under a microscope? ...
... What do cells look like under a microscope? ...