Cell Project Choices
... In addition to your 3-‐D model, you should also include a written description as to what each aspect of the city represents in terms of cell organelle/function. Be as d escriptive as possible, and ...
... In addition to your 3-‐D model, you should also include a written description as to what each aspect of the city represents in terms of cell organelle/function. Be as d escriptive as possible, and ...
Figure 5.1 Rapid Diffusion of Membrane Proteins The fluid mosaic
... The fluid mosaic model of cell membranes, described by Singer and Nicolson (1972), was critical to understanding biological membranes as proteins floating in a phospholipid matrix. Integral to this model was earlier work by Frye and Edidin (1970). These researchers examined the movement of proteins ...
... The fluid mosaic model of cell membranes, described by Singer and Nicolson (1972), was critical to understanding biological membranes as proteins floating in a phospholipid matrix. Integral to this model was earlier work by Frye and Edidin (1970). These researchers examined the movement of proteins ...
Anatomy of the Pea Plant
... anatomy by becoming familiar with the anatomy of just one plant, the pea (Pisum sativum). Compared to the anatomy of most animals, the anatomy of vascular plants is relatively simple; there are only four major organs (leaves, stems, roots and flowers) and four major types of tissues (epidermis, pare ...
... anatomy by becoming familiar with the anatomy of just one plant, the pea (Pisum sativum). Compared to the anatomy of most animals, the anatomy of vascular plants is relatively simple; there are only four major organs (leaves, stems, roots and flowers) and four major types of tissues (epidermis, pare ...
chapter 7 a tour of the cell
... Mitochondria and chloroplasts are not part of the endomembrane system. In contrast to organelles of the endomembrane system, each mitochondrion or chloroplast has its own double membrane separating its innermost space from the cytosol of the cell. Their membrane proteins are not made by the ER, ...
... Mitochondria and chloroplasts are not part of the endomembrane system. In contrast to organelles of the endomembrane system, each mitochondrion or chloroplast has its own double membrane separating its innermost space from the cytosol of the cell. Their membrane proteins are not made by the ER, ...
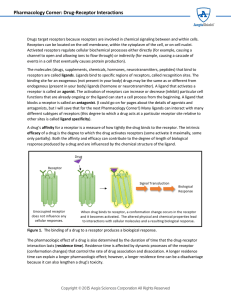
Pharmacology Corner: Drug-Receptor Interactions
... The molecules (drugs, supplements, chemicals, hormones, neurotransmitters, peptides) that bind to receptors are called ligands. Ligands bind to specific regions of receptors, called recognition sites. The binding site for an exogenous (not present in your body) drugs may be the same as or different ...
... The molecules (drugs, supplements, chemicals, hormones, neurotransmitters, peptides) that bind to receptors are called ligands. Ligands bind to specific regions of receptors, called recognition sites. The binding site for an exogenous (not present in your body) drugs may be the same as or different ...
TESTBANK Chapter Title: The History and Interviewing Process
... 2. Hypovolemic shock that results from an internal shifting of fluid from the intravascular space to the extravascular space is known as: 1. absolute hypovolemia. 2. distributive hypovolemia. 3. relative hypovolemia. 4. compensatory hypovolemia. ...
... 2. Hypovolemic shock that results from an internal shifting of fluid from the intravascular space to the extravascular space is known as: 1. absolute hypovolemia. 2. distributive hypovolemia. 3. relative hypovolemia. 4. compensatory hypovolemia. ...
Chapter 5 Test
... • The process by which water passes into or out of a cell is called • a. solubility. c. selective transport. • b. osmosis. d. endocytosis. ...
... • The process by which water passes into or out of a cell is called • a. solubility. c. selective transport. • b. osmosis. d. endocytosis. ...
cell model rubric
... 1. Use materials to build a plant or animal cell model. Your model should be three dimensional , not flat. Follow the materials guidelines below. 2. Your model must show cellular organelles in their approximate sizes and numbers. Use the pictures of the cell provided to know the sizes and numbers of ...
... 1. Use materials to build a plant or animal cell model. Your model should be three dimensional , not flat. Follow the materials guidelines below. 2. Your model must show cellular organelles in their approximate sizes and numbers. Use the pictures of the cell provided to know the sizes and numbers of ...
YEAR 10 IGCSE BIOLOGY REVISION GUIDE DBGS DIGESTION
... concentrated urine produced high water levels in the blood o less water is reabsorbed from filtrate in the kidney nephron dilute urine produced Excretion: is the removal of waste products of metabolic reactions made inside the body cells The kidney Purpose 1. removal of nitrogenous waste (urea ...
... concentrated urine produced high water levels in the blood o less water is reabsorbed from filtrate in the kidney nephron dilute urine produced Excretion: is the removal of waste products of metabolic reactions made inside the body cells The kidney Purpose 1. removal of nitrogenous waste (urea ...
7. Nervous Tissue
... 2. Nissl bodies are composed of (A) synaptic vesicles and acetylcholine (B) Free ribosomes and rough endoplasmic reticulum (C) lipoprotein and melanin (D) neurofilaments and microtubules (E) smooth endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria Answers and Explanations 1-E. Somas possess microtubules, neuro ...
... 2. Nissl bodies are composed of (A) synaptic vesicles and acetylcholine (B) Free ribosomes and rough endoplasmic reticulum (C) lipoprotein and melanin (D) neurofilaments and microtubules (E) smooth endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria Answers and Explanations 1-E. Somas possess microtubules, neuro ...
in toto dynamic imaging and modeling of chordate morphogenesis
... •genetic studies have provided insights into mechanisms driving notochord morphogenesis •models based on our genetic studies predict certain types of cellular behavior. For example, cells should be quiescent at lateral edges after intercalation. ...
... •genetic studies have provided insights into mechanisms driving notochord morphogenesis •models based on our genetic studies predict certain types of cellular behavior. For example, cells should be quiescent at lateral edges after intercalation. ...
Biological Membranes Transport
... opposes uptake; the cell is now turgid (firm) • If a plant cell and its surroundings are isotonic, there is no net movement of water into the cell; the cell becomes flaccid (limp), and the plant may wilt • In a hypertonic environment, plant cells lose water; eventually, the membrane pulls away from ...
... opposes uptake; the cell is now turgid (firm) • If a plant cell and its surroundings are isotonic, there is no net movement of water into the cell; the cell becomes flaccid (limp), and the plant may wilt • In a hypertonic environment, plant cells lose water; eventually, the membrane pulls away from ...
IB Chemistry II Lab: Voltaic Cells Purpose: To construct two voltaic
... Metals: Obtain strips of your two metals for each voltaic cell. Make sure they are clean by wiping with steel wool if needed. These will need to be cleaned and returned when finished for reuse! Half-cell containers: We will be carrying out these in petri dishes. Find the appropriate nitrate or sulfa ...
... Metals: Obtain strips of your two metals for each voltaic cell. Make sure they are clean by wiping with steel wool if needed. These will need to be cleaned and returned when finished for reuse! Half-cell containers: We will be carrying out these in petri dishes. Find the appropriate nitrate or sulfa ...
PARTS IS PARTS What`s the function?
... Match the organ with its function: Makes insulin and glucagon _______________ pancreas Place where bile & trypsin are used ________________ Duodenum (small intestine) Controls blood pressure, heart rate, and metabolism ________________ Thyroid gland Located in mesentery where stomach and duodenum m ...
... Match the organ with its function: Makes insulin and glucagon _______________ pancreas Place where bile & trypsin are used ________________ Duodenum (small intestine) Controls blood pressure, heart rate, and metabolism ________________ Thyroid gland Located in mesentery where stomach and duodenum m ...
I. Angiosperm Root, Stems and Leaves (Plant Organs)
... 2) Cambium-tissue responsible for secondary growth- the widening of roots and stems 3) Epidermis- outermost layer of cells that develop into a protective layer that produces cutin- waxy material that prevents water loss 4) Vascular tissue- tissue that transports food and water A) Xylem- dead hollow ...
... 2) Cambium-tissue responsible for secondary growth- the widening of roots and stems 3) Epidermis- outermost layer of cells that develop into a protective layer that produces cutin- waxy material that prevents water loss 4) Vascular tissue- tissue that transports food and water A) Xylem- dead hollow ...
BIOLOGY STAAR REVIEW CELL THEORY (7.12F) List the 3 pieces
... This body system circulates blood through the body, supplies cells with oxygen and nutrients and removes waste products. This body system supplies blood with oxygen in the lungs and removes carbon dioxide. This body system holds organs in place, provides a structural support for the body and its mus ...
... This body system circulates blood through the body, supplies cells with oxygen and nutrients and removes waste products. This body system supplies blood with oxygen in the lungs and removes carbon dioxide. This body system holds organs in place, provides a structural support for the body and its mus ...
The Circulatory System
... 1. remove waste products from the blood 2. maintain blood pH 3. regulates total blood volume by controlling water content in blood • Ureters • Urinary Bladder • Urethra • Skin – releases excess salts and water through pores • Lungs – remove excess carbon dioxide from the blood ...
... 1. remove waste products from the blood 2. maintain blood pH 3. regulates total blood volume by controlling water content in blood • Ureters • Urinary Bladder • Urethra • Skin – releases excess salts and water through pores • Lungs – remove excess carbon dioxide from the blood ...
Transfer of Materials Across Membranes
... 1. Water, iodine, and glucose were small enough to pass through the dialysis membrane, but protein, starch, and lipid were too large to pass through. 2. Yes, iodine and water were going into the bag at the same time glucose was leaving. 3. It is semipermeable or selectively permeable and regulates w ...
... 1. Water, iodine, and glucose were small enough to pass through the dialysis membrane, but protein, starch, and lipid were too large to pass through. 2. Yes, iodine and water were going into the bag at the same time glucose was leaving. 3. It is semipermeable or selectively permeable and regulates w ...
Ch. 8 Cells & Their Environment
... 3. What is diffusion? Why is diffusion an example of passive transport? - The movement of substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, down the concentration gradient. ...
... 3. What is diffusion? Why is diffusion an example of passive transport? - The movement of substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, down the concentration gradient. ...
10.1 Cell growth and division Lesson Objectives Explain the
... Identify the possible benefits and issues relating to stem cell research. Lesson Summary From One Cell to Many Multicellular organisms produced via sexual reproduction begin life as a single cell. Early cell divisions lead to the formation of an embryo. Then, individual cells become specialized in b ...
... Identify the possible benefits and issues relating to stem cell research. Lesson Summary From One Cell to Many Multicellular organisms produced via sexual reproduction begin life as a single cell. Early cell divisions lead to the formation of an embryo. Then, individual cells become specialized in b ...
“Mammals” study guide
... a. Sweat glands – sudoriferous – used to draw heat away from the body; mixture of salt, urea, and water in which microorganisms convert odorous products. Tubular, highly coiled glands over much of the body. 1. eccrine – secret a watery fluid, if evaporated on the skin’s surface, draws heat away from ...
... a. Sweat glands – sudoriferous – used to draw heat away from the body; mixture of salt, urea, and water in which microorganisms convert odorous products. Tubular, highly coiled glands over much of the body. 1. eccrine – secret a watery fluid, if evaporated on the skin’s surface, draws heat away from ...
function
... explains things but does not describe them; serves as the basis of scientific principles. • Theory: A proposed explanation for observations and experimental results that is supported by a wide range of evidence – may eventually be accepted by the scientific ...
... explains things but does not describe them; serves as the basis of scientific principles. • Theory: A proposed explanation for observations and experimental results that is supported by a wide range of evidence – may eventually be accepted by the scientific ...