2017 RC 4 Student Notes PPT
... The endocrine system triggers hormones to be released to control ovulation in a female’s reproductive system. The hormones are transported through the body’s circulatory system. The integumentary system covers an animal’s body which keeps pathogens from entering the body. If the skin is cut and path ...
... The endocrine system triggers hormones to be released to control ovulation in a female’s reproductive system. The hormones are transported through the body’s circulatory system. The integumentary system covers an animal’s body which keeps pathogens from entering the body. If the skin is cut and path ...
100 Biology
... 29. Chlorophyll is the green substance found in plant cell chloroplasts where photosynthesis takes place. 30. Pollination, the transfer of pollen between stamens and stigma, should not be confused with seed dispersal is when the plant spreads its seeds as far as possible. 31. Red blood cells carry o ...
... 29. Chlorophyll is the green substance found in plant cell chloroplasts where photosynthesis takes place. 30. Pollination, the transfer of pollen between stamens and stigma, should not be confused with seed dispersal is when the plant spreads its seeds as far as possible. 31. Red blood cells carry o ...
Topic Thiteen - Science - Miami
... Cancer Researchers Study Cell Division in Giant Clams Mice Cloned in China Using Skin Cells ...
... Cancer Researchers Study Cell Division in Giant Clams Mice Cloned in China Using Skin Cells ...
Cells
... Nucleus: The nucleus is a structure usually located near the center of the cell. The nucleus is a home to the cell’s chromosomes. What are chromosomes you ask? Chromosomes: They are genetic structures that contain information to make new cells. Basically, the instructions for how to make new c ...
... Nucleus: The nucleus is a structure usually located near the center of the cell. The nucleus is a home to the cell’s chromosomes. What are chromosomes you ask? Chromosomes: They are genetic structures that contain information to make new cells. Basically, the instructions for how to make new c ...
the cell membrane is beginning to pinch off, producing 2 separate cells
... cell by composed that called stored “powerhouse.” considered division that first which said phase becomes produces division many transports of are in is holds can two a saw process where animal used mitosis in that storage found food that of cells ofthat this “All the Animals, Protects The Another A ...
... cell by composed that called stored “powerhouse.” considered division that first which said phase becomes produces division many transports of are in is holds can two a saw process where animal used mitosis in that storage found food that of cells ofthat this “All the Animals, Protects The Another A ...
7. The Importance of Blood
... a straw colored liquid that serves as a transport medium for blood cells and platelets. ...
... a straw colored liquid that serves as a transport medium for blood cells and platelets. ...
2.2 Cell membranes – Questions and answers Q1. Bk Ch2 S2.2 Q1
... It is important for cells to have a large surface area compared to their volume because this allows for maximum and more efficient exchange of nutrients and wastes between the cell and the surrounding tissue fluid. ...
... It is important for cells to have a large surface area compared to their volume because this allows for maximum and more efficient exchange of nutrients and wastes between the cell and the surrounding tissue fluid. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... that control the cell's characteristics. 32. The ______________________ surrounds the nucleus. 33. Where is the nucleolus located? 34. Cells may have _______ to ______ nucleoli. 35. Nucleoli make _____________ that make __________ for the cell. 36. The ______________________ helps cells maintain cel ...
... that control the cell's characteristics. 32. The ______________________ surrounds the nucleus. 33. Where is the nucleolus located? 34. Cells may have _______ to ______ nucleoli. 35. Nucleoli make _____________ that make __________ for the cell. 36. The ______________________ helps cells maintain cel ...
Grade 8 Science Unit 4: “Cells, Tissues, Organs & Systems”
... The Cell Theory states: •The cell is the basic unit of life. •All living things are made of one or more cells. •All cells come from other living cells. ...
... The Cell Theory states: •The cell is the basic unit of life. •All living things are made of one or more cells. •All cells come from other living cells. ...
Slide ()
... Increased numbers of epithelial sodium channels at the cell surface in Liddle syndrome. Mutations causing Liddle syndrome result in markedly increased numbers of channels at the cell surface, owing to a prolonged half-life of channels at the cell surface. Dominant-negative dynamin mutations result i ...
... Increased numbers of epithelial sodium channels at the cell surface in Liddle syndrome. Mutations causing Liddle syndrome result in markedly increased numbers of channels at the cell surface, owing to a prolonged half-life of channels at the cell surface. Dominant-negative dynamin mutations result i ...
The Excretory System
... • Reabsorption – process where solutes and water are removed from the tubular fluid so that they may be transported into the blood. • Secretion – the active transfer of materials from the capillaries around the nephron to the tubular lumen in the loop of Henle so that they may be expelled. These mat ...
... • Reabsorption – process where solutes and water are removed from the tubular fluid so that they may be transported into the blood. • Secretion – the active transfer of materials from the capillaries around the nephron to the tubular lumen in the loop of Henle so that they may be expelled. These mat ...
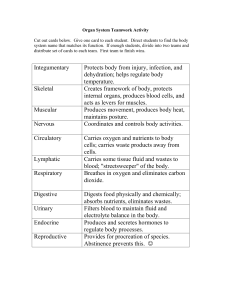
Organ System Teamwork Activity
... Cut out cards below. Give one card to each student. Direct students to find the body system name that matches its function. If enough students, divide into two teams and distribute set of cards to each team. First team to finish wins. ...
... Cut out cards below. Give one card to each student. Direct students to find the body system name that matches its function. If enough students, divide into two teams and distribute set of cards to each team. First team to finish wins. ...
Disease-causing agents such as viruses, bacteria, and protists are
... 17. Which of the following lists the levels of cell organization from least to most complex? a. Organs, cells, organ systems, tissues b. Cells, tissues, organs, organ systems c. Tissues, organs, organ systems, cells d. Cells, organs, organ systems, tissues 18. The way the body maintains homeostasis ...
... 17. Which of the following lists the levels of cell organization from least to most complex? a. Organs, cells, organ systems, tissues b. Cells, tissues, organs, organ systems c. Tissues, organs, organ systems, cells d. Cells, organs, organ systems, tissues 18. The way the body maintains homeostasis ...
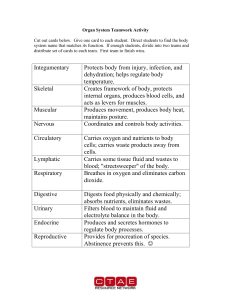
Organ System Teamwork Activity
... Cut out cards below. Give one card to each student. Direct students to find the body system name that matches its function. If enough students, divide into two teams and distribute set of cards to each team. First team to finish wins. ...
... Cut out cards below. Give one card to each student. Direct students to find the body system name that matches its function. If enough students, divide into two teams and distribute set of cards to each team. First team to finish wins. ...
Topic 11 Human Health
... collecting duct is permeable to both water which as the filtrate descends this collecting duct is removed concentrating the filtrate (urine). collecting duct also leaks some urea which to the kidney interstitial fluid. Some of this lost urea is reabsorbed by the ascending limb of the loop of henle b ...
... collecting duct is permeable to both water which as the filtrate descends this collecting duct is removed concentrating the filtrate (urine). collecting duct also leaks some urea which to the kidney interstitial fluid. Some of this lost urea is reabsorbed by the ascending limb of the loop of henle b ...
human-anatomy-and-body-systems-student
... _______________ (one for each lung) -- the bronchi are further subdivided into bronchioles -- eventually, the further subdivisions lead to tiny air sacs called _______________________ -- alveoli are in clusters, like grapes -- capillaries surrounding each alveolus is where the exchange of gases with ...
... _______________ (one for each lung) -- the bronchi are further subdivided into bronchioles -- eventually, the further subdivisions lead to tiny air sacs called _______________________ -- alveoli are in clusters, like grapes -- capillaries surrounding each alveolus is where the exchange of gases with ...
In Vitro Toxicology - ImQuest BioSciences
... types such as PBMCs, monocyte/macrophages, dendritic cells, bone marrow progenitor cells, hepatocytes, iPS neurons, iPS cardiomyocytes and RPTEC kidney cells. Additional evaluations may be performed on ex vivo tissue explants. Mechanism of Cytotoxicity: Evaluate the effect of test compounds on cel ...
... types such as PBMCs, monocyte/macrophages, dendritic cells, bone marrow progenitor cells, hepatocytes, iPS neurons, iPS cardiomyocytes and RPTEC kidney cells. Additional evaluations may be performed on ex vivo tissue explants. Mechanism of Cytotoxicity: Evaluate the effect of test compounds on cel ...
Cells: How their discovery led to the cell theory
... where the first cell came from or how it came to be. has not been disproved yet- no scientist has ever built a living cell from nonliving organic molecules ...
... where the first cell came from or how it came to be. has not been disproved yet- no scientist has ever built a living cell from nonliving organic molecules ...
Immune ppt
... Mouth and Stomach---most pathogens you swallow are destroyed by chemicals in your salivia or stomach acids ...
... Mouth and Stomach---most pathogens you swallow are destroyed by chemicals in your salivia or stomach acids ...
Xylem_Phloem_Teacher_2 - DAVIS-DAIS
... • Xylem transports water and minerals from roots to leaves and contains two types of conducting cells: tracheids and vessel elements. • Phloem transports organic nutrients from leaves to roots and has sieve-tube elements with companion cells, sieve plates. ...
... • Xylem transports water and minerals from roots to leaves and contains two types of conducting cells: tracheids and vessel elements. • Phloem transports organic nutrients from leaves to roots and has sieve-tube elements with companion cells, sieve plates. ...
CHAPTER 7 HOMEOSTASIS AND TRANSPORT Worksheet 1. A
... 33. When water enters the cell, it creates pressure. This pressure is called _____________________________ _______________________________________________. 34. A cell does not expend __________________________ when diffusion takes place. 35. __________________________ is the most common solvent in c ...
... 33. When water enters the cell, it creates pressure. This pressure is called _____________________________ _______________________________________________. 34. A cell does not expend __________________________ when diffusion takes place. 35. __________________________ is the most common solvent in c ...
plant animal 13-14
... The epidermis is covered with a coating called the ________, which serves as a waterproof later and reduces water ______ through evaporation. 2. Vascular system: The system is made up of ____ types of conducting tissues. They are xylem, which conducts______, and dissolved mineral nutrients; and ____ ...
... The epidermis is covered with a coating called the ________, which serves as a waterproof later and reduces water ______ through evaporation. 2. Vascular system: The system is made up of ____ types of conducting tissues. They are xylem, which conducts______, and dissolved mineral nutrients; and ____ ...