Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw
... invented the microscope in 1665. a. All ________________ things are made of one or more cells. b. The cell is the _______________ ______________ of life. c. All cells come from cells that already _______________. 2. __________________ are one-celled organisms; larger organisms are made of many cells ...
... invented the microscope in 1665. a. All ________________ things are made of one or more cells. b. The cell is the _______________ ______________ of life. c. All cells come from cells that already _______________. 2. __________________ are one-celled organisms; larger organisms are made of many cells ...
Cellular Organization and Cell Theory Notes
... These work and discoveries of these Scientist helped develop the Cell Theory. The invention and improvement of the microscope was directly involved with coming up with the theory The Cell Theory states: 1) All organisms are composed of one or more cells 2) The cell is the basic unit of life in all l ...
... These work and discoveries of these Scientist helped develop the Cell Theory. The invention and improvement of the microscope was directly involved with coming up with the theory The Cell Theory states: 1) All organisms are composed of one or more cells 2) The cell is the basic unit of life in all l ...
The Cell Theory
... God implanted the soul in the embryo forty days after conception. The soul controlled growth and nutrition, sensation and motion, and all rational activity. Women were nothing more than imperfect versions of men. Diagnoses could be made from the nature of excrement, and tint of skin The liver create ...
... God implanted the soul in the embryo forty days after conception. The soul controlled growth and nutrition, sensation and motion, and all rational activity. Women were nothing more than imperfect versions of men. Diagnoses could be made from the nature of excrement, and tint of skin The liver create ...
Le Louis - LaPazChirripoColegio2016-2017
... • There were a number of problems with the lipo-protein sandwich model proposed by DD • Not all membranes are identical or symmetrical, as the DD implied • Membranes with different functions have different structure, can be seen with microscope • A protein layer is not likely because it would be mos ...
... • There were a number of problems with the lipo-protein sandwich model proposed by DD • Not all membranes are identical or symmetrical, as the DD implied • Membranes with different functions have different structure, can be seen with microscope • A protein layer is not likely because it would be mos ...
Notes for Cell Cycle
... grows, its volume increases much faster than its surface area so the amount of materials needed to support a large cell can not diffuse through the cell membrane. ...
... grows, its volume increases much faster than its surface area so the amount of materials needed to support a large cell can not diffuse through the cell membrane. ...
Mini-lesson on prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
... Chloroplasts and mitochondria • Evidence suggests that chloroplasts and mitochondria were once bacteria that developed a symbiotic relationship with cells that have a nucleus • Chloroplasts and mitochondria have their own circular DNA that is not a part of the host’s genome. • Yes plants have both ...
... Chloroplasts and mitochondria • Evidence suggests that chloroplasts and mitochondria were once bacteria that developed a symbiotic relationship with cells that have a nucleus • Chloroplasts and mitochondria have their own circular DNA that is not a part of the host’s genome. • Yes plants have both ...
10.4 Guided Notes (Cell Differentiation and Stem Cells)
... – Mass of cells that develop ______________________ after fertilization must be accumulated ASAP or cells differentiate ethical controversial – Gives rise to _____________________ cell types in body – ____________________________ self-renewal (in LAB) & cell differentiation Biotechnical Applicat ...
... – Mass of cells that develop ______________________ after fertilization must be accumulated ASAP or cells differentiate ethical controversial – Gives rise to _____________________ cell types in body – ____________________________ self-renewal (in LAB) & cell differentiation Biotechnical Applicat ...
Mitosis
... centrosomes located at the pole of the cells. The nuclear membrane also disintegrates at this time, freeing the chromosomes into the surrounding cytoplasm. • Prometaphase. During prometaphase, some of the fibers attach to the centromere of each pair of sister chromatids and they begin to move toward ...
... centrosomes located at the pole of the cells. The nuclear membrane also disintegrates at this time, freeing the chromosomes into the surrounding cytoplasm. • Prometaphase. During prometaphase, some of the fibers attach to the centromere of each pair of sister chromatids and they begin to move toward ...
The Cell - Biology Junction
... Localize Chemical Reactions making the cell far more efficient ...
... Localize Chemical Reactions making the cell far more efficient ...
Postdoctoral and PhD position in Epigenetic Regulation of Plant
... Postdoctoral and PhD position in Epigenetic Regulation of Plant Stem Cells We are seeking highly motivated candidates to investigate how stem cells in the root meristem sense and adapt to environmental changes. A specific focus will be on the epigenetic regulation of st ...
... Postdoctoral and PhD position in Epigenetic Regulation of Plant Stem Cells We are seeking highly motivated candidates to investigate how stem cells in the root meristem sense and adapt to environmental changes. A specific focus will be on the epigenetic regulation of st ...
Cell Structure and Function - Tri
... synthesis via cellular respiration) use oxygen to produce ATP shaped somewhat like a peanut reactions of energy production take place on numerous membranes that form the inside of the mitochondrion ...
... synthesis via cellular respiration) use oxygen to produce ATP shaped somewhat like a peanut reactions of energy production take place on numerous membranes that form the inside of the mitochondrion ...
cells - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... Vacuole is very large, stores water and sugars for the plant ...
... Vacuole is very large, stores water and sugars for the plant ...
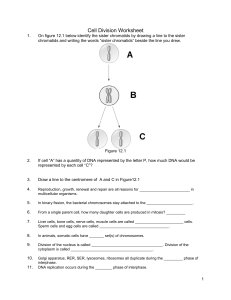
Cell Division Worksheet PDF
... B. How many chromosomes would be present in a haploid cell from this animal? ...
... B. How many chromosomes would be present in a haploid cell from this animal? ...
Part A - Onion Cells
... 4. Place a coverslip onto the slide 5. Use the SCANNING objective to focus. You probably will not see the cells at this power. 6. Switch to low power. Cells should be visible, but they will be small and look like nearly clear purplish blobs. If you are looking at something very dark purple, it is pr ...
... 4. Place a coverslip onto the slide 5. Use the SCANNING objective to focus. You probably will not see the cells at this power. 6. Switch to low power. Cells should be visible, but they will be small and look like nearly clear purplish blobs. If you are looking at something very dark purple, it is pr ...
SEVENTH GRADE LIFE SCIENCES THEME: LIFE AROUND US
... *Energy *Waste Removal *Reproduction *Movement *Specialized Cells b. Determine that the systems of living things are organized by levels of complexity: *Cells *Tissues *Organs *Systems c. Compare/contrast the characteristics that distinguish plant cells from animal cells. ...
... *Energy *Waste Removal *Reproduction *Movement *Specialized Cells b. Determine that the systems of living things are organized by levels of complexity: *Cells *Tissues *Organs *Systems c. Compare/contrast the characteristics that distinguish plant cells from animal cells. ...
Mitosis notes 9.03
... Mitosis Mitosis is the process by which the nucleus of most eukaryotic cells divides. Mitosis as four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Color each chromosome in prophase a different color. Follow each of these chromosomes through mitosis. Show this by coloring the correct struct ...
... Mitosis Mitosis is the process by which the nucleus of most eukaryotic cells divides. Mitosis as four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Color each chromosome in prophase a different color. Follow each of these chromosomes through mitosis. Show this by coloring the correct struct ...
notes p. 107-108 - Madeira City Schools
... – conclusion: only flies can make flies, rotting meat doesn’t turn into flies ...
... – conclusion: only flies can make flies, rotting meat doesn’t turn into flies ...
The Basic Units of Life
... B) Plants, animals and _____________ have got a nucleus in their cells. Around the nucleus there is a _________________ membrane. ...
... B) Plants, animals and _____________ have got a nucleus in their cells. Around the nucleus there is a _________________ membrane. ...
Plant vs Animal Cells Reading
... Eukaryotic cells come in two kinds: plant and animal. Plant cells have several features in common. They both have a cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, and vacuoles. cell membrane is like the skin of the cell. It holds everything together and controls what passes into and out of the cell. nucleus con ...
... Eukaryotic cells come in two kinds: plant and animal. Plant cells have several features in common. They both have a cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, and vacuoles. cell membrane is like the skin of the cell. It holds everything together and controls what passes into and out of the cell. nucleus con ...
Biology Discussion Notes
... • Cell membrane-an outer boundary of the cell • Cytoplasm-interior substance of the cell • Cytoskeleton-structural support for the cell • DNA –form of genetic material • Ribosomes- cellular structures that make proteins ...
... • Cell membrane-an outer boundary of the cell • Cytoplasm-interior substance of the cell • Cytoskeleton-structural support for the cell • DNA –form of genetic material • Ribosomes- cellular structures that make proteins ...
Animal and plant cells
... This is only a sample of one of thousands of Boardworks Science PowerPoints. To see more of what Boardworks can offer, why not order a full presentation, completely free? Head to: ...
... This is only a sample of one of thousands of Boardworks Science PowerPoints. To see more of what Boardworks can offer, why not order a full presentation, completely free? Head to: ...
Chapter 8- A View of the Cell
... 3.STM-Scanning Tunneling Microscope Arrangement of atoms on surface Map hills and valleys ...
... 3.STM-Scanning Tunneling Microscope Arrangement of atoms on surface Map hills and valleys ...