Stage 1: INTERPHASE
... divide into two new cells • CELL CYCLE: The regular sequence of growth and division that cells go through ...
... divide into two new cells • CELL CYCLE: The regular sequence of growth and division that cells go through ...
Chapter 3 Quiz 1 - Wayne Community College
... A&P Chapter 3 Quiz 1 1. The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane as consisting of a a. lipid bilayer with embedded proteins. b. A layer of lipid sandwiched between two layers of protein. c. phospholipid with hydrophobic heads and hydrophilic tails. d. protein bilayer with embedded lipids ...
... A&P Chapter 3 Quiz 1 1. The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane as consisting of a a. lipid bilayer with embedded proteins. b. A layer of lipid sandwiched between two layers of protein. c. phospholipid with hydrophobic heads and hydrophilic tails. d. protein bilayer with embedded lipids ...
Organelles found in both plant and animal cells
... The cytoskeleton, which gives shape to and organizes eukaryotic cells, is composed of fine protein threads called microfilaments and thin protein tubes called microtubules. Cilia and flagella are composed of microtubules arranged in the 9 + 2 arrangement, in which nine pairs of microtubules surround ...
... The cytoskeleton, which gives shape to and organizes eukaryotic cells, is composed of fine protein threads called microfilaments and thin protein tubes called microtubules. Cilia and flagella are composed of microtubules arranged in the 9 + 2 arrangement, in which nine pairs of microtubules surround ...
Unit 3 Unit Sheet
... I. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. Hooke observed dead cork cells. Leeuwenhoek was the first to observe living cells. II. All living things are made of one or mo ...
... I. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. Hooke observed dead cork cells. Leeuwenhoek was the first to observe living cells. II. All living things are made of one or mo ...
Life Processes and Living things
... shaped rather than tall to allow smooth passage through the capillaries • They are so packed with Haemoglobin that they have no room for a Nucleus ...
... shaped rather than tall to allow smooth passage through the capillaries • They are so packed with Haemoglobin that they have no room for a Nucleus ...
File
... organelles where cellular energy is produced, providing the energy needed to power chemical reactions. This process, known as cellular respiration, produces energy is in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Cells that use a lot of energy may have thousands of mitochondria. 6. Vacuoles are small ...
... organelles where cellular energy is produced, providing the energy needed to power chemical reactions. This process, known as cellular respiration, produces energy is in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Cells that use a lot of energy may have thousands of mitochondria. 6. Vacuoles are small ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are some of the structures inside a cell that help it to live and perform its role in an organism? ________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are some of the structures inside a cell that help it to live and perform its role in an organism? ________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
Unicellular and Multicellular
... bigger, what happens if you are trying to swim across it several times? ...
... bigger, what happens if you are trying to swim across it several times? ...
The Incredible Edible Cell
... √ Are all the organelles included? (10 for plants cells, 9 for animal cells) √ Are the organelles correctly labeled? Each organelle must be labeled with its name and function. You may label each organelle or use a key. √ Are the relationships between the parts (if any) shown correctly? Are the ribos ...
... √ Are all the organelles included? (10 for plants cells, 9 for animal cells) √ Are the organelles correctly labeled? Each organelle must be labeled with its name and function. You may label each organelle or use a key. √ Are the relationships between the parts (if any) shown correctly? Are the ribos ...
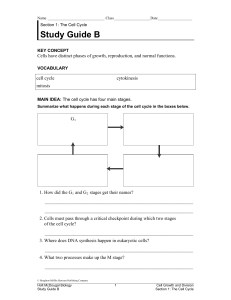
Study Guide B
... 11. Think of an example of a cycle. What does this cycle have in common with the cell cycle? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 12. What process divides a cell’s cytoplasm? How do the two word parts of your ...
... 11. Think of an example of a cycle. What does this cycle have in common with the cell cycle? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 12. What process divides a cell’s cytoplasm? How do the two word parts of your ...
Lecture #18 Date
... organ systems Different tissues have different structures that are suited to their functions Tissues are classified into ...
... organ systems Different tissues have different structures that are suited to their functions Tissues are classified into ...
Components of the Cell System
... Components of the Cell System To know prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structures and their functions How does the cell work as a system responsible for maintaining life? ...
... Components of the Cell System To know prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structures and their functions How does the cell work as a system responsible for maintaining life? ...
Introduction to Animals Worksheet
... 2. [ All / Most ] animals are multicellular. 3. The cells in the skin of your hand are [ bigger than / the same size as ] the cells in your heart. 4. Organisms that have 2 copies of each chromosome are [mobile / diploid ] 5. The absence of a cell wall allows animals [ mobility / diploidy ] 6. A holl ...
... 2. [ All / Most ] animals are multicellular. 3. The cells in the skin of your hand are [ bigger than / the same size as ] the cells in your heart. 4. Organisms that have 2 copies of each chromosome are [mobile / diploid ] 5. The absence of a cell wall allows animals [ mobility / diploidy ] 6. A holl ...
How It Looks
... • Functions: They make protein and DNA. • Location in cell: Near the nucleus, nuclear membrane, and on or around ...
... • Functions: They make protein and DNA. • Location in cell: Near the nucleus, nuclear membrane, and on or around ...
FEB 2008 QUESTION 17 Describe the role of the kidney in drug
... the kidney (via urine) is the most important method in the body for excretion the GIT (faeces) and the lungs (exhaled) are other methods FILTERED ...
... the kidney (via urine) is the most important method in the body for excretion the GIT (faeces) and the lungs (exhaled) are other methods FILTERED ...
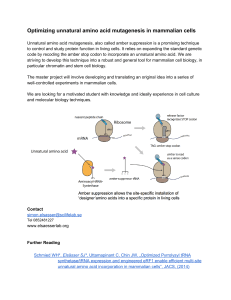
Optimizing unnatural amino acid mutagenesis in mammalian cells
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
Hybridoma Technology
... Steps in monoclonal antibody production by hybridoma technology 1. Immunize a rabbit through repeated injection of a specific antigen for the production of specific antibody, facilitated due to proliferation of the desired B cells. 2. Produce tumors in a mouse or a rabbit. 3. Culture separately the ...
... Steps in monoclonal antibody production by hybridoma technology 1. Immunize a rabbit through repeated injection of a specific antigen for the production of specific antibody, facilitated due to proliferation of the desired B cells. 2. Produce tumors in a mouse or a rabbit. 3. Culture separately the ...
ion channel activity found in cytoplasmic droplets of n…
... system expanding the knowledge in plant electrophysiology as well as offering some evolutionary insights. Experiments on Characeaen algae have significantly contributed to better understanding of the properties of plant signaling via analyzing action potentials as well as the characteristics of ion ...
... system expanding the knowledge in plant electrophysiology as well as offering some evolutionary insights. Experiments on Characeaen algae have significantly contributed to better understanding of the properties of plant signaling via analyzing action potentials as well as the characteristics of ion ...
Organelle - wiltseswall
... Modifies, stores and packages proteins into secretory vesicles to be transported out of the cell. ...
... Modifies, stores and packages proteins into secretory vesicles to be transported out of the cell. ...
Cells Summary - Elgin Academy
... through a series of enzyme-controlled reactions called respiration. The energy released from the breakdown of glucose is used to generate ATP from ADP and phosphate. The chemical energy stored in ATP can be released by breaking it down to ADP and phosphate. This energy can be used for cellular activ ...
... through a series of enzyme-controlled reactions called respiration. The energy released from the breakdown of glucose is used to generate ATP from ADP and phosphate. The chemical energy stored in ATP can be released by breaking it down to ADP and phosphate. This energy can be used for cellular activ ...