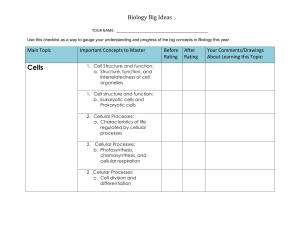
Biology Standards Checklist
... interaction types 1. Mechanisms: g. History of life on Earth: fossil record, common ancestors, cladograms ...
... interaction types 1. Mechanisms: g. History of life on Earth: fossil record, common ancestors, cladograms ...
Name - SMS Tiger Team
... A. Define circulatory system: system of the body made up of the heart, blood vessels, and blood; moves substances (gases, chemicals, nutrients, wastes) around the body B. Define excretory system: system of the body made up of the kidneys, liver, skin, lungs, and rectum; remove wastes (gaseous, liqui ...
... A. Define circulatory system: system of the body made up of the heart, blood vessels, and blood; moves substances (gases, chemicals, nutrients, wastes) around the body B. Define excretory system: system of the body made up of the kidneys, liver, skin, lungs, and rectum; remove wastes (gaseous, liqui ...
cell - s3.amazonaws.com
... • All existing cells are produced by other living cells. • The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
... • All existing cells are produced by other living cells. • The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
SYLLABUS Advanced Cell Biology BIOL 3301 (3
... Final score will be calculated as follows: 1. Exam #1 2. Exam #2 3. Exam #3 4. Final Exam 5. In-class activities ...
... Final score will be calculated as follows: 1. Exam #1 2. Exam #2 3. Exam #3 4. Final Exam 5. In-class activities ...
outline
... Exceptions: Mycoplasma (Bacteria) Thermoplasma (Archaea) a. Functions 1) Bacteria – divide into 2 groups based on a cell wall molecule called peptidoglycan (=murein) Gram positive Gram negative 2) Archaea – no peptidoglycan, some have pseudomurein, chondroitin sulfate, or protein 7. Structures Exter ...
... Exceptions: Mycoplasma (Bacteria) Thermoplasma (Archaea) a. Functions 1) Bacteria – divide into 2 groups based on a cell wall molecule called peptidoglycan (=murein) Gram positive Gram negative 2) Archaea – no peptidoglycan, some have pseudomurein, chondroitin sulfate, or protein 7. Structures Exter ...
Glossary - Nebraska Medicine
... Plasmapheresis - a procedure in which the plasma portion of the blood is removed along with harmful antibodies and replaced with a plasma-like substance. Platelets - blood cells that help prevent bleeding and help the blood to clot when vessels are broken. Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PCP) - a type of lu ...
... Plasmapheresis - a procedure in which the plasma portion of the blood is removed along with harmful antibodies and replaced with a plasma-like substance. Platelets - blood cells that help prevent bleeding and help the blood to clot when vessels are broken. Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PCP) - a type of lu ...
Pharmaceutical Terminology
... skin, nails, and glands. The skin forms a protective covering for the body that, when unbroken, prevents entry of bacteria and other invading organisms. The skin also protects the body from water loss, damaging effects of ultraviolet light, and regulates body temperature. ...
... skin, nails, and glands. The skin forms a protective covering for the body that, when unbroken, prevents entry of bacteria and other invading organisms. The skin also protects the body from water loss, damaging effects of ultraviolet light, and regulates body temperature. ...
The First Four Kingdoms
... o Archaebacteria are found in anaerobic and extreme conditions (high [salt], high temperature, and low pH), similar to what are believed to be the conditions on the early Earth. ...
... o Archaebacteria are found in anaerobic and extreme conditions (high [salt], high temperature, and low pH), similar to what are believed to be the conditions on the early Earth. ...
Animal cells usually have an irregular shape, and plant cells usually
... produce antibodies to destroy pathogens, and antitoxins to neutralise toxins. In vaccination pathogens are introduced into the body in a weakened form. The process causes the body to produce enough white blood cells to protect itself against the pathogens, while not getting ...
... produce antibodies to destroy pathogens, and antitoxins to neutralise toxins. In vaccination pathogens are introduced into the body in a weakened form. The process causes the body to produce enough white blood cells to protect itself against the pathogens, while not getting ...
Prentice Hall Review PPT. Ch. 7
... Many multicellular organisms have structures called organs that have a specific function and work with other organs. Working together, these organs carry out the life processes of the entire organism. ...
... Many multicellular organisms have structures called organs that have a specific function and work with other organs. Working together, these organs carry out the life processes of the entire organism. ...
Cell Transport - cloudfront.net
... 2. What are three types of passive transport? What do these all have in common? Be as specific and thorough as you can. 3. What does the body use iodine for? What kind of transport is necessary to transport this molecule into a cell? 4. What happens to the receptor complex in "receptor mediated endo ...
... 2. What are three types of passive transport? What do these all have in common? Be as specific and thorough as you can. 3. What does the body use iodine for? What kind of transport is necessary to transport this molecule into a cell? 4. What happens to the receptor complex in "receptor mediated endo ...
lecture 8
... apoptosis. Necrosis occurs when a cell is damaged by an external force, such as poison, a bodily injury, an infection or getting cut off from the bloodsupply (which might occur during a heart attack or stroke). When cells die from necrosis, it's a rather messy affair. The death causes inflammation t ...
... apoptosis. Necrosis occurs when a cell is damaged by an external force, such as poison, a bodily injury, an infection or getting cut off from the bloodsupply (which might occur during a heart attack or stroke). When cells die from necrosis, it's a rather messy affair. The death causes inflammation t ...
Cell Transport PowerPoint
... •Bacteria and plants have cell walls that prevent them from over-expanding. In plants the pressure exerted on the cell wall is called tugor pressure. •Animal cells are bathed in blood. Kidneys keep the blood isotonic by remove excess salt and water. ...
... •Bacteria and plants have cell walls that prevent them from over-expanding. In plants the pressure exerted on the cell wall is called tugor pressure. •Animal cells are bathed in blood. Kidneys keep the blood isotonic by remove excess salt and water. ...
lab 2
... – Groups of cells that are structurally and functionally the same – A combination of living and non-living material ...
... – Groups of cells that are structurally and functionally the same – A combination of living and non-living material ...
Cellular Biochemistry (BC4) – 21 Cell Polarity
... - signal propagation in a defined direction - contraction along an axis - directed migration and much more... ...
... - signal propagation in a defined direction - contraction along an axis - directed migration and much more... ...
Human Body Systems Test
... •The _________ system is responsible for bringing food and oxygen to every cell in your body. •The _________ system is responsible for carrying oxygen and carbon dioxide in and out of your body. •The _________ system is responsible for removing waste from your body. •The _________ system is responsi ...
... •The _________ system is responsible for bringing food and oxygen to every cell in your body. •The _________ system is responsible for carrying oxygen and carbon dioxide in and out of your body. •The _________ system is responsible for removing waste from your body. •The _________ system is responsi ...
Taxonomy and Kingdom Notes
... -He classified animals according where they lived: land, air and water. -He classified plants according to the type of stem they had: soft or woody. ...
... -He classified animals according where they lived: land, air and water. -He classified plants according to the type of stem they had: soft or woody. ...
Powerpoint
... Fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy (FCCS) has been used to characterize the dephosphorylation of ERK2 by DUSP1 and DUSP5 in endothelial cells. The effective interaction strength, KDeff was able to be determined through measurement of the observed fluorescence emissions. This experiment foun ...
... Fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy (FCCS) has been used to characterize the dephosphorylation of ERK2 by DUSP1 and DUSP5 in endothelial cells. The effective interaction strength, KDeff was able to be determined through measurement of the observed fluorescence emissions. This experiment foun ...
Kingdom Article Readings
... not have a membrane bound nucleus or membrane bound organelles. Eubacteria are found in almost every environment on Earth. The cell wall of Eubacteria contain the chemical peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan is the rigid, but flexible, macromolecule that surrounds and protects individual bacterial cells. S ...
... not have a membrane bound nucleus or membrane bound organelles. Eubacteria are found in almost every environment on Earth. The cell wall of Eubacteria contain the chemical peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan is the rigid, but flexible, macromolecule that surrounds and protects individual bacterial cells. S ...
Cells: An Introduction - Peoria Public Schools
... chloroplasts: Perform photosynthesis by taking in sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make oxygen and sugar (a form of food). Also contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which gives plants a green color. chromosomes: Long, thread-like bodies composed of DNA and protein, found in the nucleus ...
... chloroplasts: Perform photosynthesis by taking in sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make oxygen and sugar (a form of food). Also contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which gives plants a green color. chromosomes: Long, thread-like bodies composed of DNA and protein, found in the nucleus ...
The Human Body
... cartilage – strong, flexible connective tissue found at the ends of bones that cushions joints. joints – the place where two or more bones connect. moveable joints allow movement fixed joints limit movement ...
... cartilage – strong, flexible connective tissue found at the ends of bones that cushions joints. joints – the place where two or more bones connect. moveable joints allow movement fixed joints limit movement ...
Notes template for Circulatory system
... Slide 1 – What do the Circulatory and Respiratory system do together/ Slide 2 - What do blood vessels do? What kind of tissue make up blood vessels? Why are they mad of this kid of tissue? Why are red blood cells important? Thinking about what we’ve written: review these answers and respond to this ...
... Slide 1 – What do the Circulatory and Respiratory system do together/ Slide 2 - What do blood vessels do? What kind of tissue make up blood vessels? Why are they mad of this kid of tissue? Why are red blood cells important? Thinking about what we’ve written: review these answers and respond to this ...























