The Cell
... internal structures of the cell. Selective permeability Determines what comes in and out of the cell A.K.A- Cell Membrane! Found in: Animal and Plant cells ...
... internal structures of the cell. Selective permeability Determines what comes in and out of the cell A.K.A- Cell Membrane! Found in: Animal and Plant cells ...
7.2 - Cell Structure - Office of Instructional Technology
... support, shape, and protect the cell. Most prokaryotes and many eukaryotes have them. Animals do not have cell walls. Cell walls lie outside the cell membrane. Most cell walls allow materials to pass through them. ...
... support, shape, and protect the cell. Most prokaryotes and many eukaryotes have them. Animals do not have cell walls. Cell walls lie outside the cell membrane. Most cell walls allow materials to pass through them. ...
Cell Transport Powerpoint
... Hypertonic Solutions: contain a high concentration of solute relative to another solution (e.g. the cell's cytoplasm). When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water diffuses out of the cell, causing the cell to shrivel. Hypotonic Solutions: contain a low concentration of solute relative ...
... Hypertonic Solutions: contain a high concentration of solute relative to another solution (e.g. the cell's cytoplasm). When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water diffuses out of the cell, causing the cell to shrivel. Hypotonic Solutions: contain a low concentration of solute relative ...
The Organization of Cells Reading Assignments A. The Cell: The
... • Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain their own DNA nucleoid and ribosomes and can make some of their own proteins. • The endosymbiosis theory of the evolutionary origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts states that they originated when large cells engulfed, but did not digest, smaller ones. Mutual ...
... • Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain their own DNA nucleoid and ribosomes and can make some of their own proteins. • The endosymbiosis theory of the evolutionary origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts states that they originated when large cells engulfed, but did not digest, smaller ones. Mutual ...
62.1E6 INVESTIGATOR Name Thomas M. Jessell and
... ACKNOWLEDGMENTS STATEMENT We have been asked by NICHD to ensure that all investigators include an acknowledgment in publications that benefit from the use of the DSHB's products. We suggest that the following statement be used: “The (select: hybridoma, monoclonal antibody, or protein capture reagen ...
... ACKNOWLEDGMENTS STATEMENT We have been asked by NICHD to ensure that all investigators include an acknowledgment in publications that benefit from the use of the DSHB's products. We suggest that the following statement be used: “The (select: hybridoma, monoclonal antibody, or protein capture reagen ...
Nieuwsbrief 1, 2005
... stimulation resulted in upregulation of the (pre)osteoblastic marker cbfa-1/runx-2 (human 1.5 fold; goat 3 fold) at day 7. Untreated cultures also showed slightly increased (about 0.1 fold) cbfa-1/runx-2 mRNA expression, possibly due to reaching confluency at day 3-4. In addition osteogenically-stim ...
... stimulation resulted in upregulation of the (pre)osteoblastic marker cbfa-1/runx-2 (human 1.5 fold; goat 3 fold) at day 7. Untreated cultures also showed slightly increased (about 0.1 fold) cbfa-1/runx-2 mRNA expression, possibly due to reaching confluency at day 3-4. In addition osteogenically-stim ...
Name: Cell City Introduction Floating around in the cytoplasm are
... 1. The nucleus is a large, round/oval structure usually located near the center of the cell. It is the control center for all the activities of the cell. i) What company or place does the nucleus resemble in a Cell City? ii)Why do you think so? i)____________________________________________________ ...
... 1. The nucleus is a large, round/oval structure usually located near the center of the cell. It is the control center for all the activities of the cell. i) What company or place does the nucleus resemble in a Cell City? ii)Why do you think so? i)____________________________________________________ ...
PHARMACOKINETICS
... in G.I. fluid, penetrates the epithelial cells --- any disease or food may effect this process) Transport of drugs across cell membrane biological membrane: - lipid bilayers with island of protein molecules Lipid soluble substances diffuse readily into cells since, they cross the cell membrane More ...
... in G.I. fluid, penetrates the epithelial cells --- any disease or food may effect this process) Transport of drugs across cell membrane biological membrane: - lipid bilayers with island of protein molecules Lipid soluble substances diffuse readily into cells since, they cross the cell membrane More ...
Cells: Organelles - Biology Courses Server
... • Include all cells alive today except bacteria and archaea • Are larger than prokaryotic cells • Can be single cells (yeast) or multicellular • Have a much more complex architecture – Possess nucleus and a variety of organelles ...
... • Include all cells alive today except bacteria and archaea • Are larger than prokaryotic cells • Can be single cells (yeast) or multicellular • Have a much more complex architecture – Possess nucleus and a variety of organelles ...
SIOP Lesson Plan
... This is a culminating activity in reviewing the parts of a plant and animal cell. This activity is designed to reinforce the concepts of cell structures and the differences between plant and animal cells. Each food item will represent specific parts of the two cells. When the activity is completed t ...
... This is a culminating activity in reviewing the parts of a plant and animal cell. This activity is designed to reinforce the concepts of cell structures and the differences between plant and animal cells. Each food item will represent specific parts of the two cells. When the activity is completed t ...
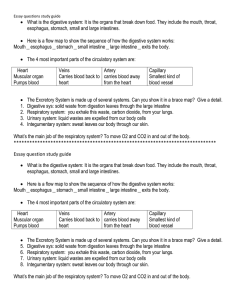
Essay questions study guide What is the digestive system: It is the
... Essay question study guide What is the digestive system: It is the organs that break down food. They include the mouth, throat, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines. Here is a flow map to show the sequence of how the digestive system works: Mouth ͢ esophagus ͢ stomach ͢ small intestine ...
... Essay question study guide What is the digestive system: It is the organs that break down food. They include the mouth, throat, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines. Here is a flow map to show the sequence of how the digestive system works: Mouth ͢ esophagus ͢ stomach ͢ small intestine ...
Harvard Summer Program Immunology Project Resource
... This resource has two parts. The first part consists of two immunology “Jeopardy” games. One is for biology students who are taking an introductory high school course and the second is a similar game for advanced or AP students. The second part is a list of web sites that will provide a teacher with ...
... This resource has two parts. The first part consists of two immunology “Jeopardy” games. One is for biology students who are taking an introductory high school course and the second is a similar game for advanced or AP students. The second part is a list of web sites that will provide a teacher with ...
Life Science -Unit 2Test C. Reid Select the best answer choice for
... The chart lists the functions of four different cell structures. Which name is the best match for structure number 4? (LS_4) A. nucleus B. ribosome C. cell wall D. vacuole 4. In plant cells, what is the function of chloroplasts? (LS_4) A. enable plant cells to produce their own food B. act as the ce ...
... The chart lists the functions of four different cell structures. Which name is the best match for structure number 4? (LS_4) A. nucleus B. ribosome C. cell wall D. vacuole 4. In plant cells, what is the function of chloroplasts? (LS_4) A. enable plant cells to produce their own food B. act as the ce ...
File
... Shows the evolutionary relationships between organisms, with the oldest organism at one end and each animal being more evolved than the last ...
... Shows the evolutionary relationships between organisms, with the oldest organism at one end and each animal being more evolved than the last ...
Chapter 1
... Physiology studies the functions of these parts or asks the question, “how do they work? ...
... Physiology studies the functions of these parts or asks the question, “how do they work? ...
The Cell - Harris7Science
... Ribosomes – manufacture of proteins Cytoplasm – substance that holds all other parts in suspension Mitochondria – Release energy for food Lyosomes – gobble up waste materials (very rare in plant cells) ...
... Ribosomes – manufacture of proteins Cytoplasm – substance that holds all other parts in suspension Mitochondria – Release energy for food Lyosomes – gobble up waste materials (very rare in plant cells) ...
Learning Guide: Origins of Life
... The permeability of the lipid bilayer. o Create the two column table with the headings (material and method). Consider the following materials that must cross the membrane. For each tell how it is accomplished: carbon dioxide, glucose, H+, oxygen, water o Describe the structure and function of tra ...
... The permeability of the lipid bilayer. o Create the two column table with the headings (material and method). Consider the following materials that must cross the membrane. For each tell how it is accomplished: carbon dioxide, glucose, H+, oxygen, water o Describe the structure and function of tra ...
plant and animal cells
... The Golgi Apparatus is a stack of closely packed folded membranes or sacs. The sacs have swollen ends which ‘bud off’ vesicles or (j) carrying substances formed in the Golgi apparatus. The (k) is a double membraned organelle that produces energy for the cell during cellular respiration. The (l) cont ...
... The Golgi Apparatus is a stack of closely packed folded membranes or sacs. The sacs have swollen ends which ‘bud off’ vesicles or (j) carrying substances formed in the Golgi apparatus. The (k) is a double membraned organelle that produces energy for the cell during cellular respiration. The (l) cont ...
5. Mitochondria - *Powerhouse of the cells.
... 3. Cytoplasm – “cell’s liquid” - Made of a gelatinous fluid (Cytosol) between the nucleus and cell membrane Cyclosis – streaming movement of the cytoplasm. *Suspends organelles in place and carries material in solution around cell ...
... 3. Cytoplasm – “cell’s liquid” - Made of a gelatinous fluid (Cytosol) between the nucleus and cell membrane Cyclosis – streaming movement of the cytoplasm. *Suspends organelles in place and carries material in solution around cell ...
Biology Practice Test 1
... A lab technician needs to determine whether cells in a test tube are prokaryotic or eukaryotic. The technician has several dyes she could use to stain the cells. Four of the dyes are described in the table ...
... A lab technician needs to determine whether cells in a test tube are prokaryotic or eukaryotic. The technician has several dyes she could use to stain the cells. Four of the dyes are described in the table ...
Mrs. Kaplan`s Science Page!
... Name the three organelles that could be seen through the microscope in a cheek cell or onion cell. Cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus ...
... Name the three organelles that could be seen through the microscope in a cheek cell or onion cell. Cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus ...
Cells Structure and Function
... 2. The cell is the most basic unit of life. 3. All cells come from other cells. ...
... 2. The cell is the most basic unit of life. 3. All cells come from other cells. ...