Vacuole File
... In animal cells, vacuoles perform mostly subordinate roles, assisting in larger processes of exocytosis and endocytosis. Animal vacuoles are smaller than their plant counterparts but also usually greater in number.[7] There are also animal cells that do not have any vacuoles.[19] Exocytosis is the e ...
... In animal cells, vacuoles perform mostly subordinate roles, assisting in larger processes of exocytosis and endocytosis. Animal vacuoles are smaller than their plant counterparts but also usually greater in number.[7] There are also animal cells that do not have any vacuoles.[19] Exocytosis is the e ...
Chapter 6 - loyolaunit1biology
... transported by phloem tissue from the leaves (where they are made) to other parts of the plant (that don’t photosynthesize) Transport also occurs between storage sites (where excess sugars are stored) to parts of the plant requiring energy This process is called translocation Sugars exit the p ...
... transported by phloem tissue from the leaves (where they are made) to other parts of the plant (that don’t photosynthesize) Transport also occurs between storage sites (where excess sugars are stored) to parts of the plant requiring energy This process is called translocation Sugars exit the p ...
Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell
... The cell is the Basic Unit of Life • Cell is the smallest unit of living organisms • Unicellular organisms are made of one cell only • The cells of multicellular organisms are specialized to perform different functions ...
... The cell is the Basic Unit of Life • Cell is the smallest unit of living organisms • Unicellular organisms are made of one cell only • The cells of multicellular organisms are specialized to perform different functions ...
Ch2Packet - Cobb Learning
... 13. Two parents produce offspring that share their characteristics through ______________________ reproduction. 14. A single parent produces offspring identical to the parent cthrough ______________________ reproduction. 15. Most single-celled organisms reproduce through ______________________ repro ...
... 13. Two parents produce offspring that share their characteristics through ______________________ reproduction. 14. A single parent produces offspring identical to the parent cthrough ______________________ reproduction. 15. Most single-celled organisms reproduce through ______________________ repro ...
John B. Gurdon and Shinya Yamanaka for the discovery
... could be reprogrammed to become immature stem cells. Surprisingly, by introducing only a few genes, he could reprogram mature cells to become pluripotent stem cells, i.e. immature cells that are able to develop into all types of cells in the body. These groundbreaking discoveries have completely cha ...
... could be reprogrammed to become immature stem cells. Surprisingly, by introducing only a few genes, he could reprogram mature cells to become pluripotent stem cells, i.e. immature cells that are able to develop into all types of cells in the body. These groundbreaking discoveries have completely cha ...
Using Linear Algebra in Biology: Red Blood Cell Production
... Finally we can write the general solution as: ...
... Finally we can write the general solution as: ...
Cellular Structures Notes
... Nickname: The shippers Function: packages, modifies, and transports materials to different location inside/outside of the cell ...
... Nickname: The shippers Function: packages, modifies, and transports materials to different location inside/outside of the cell ...
Tissues and Integument
... 1) W/o blood vessels, epithelial tissues have to acquire nutrients/oxygen via diffusion from blood vessels in CT f. High capacity to regenerate 1) With outer locations, epithelial tissues are subjected to much wear and tear; to replenish damaged/lost cells they rapidly divide 4. Classification a. Ce ...
... 1) W/o blood vessels, epithelial tissues have to acquire nutrients/oxygen via diffusion from blood vessels in CT f. High capacity to regenerate 1) With outer locations, epithelial tissues are subjected to much wear and tear; to replenish damaged/lost cells they rapidly divide 4. Classification a. Ce ...
What You Absolutely Need to Know To Pass the NYS Living
... body, so as far as your body is concerned, proteins are by far the most important of these three organic molecules. b. It is the SHAPE of proteins and how they fit together with other molecules that determines what proteins can do. c. Four specific jobs of proteins: 1) enzymes (see next page for mor ...
... body, so as far as your body is concerned, proteins are by far the most important of these three organic molecules. b. It is the SHAPE of proteins and how they fit together with other molecules that determines what proteins can do. c. Four specific jobs of proteins: 1) enzymes (see next page for mor ...
Section 7.3 Cell Transport
... One of the most important functions of the cell membrane is to keep the cell’s internal conditions relatively constant. It does this by regulating the movement of molecules from one side of the membrane to the other side. ...
... One of the most important functions of the cell membrane is to keep the cell’s internal conditions relatively constant. It does this by regulating the movement of molecules from one side of the membrane to the other side. ...
The Immune System and Disease
... with the generation of 109 to 1010 viruses every day, coupled with a high mutation rate. This leads to many variants of HIV in a single infected patient in the course of one day. This variability is compounded when a single cell is simultaneously infected by two or more different strains of HIV. ...
... with the generation of 109 to 1010 viruses every day, coupled with a high mutation rate. This leads to many variants of HIV in a single infected patient in the course of one day. This variability is compounded when a single cell is simultaneously infected by two or more different strains of HIV. ...
• Replication: reproduction • Function: catalytic functions • RNA
... DNA. Viruses have evolved a way of encapsulating and delivering their genes to human cells in a pathogenic manner. Scientists have tried to take advantage of this capability and manipulate the virus genome to remove disease-causing genes and insert therapeutic genes. • Target cells such as the pati ...
... DNA. Viruses have evolved a way of encapsulating and delivering their genes to human cells in a pathogenic manner. Scientists have tried to take advantage of this capability and manipulate the virus genome to remove disease-causing genes and insert therapeutic genes. • Target cells such as the pati ...
chapt36_lecture
... Dermal Tissue • Forms the epidermis • One cell layer thick in most plants • Forms the outer protective covering of the plant • Covered with a fatty cutin layer constituting the cuticle • Contains special cells, including guard cells, trichomes, and root hairs ...
... Dermal Tissue • Forms the epidermis • One cell layer thick in most plants • Forms the outer protective covering of the plant • Covered with a fatty cutin layer constituting the cuticle • Contains special cells, including guard cells, trichomes, and root hairs ...
Fulminant Infectious Mononucleosis and Recurrent Epstein
... (IgG1,3,4 normal), an IgA level of 2 g/L (normal range, 0.74– 2.28 g/L), and an IgM level of 6.67 g/L (normal range, 0.48– 2.57 g/L). Antibody responses to the vaccines diptheria, tetanus, and Haemophilus influenzae B (HIB) were present but reduced. The clinical symptoms were unresponsive to a glute ...
... (IgG1,3,4 normal), an IgA level of 2 g/L (normal range, 0.74– 2.28 g/L), and an IgM level of 6.67 g/L (normal range, 0.48– 2.57 g/L). Antibody responses to the vaccines diptheria, tetanus, and Haemophilus influenzae B (HIB) were present but reduced. The clinical symptoms were unresponsive to a glute ...
Pre-lab Homework Lab 4: The Cell
... • Given the function of cell/tissue types, hypothesize as to why cells have the shapes they have. OBJECTIVES: After successfully completing this lab, a student will be able to: • Describe the generalized structure of eukaryotic cells. • Describe the function of the components of a generalized eukary ...
... • Given the function of cell/tissue types, hypothesize as to why cells have the shapes they have. OBJECTIVES: After successfully completing this lab, a student will be able to: • Describe the generalized structure of eukaryotic cells. • Describe the function of the components of a generalized eukary ...
The Cell Membrane
... environment will have water leave the cells, making them shrink and shrivel. Placed in a hypotonic environment, water diffuses into the cells, causing them to swell and eventually burst - lyse or ...
... environment will have water leave the cells, making them shrink and shrivel. Placed in a hypotonic environment, water diffuses into the cells, causing them to swell and eventually burst - lyse or ...
chpt 35 plants
... of woody plants • Secondary Plant Body: tissues produced by vascular cambium and cork cambium– vascular cambium: cylinder of meristematic cells that forms secondary vascular tissue, increases vascular flow and support for shoots ...
... of woody plants • Secondary Plant Body: tissues produced by vascular cambium and cork cambium– vascular cambium: cylinder of meristematic cells that forms secondary vascular tissue, increases vascular flow and support for shoots ...
Enviromental pathology 2a. 2006
... • The primary target is the DNA (mostly during mitosis) • Tissue with high rate of cell turnover (like bone marrow and GI tract mucosa) are extremely vulnerable to radiation. • Presence of different types of cells within one organ – (vascular injury in CNS). ...
... • The primary target is the DNA (mostly during mitosis) • Tissue with high rate of cell turnover (like bone marrow and GI tract mucosa) are extremely vulnerable to radiation. • Presence of different types of cells within one organ – (vascular injury in CNS). ...
blood pressure
... • Filter solutes out of blood & reabsorb H2O + desirable solutes • Key functions – filtration • fluids (water & solutes) filtered out of blood ...
... • Filter solutes out of blood & reabsorb H2O + desirable solutes • Key functions – filtration • fluids (water & solutes) filtered out of blood ...
Movement Through the Cell Membrane
... has a higher solute concentration than the cell • Water leaves the cell, animal cells can shrink. ...
... has a higher solute concentration than the cell • Water leaves the cell, animal cells can shrink. ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... to control body systems. The nervous system helps control the body's responses to changes in the environment. The endocrine system helps control growth and development. Both systems also help maintain homeostasis. The body part where two bones come together is a joint. Muscles, bones, and nerves ...
... to control body systems. The nervous system helps control the body's responses to changes in the environment. The endocrine system helps control growth and development. Both systems also help maintain homeostasis. The body part where two bones come together is a joint. Muscles, bones, and nerves ...
interactions in animals
... body is broken into pieces, and some or all of these become separate individuals. The animal must be able to regenerate, or grow back, lost body parts, for fragmentation to occur. Parthenogenesis is a form of asexual reproduction in which an egg is produced and develops into an individual without fe ...
... body is broken into pieces, and some or all of these become separate individuals. The animal must be able to regenerate, or grow back, lost body parts, for fragmentation to occur. Parthenogenesis is a form of asexual reproduction in which an egg is produced and develops into an individual without fe ...
Slides (pdf format)
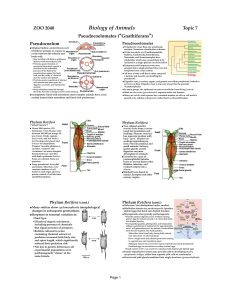
... proboscis (used to attach and pull body close to! gut wall), can cause damage. ■ Body wall comprises thin cuticle over a syncytial epidermis (nutrient absorption probably occurs across cuticle). Epidermis contains unique system of channels (lacunar system) used for circulation. ■ All vestiges of d ...
... proboscis (used to attach and pull body close to! gut wall), can cause damage. ■ Body wall comprises thin cuticle over a syncytial epidermis (nutrient absorption probably occurs across cuticle). Epidermis contains unique system of channels (lacunar system) used for circulation. ■ All vestiges of d ...