Tour of Cell Organelles - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... cytoplasm jelly-like material holding organelles in place vacuole & vesicles transport inside cells storage ...
... cytoplasm jelly-like material holding organelles in place vacuole & vesicles transport inside cells storage ...
Extended vs. Condensed: Determination of Mitochondrial
... Mitochondrial Morphology •Mitochondrial compartments contained inside the cells of a wild-type yeast generally exhibit extended mitochondrial structures (figure A) •Condensed structures are also present (figure C) •Also mixed structures •Mitochondria shown below were observed by using fluorescent m ...
... Mitochondrial Morphology •Mitochondrial compartments contained inside the cells of a wild-type yeast generally exhibit extended mitochondrial structures (figure A) •Condensed structures are also present (figure C) •Also mixed structures •Mitochondria shown below were observed by using fluorescent m ...
The Cell Organelle Worksheet
... their colors. The central vacuole also contains plant wastes that taste __bitter/bad__ to certain insects and animals, thus discouraging them from consuming the plant. The plant vacuole also plays an important structural role, containing water to the point that it exerts a turgor_ pressure against t ...
... their colors. The central vacuole also contains plant wastes that taste __bitter/bad__ to certain insects and animals, thus discouraging them from consuming the plant. The plant vacuole also plays an important structural role, containing water to the point that it exerts a turgor_ pressure against t ...
4-2 Parts of the Eukaryotic Cell
... Both types of proteins form channels for nutrients to travel and also give cell its selectively permeable status. Both the lipids and the proteins help in structure and support of the cell. ...
... Both types of proteins form channels for nutrients to travel and also give cell its selectively permeable status. Both the lipids and the proteins help in structure and support of the cell. ...
Name: Date: Title: Nucleosomes and Chromatin Structure
... A diploid human cell contains about 6.4 x 109 nucleotide pairs of DNA. This corresponds to about two metres of double helix. This DNA has to fit inside the cell nucleus which, in an average human cell, is about 5μm in diameter. This is roughly equivalent to packing sixty miles of fine thread inside ...
... A diploid human cell contains about 6.4 x 109 nucleotide pairs of DNA. This corresponds to about two metres of double helix. This DNA has to fit inside the cell nucleus which, in an average human cell, is about 5μm in diameter. This is roughly equivalent to packing sixty miles of fine thread inside ...
Cell Transport - pdecandia.com
... - phagocytosis: cells engulf solid particles too large to pass thru membrane - pinocytosis: cells engulf liquid substances ...
... - phagocytosis: cells engulf solid particles too large to pass thru membrane - pinocytosis: cells engulf liquid substances ...
File - fiserscience.com
... • Most cancers are somatic, with only 1% due to germ-line mutations • Cancers rarely arise from single gene mutations but from the accumulation of mutations in many genes (6–12) • These mutations affect multiple cellular functions: DNA repair, cell division, apoptosis, cellular differentiation, mig ...
... • Most cancers are somatic, with only 1% due to germ-line mutations • Cancers rarely arise from single gene mutations but from the accumulation of mutations in many genes (6–12) • These mutations affect multiple cellular functions: DNA repair, cell division, apoptosis, cellular differentiation, mig ...
intro.phys.psu.edu
... radio-telephones -the radio-telephone needed powerful transmitters that connect to one tower per city -the radio-telephone could only have a few per city because of limited channels ...
... radio-telephones -the radio-telephone needed powerful transmitters that connect to one tower per city -the radio-telephone could only have a few per city because of limited channels ...
EXPLORE LEARNING: CELL STRUCTURE
... The process of photosynthesis is responsible for every bit of the oxygen that is present in Earth’s atmosphere today. 2. Examine the remaining structures of the plant cell and compare the structure and function of each with their counterparts in the animal cell. 1. Compare the vacuoles in plant cell ...
... The process of photosynthesis is responsible for every bit of the oxygen that is present in Earth’s atmosphere today. 2. Examine the remaining structures of the plant cell and compare the structure and function of each with their counterparts in the animal cell. 1. Compare the vacuoles in plant cell ...
File - Dillman Biology
... Active Transport (cont’d) Active transport is the movement of molecules up (against) the concentration gradient, from low to high. Remember this time the cell must use its own energy (ATP) to move substances. ...
... Active Transport (cont’d) Active transport is the movement of molecules up (against) the concentration gradient, from low to high. Remember this time the cell must use its own energy (ATP) to move substances. ...
PhD THESIS Epigenetic mechanisms involved in stem cell
... chromatin structure and its degree of compaction. Recent analysis of epigenetic changes in human and murine stem cells have provided new data on the properties of pluripotency of stem cells and their differentiation capacity. These mechanisms lead to a hierarchy of transcription, are mediated by tra ...
... chromatin structure and its degree of compaction. Recent analysis of epigenetic changes in human and murine stem cells have provided new data on the properties of pluripotency of stem cells and their differentiation capacity. These mechanisms lead to a hierarchy of transcription, are mediated by tra ...
Section 3
... The cell goes through a cycle during its life. The cycle begins when a new cell is made and that new cell goes through specific stages or phases and divides to form new cells. Before cells can divide to produce new cells, they must make copies of their DNA. Recall that DNA is the hereditary informat ...
... The cell goes through a cycle during its life. The cycle begins when a new cell is made and that new cell goes through specific stages or phases and divides to form new cells. Before cells can divide to produce new cells, they must make copies of their DNA. Recall that DNA is the hereditary informat ...
Document
... 43. Put the following stages of mitosis (cell division) in order. Then Name them. 1st: ___________ called _____________________ 2nd: ___________ called _____________________ 3rd: ___________ called _____________________ 4th: ___________ called _____________________ 5th: ___________ called __________ ...
... 43. Put the following stages of mitosis (cell division) in order. Then Name them. 1st: ___________ called _____________________ 2nd: ___________ called _____________________ 3rd: ___________ called _____________________ 4th: ___________ called _____________________ 5th: ___________ called __________ ...
B2 1 Cells, Tissues and Organs Questions and Answers
... absorbs light/to produce food (allow reference to gaseous exchange) for 1 mark ...
... absorbs light/to produce food (allow reference to gaseous exchange) for 1 mark ...
File
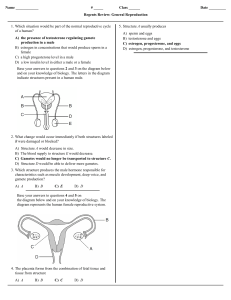
... 71. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. The reproductive cycle in a human female is not functioning properly. An imbalance of hormones is diagnosed as the cause. Identify one hormone directly involved in the human female reproductive ...
... 71. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. The reproductive cycle in a human female is not functioning properly. An imbalance of hormones is diagnosed as the cause. Identify one hormone directly involved in the human female reproductive ...
A Cell Is Like a Dirtbike
... • A plant cell has a cell wall to support it and a animal cell has a cytoskeleton to support it. • A plant cell uses both photosynthesis and cell respiration to breath. Where a animal cell only has cell respiration. • A plant cell has a chloroplast to absorb energy. Where a animal cell does not have ...
... • A plant cell has a cell wall to support it and a animal cell has a cytoskeleton to support it. • A plant cell uses both photosynthesis and cell respiration to breath. Where a animal cell only has cell respiration. • A plant cell has a chloroplast to absorb energy. Where a animal cell does not have ...
Section 3.1 Cell Theory and Comparison of Prokaryotic and
... Endosymbiosis- a relationship in which one organism lives within the body of another and both benefit from relationship. Early mitochondria and chloroplasts were once simple prokaryotic cells that were taken up by larger prokaryotes around 1.5 bya. Some of the smaller prokaryotes may have survived i ...
... Endosymbiosis- a relationship in which one organism lives within the body of another and both benefit from relationship. Early mitochondria and chloroplasts were once simple prokaryotic cells that were taken up by larger prokaryotes around 1.5 bya. Some of the smaller prokaryotes may have survived i ...
The Cell Theory and Membrane Transport
... Active Transport Movement against the concentration gradient. Molecules will move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Requires energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) and protein pumps ...
... Active Transport Movement against the concentration gradient. Molecules will move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Requires energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) and protein pumps ...
CEE 210 Environmental Biology for Engineers
... ◦ 20, 21,22,23…..2n where n is the number of generations ◦ Generation time a.k.a. Doubling time Time it takes for two cells to form from the parent cell It is also the time it takes to double the cell numbers ...
... ◦ 20, 21,22,23…..2n where n is the number of generations ◦ Generation time a.k.a. Doubling time Time it takes for two cells to form from the parent cell It is also the time it takes to double the cell numbers ...
1-_b_Intrduction
... Microorganisms and all other living organisms are classified as Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. They are distinguished on the basis of their cellular characteristics. ...
... Microorganisms and all other living organisms are classified as Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. They are distinguished on the basis of their cellular characteristics. ...