THE EUKARYOTIC CELL
... A eukaryotic cell contains complex structures enclosed within membranes. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, surrounded by a nuclear envelope, within which the genetic material is carried. Most eukaryotic cells also contain ot ...
... A eukaryotic cell contains complex structures enclosed within membranes. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, surrounded by a nuclear envelope, within which the genetic material is carried. Most eukaryotic cells also contain ot ...
Lysosomes: Nickname: Job: Contains made by the ribosomes and
... 3. Smooth ER pinches off and the digestive enzymes is contained in the _____________________________. ...
... 3. Smooth ER pinches off and the digestive enzymes is contained in the _____________________________. ...
Biology Chapter 7
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
A Tour of the Cell - Ursuline High School
... modify proteins and lipids into vesicles (small, spherical shaped sacs that bud form the Golgi apparatus). The vesicles often merge and merge with the plasma membrane to release contents to the outside of the cell. ...
... modify proteins and lipids into vesicles (small, spherical shaped sacs that bud form the Golgi apparatus). The vesicles often merge and merge with the plasma membrane to release contents to the outside of the cell. ...
Cell Organelle Organelle Function City Part Cell Membrane
... Cell Organelle Cell Membrane Nucleus ...
... Cell Organelle Cell Membrane Nucleus ...
Name - Humble ISD
... Physiology of Cells – Chapter 4 1. Compare and contrast the processes of diffusion, dialysis, facilitated diffusion, osmosis and diffusion. 2. Discuss the factors which affect osmotic pressure. 3. Discuss the “active cell transport mechanisms responsible for the movement of materials through the cel ...
... Physiology of Cells – Chapter 4 1. Compare and contrast the processes of diffusion, dialysis, facilitated diffusion, osmosis and diffusion. 2. Discuss the factors which affect osmotic pressure. 3. Discuss the “active cell transport mechanisms responsible for the movement of materials through the cel ...
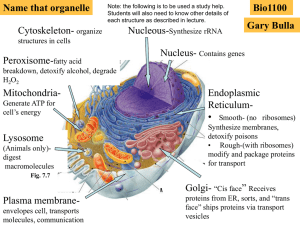
Structures found in Eukaryotes Continued 4. • Formed by • Vesicles
... Structures found in Eukaryotes Continued ...
... Structures found in Eukaryotes Continued ...
Document
... Metabolism: photosynthesis, respiration, fermentation, digestion, gas exchange, secretion, excretion, circulation--processing materials and energy Growth: cell enlargement, cell number Movement: intracellular, movement, locomotion ...
... Metabolism: photosynthesis, respiration, fermentation, digestion, gas exchange, secretion, excretion, circulation--processing materials and energy Growth: cell enlargement, cell number Movement: intracellular, movement, locomotion ...
Cells - biologybi
... DNA. Nucleolus- contains RNA. Cell membrane- separates the cell from other cells and allows molecules to pass through. Cell wall- protects and supports the cell. (Plant cells only) ...
... DNA. Nucleolus- contains RNA. Cell membrane- separates the cell from other cells and allows molecules to pass through. Cell wall- protects and supports the cell. (Plant cells only) ...
File
... Capsule- Outside the cell wall. For additional protection. Plasma membrane- Regulates what crosses into the cell Nucleiod Region- where circular DNA is found Ribosomes- Workbench, where proteins are made ...
... Capsule- Outside the cell wall. For additional protection. Plasma membrane- Regulates what crosses into the cell Nucleiod Region- where circular DNA is found Ribosomes- Workbench, where proteins are made ...
Cells - Wsfcs
... The liquid environment of the cell. The cytoplasm contains the organelles of ...
... The liquid environment of the cell. The cytoplasm contains the organelles of ...
Unit B: Cell structure
... • Nuclear membrane/envelope bilayer, separates and contains nuclear contents (DNA). • Nuclear pores: allow mRNA out of nucleus, nucleotides, nutrients & enzymes in. They are made from protein. • Chromatin: Protein & DNA; form chromosomes when cell divides. • Nucleolus:contains rRNA and Ribosomal pro ...
... • Nuclear membrane/envelope bilayer, separates and contains nuclear contents (DNA). • Nuclear pores: allow mRNA out of nucleus, nucleotides, nutrients & enzymes in. They are made from protein. • Chromatin: Protein & DNA; form chromosomes when cell divides. • Nucleolus:contains rRNA and Ribosomal pro ...
Unit 1 Lesson 3 - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Structure is the arrangement of parts Function is the activity the parts carry out Ex: plant and animal cells differ, cells in a single organism can be different depending on function Most cells in multicellular organisms have a special role. This is called differentiation. Parts of the Cell ...
... Structure is the arrangement of parts Function is the activity the parts carry out Ex: plant and animal cells differ, cells in a single organism can be different depending on function Most cells in multicellular organisms have a special role. This is called differentiation. Parts of the Cell ...