No Slide Title
... Movement of epidermal cells - loss of adhesiveness e.g. fibronectin, laminin&collagen types I&IV ...
... Movement of epidermal cells - loss of adhesiveness e.g. fibronectin, laminin&collagen types I&IV ...
THE HUMAN BODY
... • 3. The body cavities also permit organs such as the lungs, the urinary bladder, and the stomach to expand and contract while remaining securely supported. • 4. The human body has FOUR Main Body Cavities: ...
... • 3. The body cavities also permit organs such as the lungs, the urinary bladder, and the stomach to expand and contract while remaining securely supported. • 4. The human body has FOUR Main Body Cavities: ...
Chapter 21 - Human Anatomy
... • Hormonal control of the nephrons allows the body to control its internal concentration of – water and – dissolved molecules. ...
... • Hormonal control of the nephrons allows the body to control its internal concentration of – water and – dissolved molecules. ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... to control body systems. The nervous system helps control the body's responses to changes in the environment. The endocrine system helps control growth and development. Both systems also help maintain homeostasis. The body part where two bones come together is a joint. Muscles, bones, and nerves ...
... to control body systems. The nervous system helps control the body's responses to changes in the environment. The endocrine system helps control growth and development. Both systems also help maintain homeostasis. The body part where two bones come together is a joint. Muscles, bones, and nerves ...
Chapter 16 Circulation Section 2 Blood and Lymph
... important part in forming blood clots • Because of their irregular shapes they are able to latch together and form clots ...
... important part in forming blood clots • Because of their irregular shapes they are able to latch together and form clots ...
Unit 3: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration (Ch 9) Study Guide
... As sunlight increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases until total light distribution is reached. 10. How does temperature affect photosynthesis? 11. Why do cells need to store energy? to ...
... As sunlight increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases until total light distribution is reached. 10. How does temperature affect photosynthesis? 11. Why do cells need to store energy? to ...
Pathology 122 Week 1-3 Concepts
... Prototype Drug: Model representative of a drug family/class. Other drugs of the same class are compared to this one so similarities and differences in the drug group can be established. Pharmacokinetics: The body’s influence on the drug. Absorption: Site of Administration Blood(to distribution)/ ...
... Prototype Drug: Model representative of a drug family/class. Other drugs of the same class are compared to this one so similarities and differences in the drug group can be established. Pharmacokinetics: The body’s influence on the drug. Absorption: Site of Administration Blood(to distribution)/ ...
Blood Chapter
... If mom has another Rh+ child; she already has Rh Ab’s that will attack the second baby’s RBC’s at birth. to prevent this, mom is injected with RhoGAM shortly after the birth of first baby. this destroys fetal cells present before the mom’s baby starts producing Rh antibodies (therefore, timing i ...
... If mom has another Rh+ child; she already has Rh Ab’s that will attack the second baby’s RBC’s at birth. to prevent this, mom is injected with RhoGAM shortly after the birth of first baby. this destroys fetal cells present before the mom’s baby starts producing Rh antibodies (therefore, timing i ...
Plant Cells (The Basics)
... Companion cell provides energy – so-named because end walls are perforated - allows cytoplasmic connections between vertically-stacked cells . – conducts sugars and amino acids - from the leaves, to the rest of the plant ...
... Companion cell provides energy – so-named because end walls are perforated - allows cytoplasmic connections between vertically-stacked cells . – conducts sugars and amino acids - from the leaves, to the rest of the plant ...
Organ
... Organ – study of structures composed of 2 or more tissue types that performs a specific function for the body (extremely complex functions become possible – ex. Small intestines has all 4 tissue types) System – study of groups of organs that cooperate to accomplish a common purpose (each organ h ...
... Organ – study of structures composed of 2 or more tissue types that performs a specific function for the body (extremely complex functions become possible – ex. Small intestines has all 4 tissue types) System – study of groups of organs that cooperate to accomplish a common purpose (each organ h ...
Cell Cycle Regulation
... Cells divide in order for an organism to grow, develop and repair itself. Cells grow and divide in a specific fashion. When cells do not divide the way they are supposed to cancer can develop. In this activity, you will investigate the steps involved in the cell cycle, regulation of the cell cycle, ...
... Cells divide in order for an organism to grow, develop and repair itself. Cells grow and divide in a specific fashion. When cells do not divide the way they are supposed to cancer can develop. In this activity, you will investigate the steps involved in the cell cycle, regulation of the cell cycle, ...
Cell Structure and Function
... As you have already learned, the cell is the basic unit of all living things. Cells need certain conditions to live and they can combine to create complex organisms (like you!). All cells are both different and similar. Plant cells are different from animal cells, but they have many common ingredien ...
... As you have already learned, the cell is the basic unit of all living things. Cells need certain conditions to live and they can combine to create complex organisms (like you!). All cells are both different and similar. Plant cells are different from animal cells, but they have many common ingredien ...
Human Biology 4.3
... • After an egg cell develops another hormone signals the ovary to release the egg. • Egg moves from the ovary into a fallopian tube. • If within ten to twelve hours the egg cell is fertilized by a sperm cell, it will move to the uterus. • After implanting inside the thick lining of the uterus, the f ...
... • After an egg cell develops another hormone signals the ovary to release the egg. • Egg moves from the ovary into a fallopian tube. • If within ten to twelve hours the egg cell is fertilized by a sperm cell, it will move to the uterus. • After implanting inside the thick lining of the uterus, the f ...
Biology 102 Exam I Study Guide How many kingdoms are there
... This thick, gelatinous material, located external to the cell wall, called the capsule or slime layer is technically referred to as the? Bacteria can be further divided into two groups based upon the type of cell wall structure they have. They are called either ______ positive or ______ negative. Wh ...
... This thick, gelatinous material, located external to the cell wall, called the capsule or slime layer is technically referred to as the? Bacteria can be further divided into two groups based upon the type of cell wall structure they have. They are called either ______ positive or ______ negative. Wh ...
Planet Earth and Its Environment A 5000-million year
... A year later (1839) Schwann published a book on plant and animal cells, listing three main conclusions, two of which are still accepted today as the basis for the cell theory: 1. The cell is the unit of structure of all living things 2. The cell exists as a distinct entity and as a building block in ...
... A year later (1839) Schwann published a book on plant and animal cells, listing three main conclusions, two of which are still accepted today as the basis for the cell theory: 1. The cell is the unit of structure of all living things 2. The cell exists as a distinct entity and as a building block in ...
Cell Structures - Manhasset Schools
... • Some vacuoles are used to isolate materials that are harmful to the cell. • Other vacuoles are used to store needed substances such as water. Lysosomes ...
... • Some vacuoles are used to isolate materials that are harmful to the cell. • Other vacuoles are used to store needed substances such as water. Lysosomes ...
Tubular reabsorption
... Na-K-2Cl transport In thick ascending limb of Henle “loop” diuretics as furosemide, inhibits the action of the sodium 2chloride, potassium cotransporter. ...
... Na-K-2Cl transport In thick ascending limb of Henle “loop” diuretics as furosemide, inhibits the action of the sodium 2chloride, potassium cotransporter. ...
Cell Transport Powerpoint
... space. Equilibrium is a state that exists when the concentration of a substance is the same throughout a space. In order for diffusion to occur, there must be a concentration gradient. Why? If there is no concentration gradient, then the substance would be in equilibrium. Ion channel is a doughnut-s ...
... space. Equilibrium is a state that exists when the concentration of a substance is the same throughout a space. In order for diffusion to occur, there must be a concentration gradient. Why? If there is no concentration gradient, then the substance would be in equilibrium. Ion channel is a doughnut-s ...
Evaluating Innate Immune Cell Immunotoxicity of a Novel
... impact the both innate and adaptive immune responses. Extracellular vesicles (EV) are a promising novel therapeutic delivery system that target specific cells to deliver a therapeutic payload. These EV are produced by cultured cells and very little is known about how culture-derived EV interact with ...
... impact the both innate and adaptive immune responses. Extracellular vesicles (EV) are a promising novel therapeutic delivery system that target specific cells to deliver a therapeutic payload. These EV are produced by cultured cells and very little is known about how culture-derived EV interact with ...
You Light Up My Life
... the adjacent primary walls and connect the cytoplasm 2. Animal cells display three types of junctions: a. Tight junctions occur between cells of epithelial tissues in which cytoskeletal strands of one cell fuse with strands of neighboring cells causing an effective seal. b. Adhering junctions are li ...
... the adjacent primary walls and connect the cytoplasm 2. Animal cells display three types of junctions: a. Tight junctions occur between cells of epithelial tissues in which cytoskeletal strands of one cell fuse with strands of neighboring cells causing an effective seal. b. Adhering junctions are li ...
Onion, Elodea Leaf, and Cheek Cell Labs Questions
... 4. Carefully remove the wet-‐mount slide of the onion tissue from the stage of your microscope. 5. Add one drop of the Lugol solution on one side of the slide cover where it meets the slide. ...
... 4. Carefully remove the wet-‐mount slide of the onion tissue from the stage of your microscope. 5. Add one drop of the Lugol solution on one side of the slide cover where it meets the slide. ...
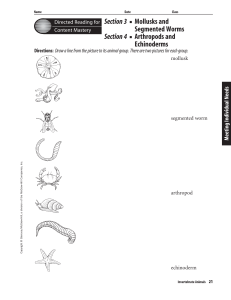
Chapter 6 Resource: Invertebrate Animals
... 5. spiny-skinned invertebrate that lives on the ocean bottom 7. circulatory system in which blood is not in vessels but surrounds organs 10. bell-shaped body plan, like that of a jellyfish 12. joint-footed animal 14. organs that exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide with water 15. tongue-like organ in ...
... 5. spiny-skinned invertebrate that lives on the ocean bottom 7. circulatory system in which blood is not in vessels but surrounds organs 10. bell-shaped body plan, like that of a jellyfish 12. joint-footed animal 14. organs that exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide with water 15. tongue-like organ in ...
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle
... The division of one prokaryotic cell reproduces an entire organism. Cell division also enables multicellular eukaryotes to develop from a single cell. (fertilized egg) Cell division also functions in renewal and repair, replacing cells that die from normal wear and tear or accidents. ...
... The division of one prokaryotic cell reproduces an entire organism. Cell division also enables multicellular eukaryotes to develop from a single cell. (fertilized egg) Cell division also functions in renewal and repair, replacing cells that die from normal wear and tear or accidents. ...
Respiration and Circulation Part 1 - Cal State LA
... The systems function together to exchange gases with the environment and transport them to the tissues ...
... The systems function together to exchange gases with the environment and transport them to the tissues ...