Finding a way to the nucleus - Purdue University
... existence of the T-complex, such a complex has not been demonstrated in plants. Interaction of VirD2/T-strands and VirE2 with other secreted Agrobacterium virulence effector proteins and plant proteins likely generates ‘super-T-complexes’ that are responsible for subcellular trafficking of T-strands ...
... existence of the T-complex, such a complex has not been demonstrated in plants. Interaction of VirD2/T-strands and VirE2 with other secreted Agrobacterium virulence effector proteins and plant proteins likely generates ‘super-T-complexes’ that are responsible for subcellular trafficking of T-strands ...
Presence of exposed phospholipids in the outer membrane of Vibrio
... Atypical permeability features of the outer membrane V . cholerae cells were found to be highly sensitive to a wide variety of compounds (Table 1). Since the MIC values may vary with the experimental conditions, the sensitivity of E. coli strain C-600 (chemotype Ra) was determined under identical co ...
... Atypical permeability features of the outer membrane V . cholerae cells were found to be highly sensitive to a wide variety of compounds (Table 1). Since the MIC values may vary with the experimental conditions, the sensitivity of E. coli strain C-600 (chemotype Ra) was determined under identical co ...
Supplemental Methods (doc 120K)
... electrophysiolgical and pharmacological characterization of VTA dopamine neurons. In vitro studies have shown that although some tyrosine hydroxylase positive neurons do fit electrophysiological characterizations, there are neurons that do not and that there are tyrosine hydroxylase negative neurons ...
... electrophysiolgical and pharmacological characterization of VTA dopamine neurons. In vitro studies have shown that although some tyrosine hydroxylase positive neurons do fit electrophysiological characterizations, there are neurons that do not and that there are tyrosine hydroxylase negative neurons ...
Cell Membrane - holyoke
... When something can move through a cell membrane without using any energy (like diffusion) it is called ___________ transport. ...
... When something can move through a cell membrane without using any energy (like diffusion) it is called ___________ transport. ...
Changes in the Nuclear Envelope Environment Affect
... The Saccharomyces cerevisiae nuclear membrane is part of a complex nuclear envelope environment also containing chromatin, integral and peripheral membrane proteins, and large structures such as nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) and the spindle pole body. To study how properties of the nuclear membrane ...
... The Saccharomyces cerevisiae nuclear membrane is part of a complex nuclear envelope environment also containing chromatin, integral and peripheral membrane proteins, and large structures such as nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) and the spindle pole body. To study how properties of the nuclear membrane ...
Swimming behavior of the monotrichous bacterium Pseudomonas
... & El-Masry, 1989; Kanda et al., 2011). Pseudomonas putida PRS2000 generally have five to seven flagella (Harwood et al., 1989). The number of flagella on P. fluorescens SBW25 cells is probably similar to that of P. aeruginosa, which often carry a single flagellum (E.P. Greenberg and R. Ramphal, pers ...
... & El-Masry, 1989; Kanda et al., 2011). Pseudomonas putida PRS2000 generally have five to seven flagella (Harwood et al., 1989). The number of flagella on P. fluorescens SBW25 cells is probably similar to that of P. aeruginosa, which often carry a single flagellum (E.P. Greenberg and R. Ramphal, pers ...
Biology of Tooth Movement
... Messenger) and cell response (Chart 1). The agonists, primary stimulus or first messenger such as hormones or mechanical forces (Orthodontic Force) may alter activity through the plasma membrane. The production of second messenger (cAMP) pathway is regulated by stimulatory (Rs) or inhibitory (Ri) re ...
... Messenger) and cell response (Chart 1). The agonists, primary stimulus or first messenger such as hormones or mechanical forces (Orthodontic Force) may alter activity through the plasma membrane. The production of second messenger (cAMP) pathway is regulated by stimulatory (Rs) or inhibitory (Ri) re ...
Figures and figure supplements
... Figure 7. Roseobacticide-mediated algal lysis is strain specific. (a) Roseobacticides were introduced into 1 ml of algal cultures of E. huxleyi strains CCMP372 and CCMP3266. After 12 hr, cell lysis accompanied by chloroplast discharge was evident only in strain CCMP372 (black arrows). White arrow po ...
... Figure 7. Roseobacticide-mediated algal lysis is strain specific. (a) Roseobacticides were introduced into 1 ml of algal cultures of E. huxleyi strains CCMP372 and CCMP3266. After 12 hr, cell lysis accompanied by chloroplast discharge was evident only in strain CCMP372 (black arrows). White arrow po ...
Implications for AIDS Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Infection of
... In contrast to HIV-infected humans, naturally SIV-infected sooty mangabeys (SMs) very rarely progress to AIDS. Although the mechanisms underlying this disease resistance are unknown, a consistent feature of natural SIV infection is the absence of the generalized immune activation associated with HIV ...
... In contrast to HIV-infected humans, naturally SIV-infected sooty mangabeys (SMs) very rarely progress to AIDS. Although the mechanisms underlying this disease resistance are unknown, a consistent feature of natural SIV infection is the absence of the generalized immune activation associated with HIV ...
Regulated Expression of Vimentin cDNA in Cells in the Presence
... vimentin into fibroblasts that contained a preexisting vimentin filament network and found that with time after injection, the modified vimentin was first detected in filaments near the nucleus and then gradually later in filaments that extended into more peripheral areas of the cytoplasm. Similarly ...
... vimentin into fibroblasts that contained a preexisting vimentin filament network and found that with time after injection, the modified vimentin was first detected in filaments near the nucleus and then gradually later in filaments that extended into more peripheral areas of the cytoplasm. Similarly ...
Experimental conditions affect the site of tetrazolium
... facilitate reduction reactions. These salts have been used in microplate assays to measure bacterial proliferation (Tsukatani et al., 2008) and in colorimetric assays to test antimicrobial susceptibility (Tsukatani et al., 2008; Tunney et al., 2004). The mechanisms of tetrazolium salt reduction are ...
... facilitate reduction reactions. These salts have been used in microplate assays to measure bacterial proliferation (Tsukatani et al., 2008) and in colorimetric assays to test antimicrobial susceptibility (Tsukatani et al., 2008; Tunney et al., 2004). The mechanisms of tetrazolium salt reduction are ...
Annotated Bibliography "Primary Information of P53 Gene
... article was very useful because it talked about the relationship between p53 and aging. This could be applied to my research to find differences between young and old population that cause the decline in p53 proteins. This source confirmed that cancer is an elderly disease – p53 functions decline as ...
... article was very useful because it talked about the relationship between p53 and aging. This could be applied to my research to find differences between young and old population that cause the decline in p53 proteins. This source confirmed that cancer is an elderly disease – p53 functions decline as ...
Regulatory B cells in autoimmune diseases
... suppress pathogenic T cells and autoreactive B cells in a cell-tocell contact-dependent manner.7 Until recently, the exact origin and molecular identity of regulatory B (Breg) cells remained elusive. Accumulating evidence suggests that the Breg cell population is heterogeneous, meaning that this pop ...
... suppress pathogenic T cells and autoreactive B cells in a cell-tocell contact-dependent manner.7 Until recently, the exact origin and molecular identity of regulatory B (Breg) cells remained elusive. Accumulating evidence suggests that the Breg cell population is heterogeneous, meaning that this pop ...
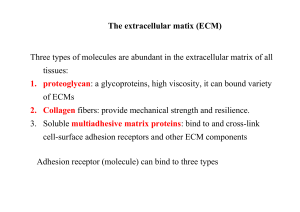
The extracellular matix (ECM) Three types of molecules are
... The covalent intramolecular and intermolecular cross-links formed between modified lysine side chains within a collagen fibril. The crosslinks are formed in several steps. First, certain lysine and hydroxylysine residues are deaminated by the extracellular enzyme lysyl oxidase to yield highly reacti ...
... The covalent intramolecular and intermolecular cross-links formed between modified lysine side chains within a collagen fibril. The crosslinks are formed in several steps. First, certain lysine and hydroxylysine residues are deaminated by the extracellular enzyme lysyl oxidase to yield highly reacti ...
Endocytosis, Actin Cytoskeleton, and Signaling
... (2002), more than 30 putative endosomal Rab GTPases were found in the Arabidopsis genome, indicating an essential role of endocytosis in plant cells. Plant Rab GTPases Ara6 and Ara7, related to the mammalian endosomal protein Rab5, as well as Pra2, related to mammalian Rab11, have been localized to ...
... (2002), more than 30 putative endosomal Rab GTPases were found in the Arabidopsis genome, indicating an essential role of endocytosis in plant cells. Plant Rab GTPases Ara6 and Ara7, related to the mammalian endosomal protein Rab5, as well as Pra2, related to mammalian Rab11, have been localized to ...
Aluminum-Induced 133-ß-D-Glucan Inhibits Cell
... Fujiwara et al., 1991), indicated an instantaneous coupling within seconds in epidermal and cortical control cells (Fig. 5, A and A’). The control plants showed approximately a 15% decline in percent dyecoupling (Table I) at a 4- to 5-mm distance from tip (DFT) compared with a 1- to 2-mm DFT. This s ...
... Fujiwara et al., 1991), indicated an instantaneous coupling within seconds in epidermal and cortical control cells (Fig. 5, A and A’). The control plants showed approximately a 15% decline in percent dyecoupling (Table I) at a 4- to 5-mm distance from tip (DFT) compared with a 1- to 2-mm DFT. This s ...
CELL
... kidney, with each organ performing a different function. • Cells also have a set of "little organs," called organelles, that are adapted and/or specialized for carrying out one or more vital functions. • Membrane-bound organelles are found only in eukaryotes. ...
... kidney, with each organ performing a different function. • Cells also have a set of "little organs," called organelles, that are adapted and/or specialized for carrying out one or more vital functions. • Membrane-bound organelles are found only in eukaryotes. ...
Staining
... Haematoxylin stains acidic components of cell (basophilic structures) – DNA, RNA, ie. ...
... Haematoxylin stains acidic components of cell (basophilic structures) – DNA, RNA, ie. ...
Microbiology Bacteria, Protists, and Fungi
... c. When scientists found these creatures they were so excited about them. ? Why? d. Little known ? Why? e. Have you heard about the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)? ? A DNA replication method in lab ? An enzyme used for PCR is extracted from thermophilies. ...
... c. When scientists found these creatures they were so excited about them. ? Why? d. Little known ? Why? e. Have you heard about the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)? ? A DNA replication method in lab ? An enzyme used for PCR is extracted from thermophilies. ...
ARVO 2017 Annual Meeting Abstracts 514 Non
... Purpose: We recently reported that retinal microglia in adult mice are maintained locally without significant contribution from hematopoiesis. An important emerging question is whether local paracrine factors in the retina are needed to help maintain normal microglia. We addressed this problem by fo ...
... Purpose: We recently reported that retinal microglia in adult mice are maintained locally without significant contribution from hematopoiesis. An important emerging question is whether local paracrine factors in the retina are needed to help maintain normal microglia. We addressed this problem by fo ...
Expression of the papillomavirus E2 protein in HeLa cells leads to
... The papillomavirus E2 protein plays a central role in the viral life cycle as it regulates both transcription and replication of the viral genome. In this study, we showed that transient expression of bovine papillomavirus type 1 or human papillomavirus type 18 (HPV18) E2 proteins in HeLa cells acti ...
... The papillomavirus E2 protein plays a central role in the viral life cycle as it regulates both transcription and replication of the viral genome. In this study, we showed that transient expression of bovine papillomavirus type 1 or human papillomavirus type 18 (HPV18) E2 proteins in HeLa cells acti ...
1 - AState.edu
... • All cells have several basic features. • They are all bounded by a thin plasma membrane. • Inside all cells is a thick, jelly-like fluid called the cytosol, in which cellular components are suspended. • All cells have one or more chromosomes carrying genes made of DNA. • All cells have ribosomes, ...
... • All cells have several basic features. • They are all bounded by a thin plasma membrane. • Inside all cells is a thick, jelly-like fluid called the cytosol, in which cellular components are suspended. • All cells have one or more chromosomes carrying genes made of DNA. • All cells have ribosomes, ...
Development of neural tube basal lamina during neurulation and
... examined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) the entire trunk from the posterior neuropore to the cervical region. From this spectrum, we have chosen six levels to illustrate the development of BL (Fig. 1A). At the most posterior levels, the future NC cells are found within the ridges of the e ...
... examined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) the entire trunk from the posterior neuropore to the cervical region. From this spectrum, we have chosen six levels to illustrate the development of BL (Fig. 1A). At the most posterior levels, the future NC cells are found within the ridges of the e ...
The Arabidopsis sku6-spiral1 gene encodes a plus end
... Online version contains Web-only data. Article, publication date, and citation information can be found at www.plantcell.org/cgi/doi/10.1105/tpc.020644. ...
... Online version contains Web-only data. Article, publication date, and citation information can be found at www.plantcell.org/cgi/doi/10.1105/tpc.020644. ...
Full text - 2nd International Conference of the
... observations should earn a place for himself in the pantheon of distinguished plant scientists. Botany students learn about these connections, which have been found in all classes of plants and plant tissues, under the name given to them, ―plasmodesmata‖, by Strasburger in 1901.15 The full elucidati ...
... observations should earn a place for himself in the pantheon of distinguished plant scientists. Botany students learn about these connections, which have been found in all classes of plants and plant tissues, under the name given to them, ―plasmodesmata‖, by Strasburger in 1901.15 The full elucidati ...