Properties of Viruses
... *Latin for “poison” or “slimy liquid” Science Nerd Definition: A small subcellular form that is… ...
... *Latin for “poison” or “slimy liquid” Science Nerd Definition: A small subcellular form that is… ...
Cell Parts (cont.)
... Cell (Plasma) Membrane--”gatekeeper” Encloses the cell (double layer of fat and proteins) ALL cells have one Selectively permeable ...
... Cell (Plasma) Membrane--”gatekeeper” Encloses the cell (double layer of fat and proteins) ALL cells have one Selectively permeable ...
What are cells?
... membranes. Organisms with prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes. Most prokaryotes are unicellular organisms, such as bacteria. ...
... membranes. Organisms with prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes. Most prokaryotes are unicellular organisms, such as bacteria. ...
CK12 Nucleus
... Inside of the nucleus, you will find the chromosomes. Chromosomes are individual strands of DNA wrapped around proteins. They contain genes, or small units of genetic material, that control many of the traits and characteristics you are born with. Human cells have 46 chromosomes in each cell except ...
... Inside of the nucleus, you will find the chromosomes. Chromosomes are individual strands of DNA wrapped around proteins. They contain genes, or small units of genetic material, that control many of the traits and characteristics you are born with. Human cells have 46 chromosomes in each cell except ...
The Cell in its Environment
... unneeded materials inside the cell by sending them out in 3 different ways… ...
... unneeded materials inside the cell by sending them out in 3 different ways… ...
Unit: Cell Biology | PDF 98.6 KB - Edexcel
... Familiarity with the internal structure of the cell and the variety of cell types will be enhanced through the use of microscopy and electron micrographs. The importance of the cell membrane in controlling the internal environment of the cell and in communication will be emphasised. The process of i ...
... Familiarity with the internal structure of the cell and the variety of cell types will be enhanced through the use of microscopy and electron micrographs. The importance of the cell membrane in controlling the internal environment of the cell and in communication will be emphasised. The process of i ...
Life Systems: Animals vs
... them use post-it flags or labels to practice sorting the different parts of cells in each category. -After practicing, have students complete the Cell Quiz. ASOL covered in this activity: 8S-LS 1 The student will investigate and understand that all living things are composed of cells. Key concepts i ...
... them use post-it flags or labels to practice sorting the different parts of cells in each category. -After practicing, have students complete the Cell Quiz. ASOL covered in this activity: 8S-LS 1 The student will investigate and understand that all living things are composed of cells. Key concepts i ...
WHO ARE YOU?
... Eubacteria. • Eubacteria are both autotrophic and heterotrophic. • Includes the disease-causing bacteria such as tooth decay or food poisoning. • The Combined Kingdoms, Archaebacteria and Eubacteria include the greatest number of living things on Earth. • ALL OF THE PROKARYOTES ARE IN THESE TWO KING ...
... Eubacteria. • Eubacteria are both autotrophic and heterotrophic. • Includes the disease-causing bacteria such as tooth decay or food poisoning. • The Combined Kingdoms, Archaebacteria and Eubacteria include the greatest number of living things on Earth. • ALL OF THE PROKARYOTES ARE IN THESE TWO KING ...
Cell - structural and functional unit of life -
... End result: two identical DNA molecules formed from original During mitotic cell division one complete copy given to new cell; one retained in original cell Process is called semiconservative replication Each DNA composed of one old and one new strand ...
... End result: two identical DNA molecules formed from original During mitotic cell division one complete copy given to new cell; one retained in original cell Process is called semiconservative replication Each DNA composed of one old and one new strand ...
Organismal Development 1 PPT
... bacteria. Eukaryotic viruses work in a similar fashion and also carry DNA. Once inserted into the genome, this DNA will now be read as part of the original genome. The new bacterial genome will now have new and novel functions. ...
... bacteria. Eukaryotic viruses work in a similar fashion and also carry DNA. Once inserted into the genome, this DNA will now be read as part of the original genome. The new bacterial genome will now have new and novel functions. ...
Week6-Video
... action, the student will then need to create, test and complete an original experiment involving some form of passive transport. ...
... action, the student will then need to create, test and complete an original experiment involving some form of passive transport. ...
http://personal
... (Click next page at the bottom to continue. From now on, each time you complete a page ...
... (Click next page at the bottom to continue. From now on, each time you complete a page ...
Evidence 1: Cell Comparison Regular Option 2: Reading Prokaryotes
... bacteria are structures called pili (pilus-singular) that help bacteria adhere to surfaces. Color and label all the pili LIGHT GREEN. Some bacteria are motile (can move). Many of these bacteria have long, whip like structures called flagella (flagellum-singular). Color and label the flagella DARK GR ...
... bacteria are structures called pili (pilus-singular) that help bacteria adhere to surfaces. Color and label all the pili LIGHT GREEN. Some bacteria are motile (can move). Many of these bacteria have long, whip like structures called flagella (flagellum-singular). Color and label the flagella DARK GR ...
cell analogy
... allows materials to be carried throughout the city. The ER is a transport system that carries materials throughout the cell. The machine shops are like the cell's ribosomes. The machine shops are built along the roads, here they create materials to build the city, instruction is received at the tech ...
... allows materials to be carried throughout the city. The ER is a transport system that carries materials throughout the cell. The machine shops are like the cell's ribosomes. The machine shops are built along the roads, here they create materials to build the city, instruction is received at the tech ...
Biol2174 Ionic composition of cells
... Structure determination • Roderick MacKinnon and colleagues published the first structure of an ion channel in 1998. • The MacKinnon laboratory chose to work with bacterial potassium channels which could be churned out in large quantities by E. coli and also turned out to be extremely stable. • Eve ...
... Structure determination • Roderick MacKinnon and colleagues published the first structure of an ion channel in 1998. • The MacKinnon laboratory chose to work with bacterial potassium channels which could be churned out in large quantities by E. coli and also turned out to be extremely stable. • Eve ...
Which organelle breaks down organelles that are no longer useful?
... Which of the following statements about the nucleus is NOT true? A. The nucleus usually contains a nucleolus region which is where ribosome assembly begins B. The nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear envelope that lets materials in and out. C. The nucleus stores the coded instructions for making the ...
... Which of the following statements about the nucleus is NOT true? A. The nucleus usually contains a nucleolus region which is where ribosome assembly begins B. The nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear envelope that lets materials in and out. C. The nucleus stores the coded instructions for making the ...
Click on “Construct a cell”
... a. All ____________ things are made up of _________. Each of us has about 50 million cells - an enormous number which is difficult to imagine. Each cell is a sort of bag made from a sort of skin called a __________________. The inside of a cell is ____________ and ____________like. Cells are very __ ...
... a. All ____________ things are made up of _________. Each of us has about 50 million cells - an enormous number which is difficult to imagine. Each cell is a sort of bag made from a sort of skin called a __________________. The inside of a cell is ____________ and ____________like. Cells are very __ ...
File
... The direction that water moves during osmosis depends on the concentration of solutes on either side of the membrane There is a net movement of H2O from high to low concentration ...
... The direction that water moves during osmosis depends on the concentration of solutes on either side of the membrane There is a net movement of H2O from high to low concentration ...
The cell is the basic unit of living things.
... The work of the French scientist Louis Pasteur shows how an understanding of cell theory can have practical uses. Pasteur lived in the 1800s, when there was no mechanical refrigeration in homes. People were used to having foods spoil, like milk going sour. During this time, many people died from dis ...
... The work of the French scientist Louis Pasteur shows how an understanding of cell theory can have practical uses. Pasteur lived in the 1800s, when there was no mechanical refrigeration in homes. People were used to having foods spoil, like milk going sour. During this time, many people died from dis ...
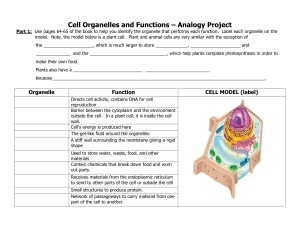
Cell Organelles and Functions – Analogy Project
... Part 1: Use pages 64-65 of the book to help you identify the organelle that performs each function. Label each organelle on the model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store ________ ...
... Part 1: Use pages 64-65 of the book to help you identify the organelle that performs each function. Label each organelle on the model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store ________ ...
Regent Review: Cell Biology - Holding
... Made of 2 or more cells. Are more complex than unicellular organisms. Have tissues, organs and organ systems that carry out all life processes. Compare prokaryotes versus eukaryotes: Prokaryotic cells are bacteria cells (archeabacteria and eubacteria) that are unicellular and contain only cytoplasm, ...
... Made of 2 or more cells. Are more complex than unicellular organisms. Have tissues, organs and organ systems that carry out all life processes. Compare prokaryotes versus eukaryotes: Prokaryotic cells are bacteria cells (archeabacteria and eubacteria) that are unicellular and contain only cytoplasm, ...