Cells
... No nucleus or membrane-bound Has a nucleus and organelles organelles Original source of all life, according to evolution ...
... No nucleus or membrane-bound Has a nucleus and organelles organelles Original source of all life, according to evolution ...
File
... share similar origin Prokaryotic cells engulfed by ancestors of eukaryotic cells Evidence: Double-membrane structure Have own ribosomes & DNA Reproduce independently within cell ...
... share similar origin Prokaryotic cells engulfed by ancestors of eukaryotic cells Evidence: Double-membrane structure Have own ribosomes & DNA Reproduce independently within cell ...
12-1 pm Location: Room HSW1057 UCSF
... Presented By: Antonia Livolsi, Ph.D, Research Application Scientist Traditional methods for examining gene expression involve lysed or fixed cell populations. The ability to do so in live cells would allow for more physiologically relevant information based on a cell’s response to given stimuli. Det ...
... Presented By: Antonia Livolsi, Ph.D, Research Application Scientist Traditional methods for examining gene expression involve lysed or fixed cell populations. The ability to do so in live cells would allow for more physiologically relevant information based on a cell’s response to given stimuli. Det ...
Biology Study guide
... Microscope use and calculations Diagram with parts and function Total magnification Field of view ...
... Microscope use and calculations Diagram with parts and function Total magnification Field of view ...
The Discovery of Cells
... The Cell Theory • Cells- The basic units of all living organisms. The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things. 3. All cells come from other cells. ...
... The Cell Theory • Cells- The basic units of all living organisms. The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things. 3. All cells come from other cells. ...
Science 9, Unit 1: Reproduction
... 6. Contains the cell's information 7. Outer layer of plant cells 8. Where proteins are made 10. Powerhouse of the cell 11. Basic unit of structure and function ...
... 6. Contains the cell's information 7. Outer layer of plant cells 8. Where proteins are made 10. Powerhouse of the cell 11. Basic unit of structure and function ...
Science 9, Unit 1: Reproduction
... 6. Contains the cell's information 7. Outer layer of plant cells 8. Where proteins are made 10. Powerhouse of the cell 11. Basic unit of structure and function ...
... 6. Contains the cell's information 7. Outer layer of plant cells 8. Where proteins are made 10. Powerhouse of the cell 11. Basic unit of structure and function ...
Study Guide
... Study Guide Chapter 2, Section 1 – Cell Structure & Function Summary Common Cell Traits All cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic (cells that lack a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus). Cell Organiza ...
... Study Guide Chapter 2, Section 1 – Cell Structure & Function Summary Common Cell Traits All cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic (cells that lack a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus). Cell Organiza ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... 1. All living things are composed of ___________. 2. Cells are the basic units of _______________ and ________________. 3. Cells are produced only from other __________ cells ** These observations were made from ____________, ______________ and ______________. Prokaryotic Cells 1. Lived at least ___ ...
... 1. All living things are composed of ___________. 2. Cells are the basic units of _______________ and ________________. 3. Cells are produced only from other __________ cells ** These observations were made from ____________, ______________ and ______________. Prokaryotic Cells 1. Lived at least ___ ...
Unit 3 Test Review
... 1. What is a prokaryote? 2. What is an example of an organism that has prokaryotic cells? 3. What is a eukaryote? 4. What is an example of an organism that has eukaryotic cells? 5. What is an organelle? 6. List 4 ways that prokaryotes are different from eukaryotes. 7. Draw and label a bacteria, an a ...
... 1. What is a prokaryote? 2. What is an example of an organism that has prokaryotic cells? 3. What is a eukaryote? 4. What is an example of an organism that has eukaryotic cells? 5. What is an organelle? 6. List 4 ways that prokaryotes are different from eukaryotes. 7. Draw and label a bacteria, an a ...
Osmosis and Mitosis - Perth Grammar School
... Remember to save your work as you go along!! Either type answers into field or choose using drop down boxes.. Name two substances important to cells, which can diffuse into the cell. When a membrane is described as selectively permeable, what does this mean? What is the main differences between and ...
... Remember to save your work as you go along!! Either type answers into field or choose using drop down boxes.. Name two substances important to cells, which can diffuse into the cell. When a membrane is described as selectively permeable, what does this mean? What is the main differences between and ...
CELL CYCLE Enduring Understandings • Cells need to divide in a
... • How is cell division controlled? • How does this unit provide evidence for the theory of endosymbiosis? • How does this unit provide evidence of the relatedness of living things in the world? • How do differences between and among cell division correlate to specific functions and how is this evide ...
... • How is cell division controlled? • How does this unit provide evidence for the theory of endosymbiosis? • How does this unit provide evidence of the relatedness of living things in the world? • How do differences between and among cell division correlate to specific functions and how is this evide ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs, Organ Systems
... up of many tissues that work together and do the same job Some organs in the human body include: ...
... up of many tissues that work together and do the same job Some organs in the human body include: ...
Facts About Cells
... Facts About Cells Cells are the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism All cells contain living material called cytoplasm All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that controls what enters & leaves the cell ...
... Facts About Cells Cells are the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism All cells contain living material called cytoplasm All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that controls what enters & leaves the cell ...
lesson_10
... Unit Description: When a living thing grows, what happens to its cells? Does an animal get larger because each cell increases in size or because it produces more of them? In most cases, living things grow by producing more cells. Students will begin to explore how cells grow and are produced. ...
... Unit Description: When a living thing grows, what happens to its cells? Does an animal get larger because each cell increases in size or because it produces more of them? In most cases, living things grow by producing more cells. Students will begin to explore how cells grow and are produced. ...
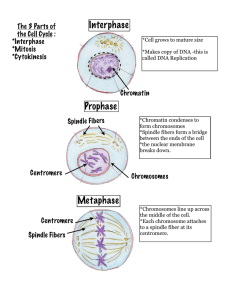
Interphase Prophase Metaphase
... *the centromeres split and the 2 chromatids separate. *the chromatids move along the spindle fibers to opposite ends of the cell. * the cell is stretched out as the opposite ends pull apart. ...
... *the centromeres split and the 2 chromatids separate. *the chromatids move along the spindle fibers to opposite ends of the cell. * the cell is stretched out as the opposite ends pull apart. ...
cells cells - Springwater River Otters
... The main structures- yeah, we call them organelles. Now let's break it down and get some information- How do cells work? It's a crazy combination! -ChorusThe cell membrane is the border patrol, Who can cross over? The membrane lets 'em know The gooey stuff inside, is called the cytoplasm It holds th ...
... The main structures- yeah, we call them organelles. Now let's break it down and get some information- How do cells work? It's a crazy combination! -ChorusThe cell membrane is the border patrol, Who can cross over? The membrane lets 'em know The gooey stuff inside, is called the cytoplasm It holds th ...
Mitosis Worksheet
... The diagram below shows six cells in various phases of the cell cycle. Note the cells are not arranged in the order in which mitosis occurs and one of the phases of mitosis occurs twice. Use the diagram to answer questions 1-7. ...
... The diagram below shows six cells in various phases of the cell cycle. Note the cells are not arranged in the order in which mitosis occurs and one of the phases of mitosis occurs twice. Use the diagram to answer questions 1-7. ...
Study Guide for Chapter 5 – Lesson 1, “What are Cells?” Be a
... Who discovered cells? __________________________________________________________________ Why did he name them cells? _____________________________________________________________________________________ What is a cell? _________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Who discovered cells? __________________________________________________________________ Why did he name them cells? _____________________________________________________________________________________ What is a cell? _________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Cells and Cell Organelles assignment
... Cells and Cell Organelles The following questions should be answered in complete sentences that make sense. Your answer should also include definitions of any other biological terms you use in your answer. Provide enough of a description in your answer so as to explain the basics of the concept to s ...
... Cells and Cell Organelles The following questions should be answered in complete sentences that make sense. Your answer should also include definitions of any other biological terms you use in your answer. Provide enough of a description in your answer so as to explain the basics of the concept to s ...
Test Review: Unit 3 Cells and microscopes Directions: Answers do
... 13. What is cell differentiation? 14. What is the function of: a. Epithelial cells: b. Bone cells: c. Nerve cells: 15. What determines the function of a cell? 16. Which organelle contains the instructions that built these cells? Why aren’t the cells all the same? 17. What tool allowed scientists to ...
... 13. What is cell differentiation? 14. What is the function of: a. Epithelial cells: b. Bone cells: c. Nerve cells: 15. What determines the function of a cell? 16. Which organelle contains the instructions that built these cells? Why aren’t the cells all the same? 17. What tool allowed scientists to ...
CELL ORGANELLES 1. How does the structure of a cell suggest its
... 7. In which kinds of human cells would you expect to find the most mitochondria? The most lysosomes? The most ribosomes? Explain your answers. ...
... 7. In which kinds of human cells would you expect to find the most mitochondria? The most lysosomes? The most ribosomes? Explain your answers. ...
Cell biology - Central Magnet School
... A few cells are large enough to be seen by the “naked” eye ...
... A few cells are large enough to be seen by the “naked” eye ...
Test Review: Unit 4 Cells and microscopes What is a prokaryote
... 2. What is an example of an organism that has prokaryotic cells? ...
... 2. What is an example of an organism that has prokaryotic cells? ...