Making Proteins - Foothill Technology High School
... How are proteins created by the “free” ribosomes differ in destination from the proteins created by the “attached” ribosomes of the ER? Attached Ribosomes: They proteins make proteins Free Ribosomes: They make that stay that withinare either the cytoplasm. The cell uses these proteins itself. 1) se ...
... How are proteins created by the “free” ribosomes differ in destination from the proteins created by the “attached” ribosomes of the ER? Attached Ribosomes: They proteins make proteins Free Ribosomes: They make that stay that withinare either the cytoplasm. The cell uses these proteins itself. 1) se ...
Lab. 2 Cell Division 1. Mitosis Division
... The cell is engaged in metabolic activity and performing it’s prepare for mitosis. Chromosomes are not clearly discerned in the nucleus, although a dark spot called the nucleolus may be visible. The cell may contain a pair of centrioles (or microtubule organizing centers in plants) both of which are ...
... The cell is engaged in metabolic activity and performing it’s prepare for mitosis. Chromosomes are not clearly discerned in the nucleus, although a dark spot called the nucleolus may be visible. The cell may contain a pair of centrioles (or microtubule organizing centers in plants) both of which are ...
Slide ()
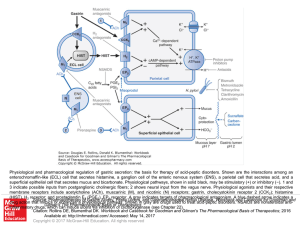
... Physiological and pharmacological regulation of gastric secretion: the basis for therapy of acid-peptic disorders. Shown are the interactions among an enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cell that secretes histamine, a ganglion cell of the enteric nervous system (ENS), a parietal cell that secretes acid, an ...
... Physiological and pharmacological regulation of gastric secretion: the basis for therapy of acid-peptic disorders. Shown are the interactions among an enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cell that secretes histamine, a ganglion cell of the enteric nervous system (ENS), a parietal cell that secretes acid, an ...
Membrane Practice Test
... (1.) Cells use this process to export products such as insulin or thyroxine. ...
... (1.) Cells use this process to export products such as insulin or thyroxine. ...
Osmosis in Plant Cells - Middlesex High School
... The presence of a cell wall and a large fluid-filled central vacuole in a plant or algal cell will affect the cell’s response to solutions of differing concentrations. When a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water moves out of the cell; the cell wall shrinks and may pull away from the ...
... The presence of a cell wall and a large fluid-filled central vacuole in a plant or algal cell will affect the cell’s response to solutions of differing concentrations. When a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water moves out of the cell; the cell wall shrinks and may pull away from the ...
Oncofertility 2b. Student Lab A Study of the Relationship between
... When cells grow to a certain size, their rate of growth slows down until they stop growing entirely. They have reached their size limit. When one of these larger cells divides into two smaller cells, the rate of growth again increases. We will study one of the factors that limits cell size and growt ...
... When cells grow to a certain size, their rate of growth slows down until they stop growing entirely. They have reached their size limit. When one of these larger cells divides into two smaller cells, the rate of growth again increases. We will study one of the factors that limits cell size and growt ...
the fine structure of von ebner`s gland of the rat
... often certain elements of ER had a vesicular appearance . Transitional elements of the ER were found near the Golgi complex (Figs . 4, 5) . Small vesicles 400-700 A in diameter appeared to bud off of the ribosome-free portions of the transitional ER . Mitochondria were numerous and were scattered th ...
... often certain elements of ER had a vesicular appearance . Transitional elements of the ER were found near the Golgi complex (Figs . 4, 5) . Small vesicles 400-700 A in diameter appeared to bud off of the ribosome-free portions of the transitional ER . Mitochondria were numerous and were scattered th ...
AS Biology FOUNDATION Chapter 4 CELL MEMBRANES and
... All living things are surrounded by a membrane. A cell membrane is also known as plasma membrane. ...
... All living things are surrounded by a membrane. A cell membrane is also known as plasma membrane. ...
Diffusion Lab PPT
... All living things are surrounded by a membrane. A cell membrane is also known as plasma membrane. ...
... All living things are surrounded by a membrane. A cell membrane is also known as plasma membrane. ...
Bio102A organic notes (2)
... proteins have a large variety of sizes & shapes If the shape changes, it becomes a new protein ...
... proteins have a large variety of sizes & shapes If the shape changes, it becomes a new protein ...
REVIEW PowerPoint - Ch. 1-5
... a. Prokaryotic cells have a cell wall, but eukaryotic cells never do. b. Prokaryotic cells are much larger than eukaryotic cells c. Prokaryotic cells have flagella, but eukaryotic cells do not d. Prokaryotic cells do not have a membrane-bound nucleus, but eukaryotic cells do have such a nucleus. e. ...
... a. Prokaryotic cells have a cell wall, but eukaryotic cells never do. b. Prokaryotic cells are much larger than eukaryotic cells c. Prokaryotic cells have flagella, but eukaryotic cells do not d. Prokaryotic cells do not have a membrane-bound nucleus, but eukaryotic cells do have such a nucleus. e. ...
Enzyme Worksheet
... are made primarily of carbon. Each small organic molecule can be a unit of a large organic molecule called a macromolecule. There are four classes of macromolecules (polysaccharides or carbohydrates, triglycerides or lipids, polypeptides or proteins, and nucleic acids such as DNA & RNA). Carbohydrat ...
... are made primarily of carbon. Each small organic molecule can be a unit of a large organic molecule called a macromolecule. There are four classes of macromolecules (polysaccharides or carbohydrates, triglycerides or lipids, polypeptides or proteins, and nucleic acids such as DNA & RNA). Carbohydrat ...
Cells
... Some things can go through, while others cannot. The plasma membrane, with its embedded molecules, controls this. ...
... Some things can go through, while others cannot. The plasma membrane, with its embedded molecules, controls this. ...
Lecture 2: Cellular signalling and cell division
... Controlled transport of chemicals, ions and macromolecules Exocytosis and endocytosis Signal transduction Generation of action potential ...
... Controlled transport of chemicals, ions and macromolecules Exocytosis and endocytosis Signal transduction Generation of action potential ...
Planet Earth and Its Environment A 5000
... By the time the daughter cells have grown to the size of the original parent cell, they have a similar number or organelles as the original cell had. ...
... By the time the daughter cells have grown to the size of the original parent cell, they have a similar number or organelles as the original cell had. ...
Spec for students digestion and metabolism
... Lipases break down lipids (fats) to glycerol and fatty acids. The products of digestion are used to build new carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. Some glucose is used in respiration. Bile is made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder. It is alkaline to neutralise hydrochloric acid from the sto ...
... Lipases break down lipids (fats) to glycerol and fatty acids. The products of digestion are used to build new carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. Some glucose is used in respiration. Bile is made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder. It is alkaline to neutralise hydrochloric acid from the sto ...
File
... get rid of wastes and to export materials. • This is accomplished by the processes of diffusion, and osmosis, which are passive mechanisms. Other passive mechanisms which allow materials to pass in and out of cells such as facilitated transport. • There are also active transport mechanisms, which re ...
... get rid of wastes and to export materials. • This is accomplished by the processes of diffusion, and osmosis, which are passive mechanisms. Other passive mechanisms which allow materials to pass in and out of cells such as facilitated transport. • There are also active transport mechanisms, which re ...
Study the following for the test on Thursday (3/10/11)
... -Low turgor pressure – force outside of the cell wall is _________ than the cell wall, force of vacuole is ____________ - what happens to the plant? -What happens to a plant cell during high turgor pressure? What is happening to the plant? - Photosynthesis - know the equation for photosynthesis – wh ...
... -Low turgor pressure – force outside of the cell wall is _________ than the cell wall, force of vacuole is ____________ - what happens to the plant? -What happens to a plant cell during high turgor pressure? What is happening to the plant? - Photosynthesis - know the equation for photosynthesis – wh ...
Document
... Quaternary structure: Some proteins are composed of only one polypeptide chain, such as myoglobin. But most are made up of more than one chain, or subunits. It is called as quaternary structure that the subunits linked together often by noncovalent bonds between hydrophobic “patches” on the compleme ...
... Quaternary structure: Some proteins are composed of only one polypeptide chain, such as myoglobin. But most are made up of more than one chain, or subunits. It is called as quaternary structure that the subunits linked together often by noncovalent bonds between hydrophobic “patches” on the compleme ...
Carrier Proteins - HCC Learning Web
... back-pressure on the cell that opposes further uptake. – At this point the cell is turgid (very firm), a healthy state for most plant cells. Turgid cells contribute to the mechanical support of the plant. • If a plant cell and its surroundings are isotonic, there is no movement of water into the cel ...
... back-pressure on the cell that opposes further uptake. – At this point the cell is turgid (very firm), a healthy state for most plant cells. Turgid cells contribute to the mechanical support of the plant. • If a plant cell and its surroundings are isotonic, there is no movement of water into the cel ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology
... 1. What is another way of referring to action potentials? 2. What is a neurotransmitter and what is its function? 3. What is a neuroeffector junction? 4. Draw a diagram in which you label the synaptic knob, the synaptic cleft, and the pre- and post-synaptic neurons. Show the synaptic vesicles and th ...
... 1. What is another way of referring to action potentials? 2. What is a neurotransmitter and what is its function? 3. What is a neuroeffector junction? 4. Draw a diagram in which you label the synaptic knob, the synaptic cleft, and the pre- and post-synaptic neurons. Show the synaptic vesicles and th ...