Cells AP Bio Test Review ANSWERS
... 21. Small cells, membrane extensions (cilia, villi), folded membranes, flat shape ...
... 21. Small cells, membrane extensions (cilia, villi), folded membranes, flat shape ...
five unit: “the cell and the smallest living being”
... The cell -A cell is the smallest part of a living being. We need a microscope to see it. The size of cells is measured by a micrometer. -There are some cells without a nucleus. They are prokaryotic cells. These are bacteria cells. The rest of the cells are eukaryotic, and they have a nucleus. -Anima ...
... The cell -A cell is the smallest part of a living being. We need a microscope to see it. The size of cells is measured by a micrometer. -There are some cells without a nucleus. They are prokaryotic cells. These are bacteria cells. The rest of the cells are eukaryotic, and they have a nucleus. -Anima ...
Cell parts practice
... ______ Phospholipid bilayer that controls what enters and leaves the cell ______ Found outside of the cell membrane in plants & bacteria; provides support & protection ...
... ______ Phospholipid bilayer that controls what enters and leaves the cell ______ Found outside of the cell membrane in plants & bacteria; provides support & protection ...
Plurioptent stem cell translation: basic and
... from the same accomplishment in humans, translational applications of this science are now underway. This includes the use of animal and human pluripotent stem cells in drug screening, to model disease and in humans cellular therapies. However, the transformation of these practices into robust manuf ...
... from the same accomplishment in humans, translational applications of this science are now underway. This includes the use of animal and human pluripotent stem cells in drug screening, to model disease and in humans cellular therapies. However, the transformation of these practices into robust manuf ...
Looking Inside Cells (a tiny tour)
... 12. Compare plant and animal cells • Plant cells have 2 structures that animal cells do not: cell wall, which gives them a boxy shape chloroplasts, which allow them to capture sunlight energy. ...
... 12. Compare plant and animal cells • Plant cells have 2 structures that animal cells do not: cell wall, which gives them a boxy shape chloroplasts, which allow them to capture sunlight energy. ...
Chapter7.1_History of the Cell
... 1. All living things are made of cells. (Schleiden = plants, Schwann = animals) 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. (Virchow) ...
... 1. All living things are made of cells. (Schleiden = plants, Schwann = animals) 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. (Virchow) ...
Respiratory Levels of Organization
... and respiratory system, called the respiratory membrane. Oxygen diffuses from the inhaled air in the lungs across the aveolar and capillary membranes and into the blood plasma. It then enters the red blood cells where it will be carried on hemoglobin molecules to the other tissues of the body. Gas e ...
... and respiratory system, called the respiratory membrane. Oxygen diffuses from the inhaled air in the lungs across the aveolar and capillary membranes and into the blood plasma. It then enters the red blood cells where it will be carried on hemoglobin molecules to the other tissues of the body. Gas e ...
)151t€\f-
... 8. Organelles carry out specific processes involving chemical reactions. ln the chart below, identify two organelles and, for each, identify a process involving chemical reactions that occurs there. Describe one specific way each process identified is important to the functioning of the organism. [4 ...
... 8. Organelles carry out specific processes involving chemical reactions. ln the chart below, identify two organelles and, for each, identify a process involving chemical reactions that occurs there. Describe one specific way each process identified is important to the functioning of the organism. [4 ...
EOC Review Part 3
... All (save for a few) enzymes end in what suffix? -ase Label the picture (right) with the following enzymatic reaction: Substrate, Product(s), Enzyme-substrate complex, Enzyme See diagram to right. In the first graph, at what temperature does the enzyme work best? 37ºC At what temperature does this e ...
... All (save for a few) enzymes end in what suffix? -ase Label the picture (right) with the following enzymatic reaction: Substrate, Product(s), Enzyme-substrate complex, Enzyme See diagram to right. In the first graph, at what temperature does the enzyme work best? 37ºC At what temperature does this e ...
Chapter 3
... Membranes and Cell Compartments Plasma membrane Surrounds cell, partially fluid Semi(selectively)permeable Barrier that protects cell, gives cell support and some shape Allows passage of gases and nutrients into and out of cell only at surface Metabolic activities occur in or on membranes ...
... Membranes and Cell Compartments Plasma membrane Surrounds cell, partially fluid Semi(selectively)permeable Barrier that protects cell, gives cell support and some shape Allows passage of gases and nutrients into and out of cell only at surface Metabolic activities occur in or on membranes ...
cell review
... 32. How is the nucleus the same as the cell membrane and how is it defferent 33. What makes up the cell membrane? 34. What is the process that allows movement in and out of the cell by following a concentration gradient? 35. Filtration and osmosis is a type of what membrane transport? 36. How is pri ...
... 32. How is the nucleus the same as the cell membrane and how is it defferent 33. What makes up the cell membrane? 34. What is the process that allows movement in and out of the cell by following a concentration gradient? 35. Filtration and osmosis is a type of what membrane transport? 36. How is pri ...
KEY to Cell Part Chart FUNCTIONS
... the cell membrane and the nucleus of the cell; location of many cell organelles, the cytoskeleton, and many chemical reactions ...
... the cell membrane and the nucleus of the cell; location of many cell organelles, the cytoskeleton, and many chemical reactions ...
Cytokinesis in Plant Cells and Animal Cells
... In plant cells, pockets of cell-wall material, called vesicles, line up across the middle of the cell. The vesicles fuse together in two sheets to form new cell walls and cell membranes between the daughter cells. Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. ...
... In plant cells, pockets of cell-wall material, called vesicles, line up across the middle of the cell. The vesicles fuse together in two sheets to form new cell walls and cell membranes between the daughter cells. Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. ...
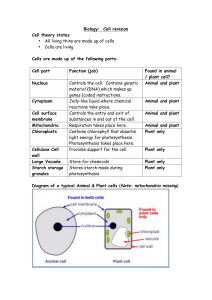
Biology Cell revision
... Carries oxygen around the body Traps and removes dust from the lungs Carry electrical messengers Absorbs sunlight to help carry out photosynthesis Large surface area to absorb water and minerals. ...
... Carries oxygen around the body Traps and removes dust from the lungs Carry electrical messengers Absorbs sunlight to help carry out photosynthesis Large surface area to absorb water and minerals. ...
Nerve Cells (Human)
... a few millimeters long; others are more than a yard long. Axons are sheathed in a fatty substance called myelin which helps with the conduction of electrical impulses. c Dendrites These are networks of short fibers that branch out from the axon or cell body and link the ends of axons from other neur ...
... a few millimeters long; others are more than a yard long. Axons are sheathed in a fatty substance called myelin which helps with the conduction of electrical impulses. c Dendrites These are networks of short fibers that branch out from the axon or cell body and link the ends of axons from other neur ...
Cells – the Basic Unit of Life
... Green – Transportation: any movement of materials within or out of the cell; this includes moving the cell itself Brown – Packing; Packing and storing of any substance Yellow – Energy; the making of molecules or breaking down of molecules for the purpose of energy usage Blue – Homeostasis: any struc ...
... Green – Transportation: any movement of materials within or out of the cell; this includes moving the cell itself Brown – Packing; Packing and storing of any substance Yellow – Energy; the making of molecules or breaking down of molecules for the purpose of energy usage Blue – Homeostasis: any struc ...
Basal phyla - Robert D. Podolsky
... branches along which characters evolved. Fill in the state change next to each label to identify the shared, derived character that evolved along the branches leading to each clade. Base your answers only on the phylogenetic hypothesis for the organisms shown. [Note that characters could change or r ...
... branches along which characters evolved. Fill in the state change next to each label to identify the shared, derived character that evolved along the branches leading to each clade. Base your answers only on the phylogenetic hypothesis for the organisms shown. [Note that characters could change or r ...
File
... About 60 percent of the adult human body is fluid, mainly a water solution of ions and other substances. Although most of this fluid is inside the cells and is called intracellular fluid, about one third is in the spaces outside the cells and is called extracellular fluid. In the extracellular flui ...
... About 60 percent of the adult human body is fluid, mainly a water solution of ions and other substances. Although most of this fluid is inside the cells and is called intracellular fluid, about one third is in the spaces outside the cells and is called extracellular fluid. In the extracellular flui ...
ExamView Pro - Review Sheet #2.tst
... c. All cells have a nucleus and a cell membrane. d. All living things are made up of one or more cells. 5. Which of the following is NOT found in plant cells? a. lysosome c. cell membrane b. ribosome d. Golgi complex 6. You are made up of about 100 trillion cells; however, you began as a. an organ. ...
... c. All cells have a nucleus and a cell membrane. d. All living things are made up of one or more cells. 5. Which of the following is NOT found in plant cells? a. lysosome c. cell membrane b. ribosome d. Golgi complex 6. You are made up of about 100 trillion cells; however, you began as a. an organ. ...
STERNGRR
... • Now that we know what is living, what must organisms do to stay alive? – (SEE PAGE 15) ...
... • Now that we know what is living, what must organisms do to stay alive? – (SEE PAGE 15) ...
Protective layer external to the cell membrane, consists of cellulose
... Protective layer external to the cell membrane, consists of chitin ...
... Protective layer external to the cell membrane, consists of chitin ...