Grade 8 Science Chapter 10 Review Sheet_2016_ANSWERS
... 22. The mitochondria produces energy for the cell by breaking down food particles to release stored energy. 23. What are three key differences between plant cells and animal cells? i) plant cells have chloroplasts, animal cells do not ii) plant cells have cell walls, animal cells do not. Therefore ...
... 22. The mitochondria produces energy for the cell by breaking down food particles to release stored energy. 23. What are three key differences between plant cells and animal cells? i) plant cells have chloroplasts, animal cells do not ii) plant cells have cell walls, animal cells do not. Therefore ...
2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells What is a Prokaryotic Cell
... The advantage of having ribosomes attached to ER is that as the ribosomes synthesize proteins they can be transported by the ER to become parts of cell membranes, enzymes for the cell or messengers between cells. The smooth ER has many functions such as production of membrane phospholipids, producti ...
... The advantage of having ribosomes attached to ER is that as the ribosomes synthesize proteins they can be transported by the ER to become parts of cell membranes, enzymes for the cell or messengers between cells. The smooth ER has many functions such as production of membrane phospholipids, producti ...
Reading Quiz 4 (with answers)
... (c) an early region of rocky, dry land on the forming planet. (d) a rock-like ocean growth that occurred on ancient earth and still can be found today. (e) a ‘spore’ that seeds life. (p. 199). Protocells are suggested tiny enclosures that allow molecular processes to proceed relatively unmolested by ...
... (c) an early region of rocky, dry land on the forming planet. (d) a rock-like ocean growth that occurred on ancient earth and still can be found today. (e) a ‘spore’ that seeds life. (p. 199). Protocells are suggested tiny enclosures that allow molecular processes to proceed relatively unmolested by ...
B2 1 Cells, Tissues and Organs Questions and Answers
... (allow reference to gaseous exchange) for 1 mark ...
... (allow reference to gaseous exchange) for 1 mark ...
Sheet#2,Dr.Nisreen, Noor Tahboub
... We have 3 panels; normal,reversible and irreversible injured cell In the normal cell: 1-the plasma membrane is regular 2-the nucleus is clear 3-chromatin is open (no condensation) 4-all the organelles are perfect In the reversible injured cell: under microscope we will see morphological changes or s ...
... We have 3 panels; normal,reversible and irreversible injured cell In the normal cell: 1-the plasma membrane is regular 2-the nucleus is clear 3-chromatin is open (no condensation) 4-all the organelles are perfect In the reversible injured cell: under microscope we will see morphological changes or s ...
Chapter 1 : Classification of living things (1) Learning objectives: 1
... Cell wall of diatoms has lots of silicone (major elements of sand and semi-conductors). Structure of the Cell wall of diatoms is very strange, it is made of two parts jointing together like a Petri-dish. When diatoms die, the porour, silicone containing shell, become ‘’, frequently added to cosmetic ...
... Cell wall of diatoms has lots of silicone (major elements of sand and semi-conductors). Structure of the Cell wall of diatoms is very strange, it is made of two parts jointing together like a Petri-dish. When diatoms die, the porour, silicone containing shell, become ‘’, frequently added to cosmetic ...
Chameleon Behavior of a Phospholipid-Like
... Chameleon Behavior of a Phospholipid-Like Siderophore Amphiphilic siderophores are exquisitely engineered by bacteria to facilitate the iron uptake necessary for growth. The first structure determination of a citrate based siderophore has revealed a remarkable conformational reorganization upon bind ...
... Chameleon Behavior of a Phospholipid-Like Siderophore Amphiphilic siderophores are exquisitely engineered by bacteria to facilitate the iron uptake necessary for growth. The first structure determination of a citrate based siderophore has revealed a remarkable conformational reorganization upon bind ...
01 - edl.io
... b. chromatin d. centromere _____ 12. In eurkaryotes, a structural unit made up of DNA wound around a center of histone proteins is called a a. chromatid. c. centrosome. b. nucleosome. d. looped domain. _____ 13. The structure that directs chromosome movement during mitosis and aids in the formation ...
... b. chromatin d. centromere _____ 12. In eurkaryotes, a structural unit made up of DNA wound around a center of histone proteins is called a a. chromatid. c. centrosome. b. nucleosome. d. looped domain. _____ 13. The structure that directs chromosome movement during mitosis and aids in the formation ...
Slide 1
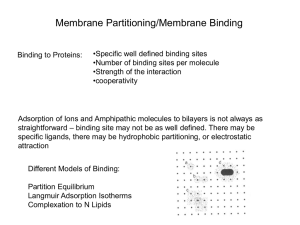
... concentration of free molecule in solution (P). Binding Isotherms are typically analyzed by measuring either the amount of the free ligand in solution or that bound to the bilayer and knowing the total concentration of lipid. An expression was given in Fridays paper presentation: Typically you deriv ...
... concentration of free molecule in solution (P). Binding Isotherms are typically analyzed by measuring either the amount of the free ligand in solution or that bound to the bilayer and knowing the total concentration of lipid. An expression was given in Fridays paper presentation: Typically you deriv ...
Tentative Homework Schedule summer
... Draw a eukaryotic cell Label the following (Golgi, mitochondria, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, nucleus, plasma membrane, ribosome, rough ER, smooth ER, vesicle) Pick 3 of the above and briefly describe its structure/function ---------------------------------------------------------------------------D ...
... Draw a eukaryotic cell Label the following (Golgi, mitochondria, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, nucleus, plasma membrane, ribosome, rough ER, smooth ER, vesicle) Pick 3 of the above and briefly describe its structure/function ---------------------------------------------------------------------------D ...
Cells
... • After the nucleus has divided, cytokinesis (division of the cytoplasm) occurs. • This is the last phase of the cell ...
... • After the nucleus has divided, cytokinesis (division of the cytoplasm) occurs. • This is the last phase of the cell ...
CELL - Gyanpedia
... solution is known as a hypertonic solution. Again, water crosses the cell membrane in both directions, but this time more water leaves the cell than enters it. Therefore the cell will shrink. Thus, osmosis is a special case of diffusion through a selectively permeable membrane. ...
... solution is known as a hypertonic solution. Again, water crosses the cell membrane in both directions, but this time more water leaves the cell than enters it. Therefore the cell will shrink. Thus, osmosis is a special case of diffusion through a selectively permeable membrane. ...
Cell Diversity Compare and Contrast Worksheet
... Cell Diversity Compare and Contrast Worksheet Instructions: Using a biology textbook, answer the following questions to help you understand the diversity of structures and functions that different cells exhibit. 1. Define “prokaryotic cell”, and describe some properties of organisms that have prokar ...
... Cell Diversity Compare and Contrast Worksheet Instructions: Using a biology textbook, answer the following questions to help you understand the diversity of structures and functions that different cells exhibit. 1. Define “prokaryotic cell”, and describe some properties of organisms that have prokar ...
G:\CLASSES\BI 345n6\BI345n6_F10\tests\midterm1_F10.wpd
... (5 points) What is the significance of the bacterium Aquifex pyrophilus having a cell membrane with only phospholipids, but with both ester and ether linkages? ...
... (5 points) What is the significance of the bacterium Aquifex pyrophilus having a cell membrane with only phospholipids, but with both ester and ether linkages? ...
Wet Mount Lab Activity and Assignment
... Place the slide on the stage of the microscope, set it to low power, adjust the focus so the onion slice is clear. Draw four or five cells as seen. Label the cell walls. 8. Switch to higher power and try to identify the cell membrane, nucleus, and cytoplasm. ...
... Place the slide on the stage of the microscope, set it to low power, adjust the focus so the onion slice is clear. Draw four or five cells as seen. Label the cell walls. 8. Switch to higher power and try to identify the cell membrane, nucleus, and cytoplasm. ...
ALL LIFE IS CELLULAR!
... Cells have a support structure called the cytoskeleton within the cytoplasm. The cytoskeleton is composed of microtubules and microfilaments. Microtubules are thin, hollow cylinders made of protein and microfilaments are thin solid protein fibers. ...
... Cells have a support structure called the cytoskeleton within the cytoplasm. The cytoskeleton is composed of microtubules and microfilaments. Microtubules are thin, hollow cylinders made of protein and microfilaments are thin solid protein fibers. ...
Animal Cell Back to Plant Cell Structure Function
... Cell Coloring Instructions: Use the following color coding according to the functions of the cell organelles. Full credit (50 ...
... Cell Coloring Instructions: Use the following color coding according to the functions of the cell organelles. Full credit (50 ...
cell/city project grading rubric
... not clearly represented or stated. -The information/images are organized in a manner that poorly reflects the organization of the cell/city. -The information is less legible and/or lacks direct association the function of cell/city -Less than 60% of the -76-85% of the organelles/cell components orga ...
... not clearly represented or stated. -The information/images are organized in a manner that poorly reflects the organization of the cell/city. -The information is less legible and/or lacks direct association the function of cell/city -Less than 60% of the -76-85% of the organelles/cell components orga ...
cells
... scientists continued to study cells and added new information to the initial observations. The major concepts surrounding cells are now known as the cell theory. The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living thi ...
... scientists continued to study cells and added new information to the initial observations. The major concepts surrounding cells are now known as the cell theory. The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living thi ...
Cleavage stage and cell division Cleavage stage and cell
... The phases must follow in correct order, and one phase g must be completed before the next phase can begin. Errors in this coordination may lead to chromosomal alterations. Chromosomes or parts of chromosomes may be lost, rearranged or distributed unequally between the two daughter cells, often seen ...
... The phases must follow in correct order, and one phase g must be completed before the next phase can begin. Errors in this coordination may lead to chromosomal alterations. Chromosomes or parts of chromosomes may be lost, rearranged or distributed unequally between the two daughter cells, often seen ...
Protists…A Study of Cells and the Microscope
... 4. Draw the amoeba on your answer sheet. Write the total magnification you used to make your drawing. 5. This cell is eukaryotic and should have a control center or nucleus. It would appear as a darker area inside the cell. Draw and label this part. 6. Amoeba has pseudopods, or “false feet”, that st ...
... 4. Draw the amoeba on your answer sheet. Write the total magnification you used to make your drawing. 5. This cell is eukaryotic and should have a control center or nucleus. It would appear as a darker area inside the cell. Draw and label this part. 6. Amoeba has pseudopods, or “false feet”, that st ...