Cells - Marric.us
... about the same size as bacteria (prokaryotes) 2. Mitochondria and chloroplasts are surround by two membranes ...
... about the same size as bacteria (prokaryotes) 2. Mitochondria and chloroplasts are surround by two membranes ...
cell structure and function
... • The cytoplasmic membrane is a double-layered structure, called a phospholipid bilayer, composed of molecules with hydrophobic lipid tails and hydrophilic phosphate heads. • The selectively permeable cytoplasmic membrane, not only,separates the contents of the cell from the outside environment, but ...
... • The cytoplasmic membrane is a double-layered structure, called a phospholipid bilayer, composed of molecules with hydrophobic lipid tails and hydrophilic phosphate heads. • The selectively permeable cytoplasmic membrane, not only,separates the contents of the cell from the outside environment, but ...
The Cell City Culminating Task
... The Cell: Culminating Task Over the past few weeks, we have been learning about different cell organelles and the functions of these structures. The functions of these organelles can be compared to those of the various parts of a city. For example, the nucleus of the cell could be compared to the ci ...
... The Cell: Culminating Task Over the past few weeks, we have been learning about different cell organelles and the functions of these structures. The functions of these organelles can be compared to those of the various parts of a city. For example, the nucleus of the cell could be compared to the ci ...
Plants Up Close
... that onion cells are rectangular in shape and that the cells stack together neatly. The round dots inside of the cells are nuclei; they control heredity and cell division. • Review with the class what Students should also be able to see magnification is and why it is two layers lining the cell; the ...
... that onion cells are rectangular in shape and that the cells stack together neatly. The round dots inside of the cells are nuclei; they control heredity and cell division. • Review with the class what Students should also be able to see magnification is and why it is two layers lining the cell; the ...
Cell City Project of
... Cell City Analogy Worksheet Our plant cell is being compared to:____________________ (Turn this completed page in with your poster) ...
... Cell City Analogy Worksheet Our plant cell is being compared to:____________________ (Turn this completed page in with your poster) ...
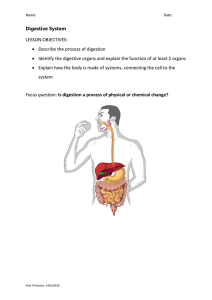
Digestive System
... The movement of molecules from high to low concentration until they are evenly distributed Osmosis: The movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane from high to low concentration Metabolism: All the physical and chemical processes in an organism that create energy and maintain growth, from d ...
... The movement of molecules from high to low concentration until they are evenly distributed Osmosis: The movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane from high to low concentration Metabolism: All the physical and chemical processes in an organism that create energy and maintain growth, from d ...
Membrane Permeability Suggested Additional
... from 10 stopped-flow accumulations. ( ) An example of the stopped-flow assay that measures rates of transport of different carbohydrates into reconstituted vesicles, applied in this example to ribitol, a conducted alditol. Vesicles were reconstituted with GlpF (red) or without GlpF (green) and then ...
... from 10 stopped-flow accumulations. ( ) An example of the stopped-flow assay that measures rates of transport of different carbohydrates into reconstituted vesicles, applied in this example to ribitol, a conducted alditol. Vesicles were reconstituted with GlpF (red) or without GlpF (green) and then ...
Cell Growth Power Point
... and organelles, so they divide much faster than eukaryotic cells. • The rate at which your cells divide is linked to your body’s need for those cells. • In human cells, the S, G2, and M stages together ...
... and organelles, so they divide much faster than eukaryotic cells. • The rate at which your cells divide is linked to your body’s need for those cells. • In human cells, the S, G2, and M stages together ...
Cellular Transport Vocabulary Words
... 7. Endocytosis-Active transport of molecules into a cell. Usually against the concentration gradient. (low to high) 8. Pinocytosis-“Cell drinking” Active transport of tiny amounts of water into a cell. Usually against the concentration gradient. (low to high) 9. Phagocytosis- “Cell eating” Active t ...
... 7. Endocytosis-Active transport of molecules into a cell. Usually against the concentration gradient. (low to high) 8. Pinocytosis-“Cell drinking” Active transport of tiny amounts of water into a cell. Usually against the concentration gradient. (low to high) 9. Phagocytosis- “Cell eating” Active t ...
Cellular Transport Vocabulary Words
... to an area of lower concentration (energy that moves the molecules is provided by Brownian Movement)…… as in colliding pool balls in billiards. 2. Diffusion-Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. (passive) 3. Osmosis-Movement of water molecules fr ...
... to an area of lower concentration (energy that moves the molecules is provided by Brownian Movement)…… as in colliding pool balls in billiards. 2. Diffusion-Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. (passive) 3. Osmosis-Movement of water molecules fr ...
Microscopy and Cell Structure
... These organisms form a swarm of cells Allows for the release of enzymes which degrade organic material In the absence of water cells for fruiting bodies ...
... These organisms form a swarm of cells Allows for the release of enzymes which degrade organic material In the absence of water cells for fruiting bodies ...
Synaptic transmission disorder
... An action potential in the presynaptic cell triggers vesicles to move toward the cell membrane Vesicles are guided toward membrane by proteins Guilding proteins act like ropes that help to pull the ves ...
... An action potential in the presynaptic cell triggers vesicles to move toward the cell membrane Vesicles are guided toward membrane by proteins Guilding proteins act like ropes that help to pull the ves ...
Content Outline
... 2. Cell membrane–_________________ layer around all cells a. For cells with cell walls, the _________________ is inside the cell wall b. A cell membrane allows ________ and _____________ into the cell and waste products out of the cell. 3. Cytoplasm–gelatin like substance inside cell membrane a. ___ ...
... 2. Cell membrane–_________________ layer around all cells a. For cells with cell walls, the _________________ is inside the cell wall b. A cell membrane allows ________ and _____________ into the cell and waste products out of the cell. 3. Cytoplasm–gelatin like substance inside cell membrane a. ___ ...
Science Curriculum Map
... including but not restricted to epithelial, blood and muscle. Or complete the tree map on the types of cells for plants including roots, stems and leaves. ...
... including but not restricted to epithelial, blood and muscle. Or complete the tree map on the types of cells for plants including roots, stems and leaves. ...
Cells Study Guide Answers
... 13. Explain why a muscle cell in your leg would have more mitochondria than a bone cell would? Muscle cell needs more energy – mitochondria produce energy for the cell 14. Describe two structures that some cells have to help them move around. Cilia – tiny hairs that move back and forth Flagella – ta ...
... 13. Explain why a muscle cell in your leg would have more mitochondria than a bone cell would? Muscle cell needs more energy – mitochondria produce energy for the cell 14. Describe two structures that some cells have to help them move around. Cilia – tiny hairs that move back and forth Flagella – ta ...
Biology Core
... 9. Describe why cells cannot grow too large. When cells grow, the surface are, which is in charge of the rate of enter/exit of materials in the cell, grows at a slower rate compared to the volume, which controls the rate materials are used/produced. Because of this, materials cannot get quickly enou ...
... 9. Describe why cells cannot grow too large. When cells grow, the surface are, which is in charge of the rate of enter/exit of materials in the cell, grows at a slower rate compared to the volume, which controls the rate materials are used/produced. Because of this, materials cannot get quickly enou ...
Biology I Lab Activity – Simulating Mitosis with
... Telophase is the final stage of mitosis. During telophase, chromosomes- reach the opposite ends of the parent cell. The chromosomes begin de-condensing back into chromatin, the spindle breaks apart, and the nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear. To model telophase, place each chromosome at opposit ...
... Telophase is the final stage of mitosis. During telophase, chromosomes- reach the opposite ends of the parent cell. The chromosomes begin de-condensing back into chromatin, the spindle breaks apart, and the nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear. To model telophase, place each chromosome at opposit ...
Cells—The Building Blocks of Life
... chickens. Each egg is a single, large cell. The largest cell is the ostrich egg. It is about 20 inches across! Although there are many types of cells, all cells have several things in common: ...
... chickens. Each egg is a single, large cell. The largest cell is the ostrich egg. It is about 20 inches across! Although there are many types of cells, all cells have several things in common: ...
Occurrence (Distribution of bacteria)
... Motility in bacteria • Bacteria are either nonmotile or motile. Motile forms are either creeping or swimming. Creeping bacteria (e.g. Myobacterium) move or creep slowly on a supporting surface as a result of wave-like contractions ( contract and relax) of their bodies. Swimming bacteria move freely ...
... Motility in bacteria • Bacteria are either nonmotile or motile. Motile forms are either creeping or swimming. Creeping bacteria (e.g. Myobacterium) move or creep slowly on a supporting surface as a result of wave-like contractions ( contract and relax) of their bodies. Swimming bacteria move freely ...
Sample APBio Exam1 - Bruce Rife`s Web Page
... 3. solubility of the protein in water 4. the number of amino acids in the protein a. 1 d. 4 b. 2 e. 1, 2, and 3 c. 3 25. Which of the following factors can result in the denaturation of a protein? a. heat d. changes in salt concentration b. changes in pH e. all of these c. chemicals that destroy hyd ...
... 3. solubility of the protein in water 4. the number of amino acids in the protein a. 1 d. 4 b. 2 e. 1, 2, and 3 c. 3 25. Which of the following factors can result in the denaturation of a protein? a. heat d. changes in salt concentration b. changes in pH e. all of these c. chemicals that destroy hyd ...
Cell City Project - Mrs. Redwine`s Class
... On a plain piece of white paper you will sketch, color, and label your cell city. Each part will be labeled with its name and the name of the organelle that has a similar function. You must complete the chart attached to this and your map. This chart will help you create your analogies. ...
... On a plain piece of white paper you will sketch, color, and label your cell city. Each part will be labeled with its name and the name of the organelle that has a similar function. You must complete the chart attached to this and your map. This chart will help you create your analogies. ...
m5zn_7e2104c47c4f1d9
... polar and non polar regions. the polar part is the phosphate containing “head” which is hydrophilic “mixes with water”. The non-polars are the two fatty acid “tails” which are hydrophobic “do not mix with water”. The molecules orient in the bilayer so that the heads face outward on either side. The ...
... polar and non polar regions. the polar part is the phosphate containing “head” which is hydrophilic “mixes with water”. The non-polars are the two fatty acid “tails” which are hydrophobic “do not mix with water”. The molecules orient in the bilayer so that the heads face outward on either side. The ...
Ch. 5. Protein Purification and Characterization Techniques
... Paul D. Adams • University of Arkansas ...
... Paul D. Adams • University of Arkansas ...
T Cell Development
... X linked disorder Affects platelet numbers/function Affects T cell function Cytoskeleton of lymphocytes affected ...
... X linked disorder Affects platelet numbers/function Affects T cell function Cytoskeleton of lymphocytes affected ...