• Cells were discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke • Early studies of
... • Hallmark is compartmentalization – Achieved through use of membrane-bound organelles and endomembrane system • Possess a cytoskeleton for support and to maintain cellular structure ...
... • Hallmark is compartmentalization – Achieved through use of membrane-bound organelles and endomembrane system • Possess a cytoskeleton for support and to maintain cellular structure ...
Tiny Cells and Agar Gels
... If one were to fill the same area with these smaller cells as was occupied by our large example, the volume covered would remain the same, but the total surface area provided by many smaller cells would be much increased, allowing for more efficient exchange. Put another way, a group of smaller cell ...
... If one were to fill the same area with these smaller cells as was occupied by our large example, the volume covered would remain the same, but the total surface area provided by many smaller cells would be much increased, allowing for more efficient exchange. Put another way, a group of smaller cell ...
Cell organelles ppt
... Site of protein synthesis Found attached to rough ER or floating free in cytosol Produced in a part of the nucleus called the nucleolus That looks familiar…what is a polypeptide? ...
... Site of protein synthesis Found attached to rough ER or floating free in cytosol Produced in a part of the nucleus called the nucleolus That looks familiar…what is a polypeptide? ...
• Individual chromosomes are made up of 2 identical strands of
... Chromosomes become visible and shorten and thicken Nuclear membrane fades Spindle forms Double-stranded chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell and attach to the spindle at the Centromere. ...
... Chromosomes become visible and shorten and thicken Nuclear membrane fades Spindle forms Double-stranded chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell and attach to the spindle at the Centromere. ...
The History of the Cell Theory
... •The microscope van Leeuwenhoek used is considered a simple light microscope because it contained one lens and used natural light to view objects. Development of Light Microscopes •Compound light microscopes use a series of lenses to magnify objects in steps. •These microscopes can magnify objects u ...
... •The microscope van Leeuwenhoek used is considered a simple light microscope because it contained one lens and used natural light to view objects. Development of Light Microscopes •Compound light microscopes use a series of lenses to magnify objects in steps. •These microscopes can magnify objects u ...
sParamecium: Paramecium is a genus of unicellular ciliate protozoa
... Paramecium is a genus of unicellular ciliate protozoa. It is covered with simple cilia, allowing the cell to move. If the Paramecium hits an obstacle it moves back, turns slightly and goes forward again. If it runs into the solid object again, it will repeat this process until it can get past the ob ...
... Paramecium is a genus of unicellular ciliate protozoa. It is covered with simple cilia, allowing the cell to move. If the Paramecium hits an obstacle it moves back, turns slightly and goes forward again. If it runs into the solid object again, it will repeat this process until it can get past the ob ...
Prokaryote to Eukaryote
... • The evidence shows that there were organisms that behaved like mitochondria, that lived in an oxygen-free environment, and organisms that behaved like chloroplasts that released the oxygen we breathe into the atmosphere. • They live on in our cells, a part of them, but still have the characteristi ...
... • The evidence shows that there were organisms that behaved like mitochondria, that lived in an oxygen-free environment, and organisms that behaved like chloroplasts that released the oxygen we breathe into the atmosphere. • They live on in our cells, a part of them, but still have the characteristi ...
Chapter 7 Summaries
... Compound light microscopes have lenses that focus light. They magnify objects by up to 1000 times. Chemical stains and fluorescent dyes make cell structures easier to see. Electron microscopes use beams of electrons focused by magnetic fields. They offer much higher resolution than light microscopes ...
... Compound light microscopes have lenses that focus light. They magnify objects by up to 1000 times. Chemical stains and fluorescent dyes make cell structures easier to see. Electron microscopes use beams of electrons focused by magnetic fields. They offer much higher resolution than light microscopes ...
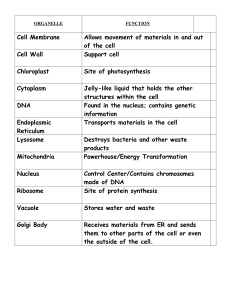
Cell Organelle Table
... Machines that makes proteins according to the directions of the DNA – not bound by membrane Modify and sorts proteins from RER, Loads them into vesicles and sends them to destinations Transport proteins (enzymes), lipids (steroids) and carbohydrates to specific locations Single membrane bound struct ...
... Machines that makes proteins according to the directions of the DNA – not bound by membrane Modify and sorts proteins from RER, Loads them into vesicles and sends them to destinations Transport proteins (enzymes), lipids (steroids) and carbohydrates to specific locations Single membrane bound struct ...
big
... • In some creatures these are have similar size, shape and activity; in others they can be quite different. • Often large, non-motile eggs, and small, motile sperm ...
... • In some creatures these are have similar size, shape and activity; in others they can be quite different. • Often large, non-motile eggs, and small, motile sperm ...
Lecture 19
... • In some creatures these are have similar size, shape and activity; in others they can be quite different. • Often large, non-motile eggs, and small, motile sperm ...
... • In some creatures these are have similar size, shape and activity; in others they can be quite different. • Often large, non-motile eggs, and small, motile sperm ...
Regulation of the Cell Cycle / Cancer
... capillary beds (lungs, liver, kidneys) or cycle through the lymphatic system and get stuck in the lymph nodes • Uncontrolled proliferation: constant cell cycling/mitosis – chemotherapy drugs attack all cells in cell cycle by blocking the formation of spindle fibers ...
... capillary beds (lungs, liver, kidneys) or cycle through the lymphatic system and get stuck in the lymph nodes • Uncontrolled proliferation: constant cell cycling/mitosis – chemotherapy drugs attack all cells in cell cycle by blocking the formation of spindle fibers ...
Cell: The Basic Unit of Life
... Cells are chemical factories that run on energy, take in raw materials, produce chemical products, and discard waste materials. Cells replicate themselves. That means they can reproduce an exact copy of themselves. The new copy can do all the same things as the original cells. A living cell can prod ...
... Cells are chemical factories that run on energy, take in raw materials, produce chemical products, and discard waste materials. Cells replicate themselves. That means they can reproduce an exact copy of themselves. The new copy can do all the same things as the original cells. A living cell can prod ...
Performance Indicator 7.L.3A.3
... • The gel-like fluid inside of a cell made of mostly water. • The other organelles are embedded in the cytoplasm • The cytoplasm is essential for many cellular reactions to occur ...
... • The gel-like fluid inside of a cell made of mostly water. • The other organelles are embedded in the cytoplasm • The cytoplasm is essential for many cellular reactions to occur ...
Cells and Systems Unit Exam Study Guide Topic 1: Living Organisms
... Know the five characteristics of living organisms, and be able to give an example of each Know the definition of a cell CELL -> TISSUE -> ORGAN -> SYSTEM -> ORGANISM ...
... Know the five characteristics of living organisms, and be able to give an example of each Know the definition of a cell CELL -> TISSUE -> ORGAN -> SYSTEM -> ORGANISM ...
7th Grade Science Cell Unit
... 7.L.3A Cells are the most basic unit of any living organism. All organisms are composed of one (unicellular) or many cells (multicellular) and require food and water, a way to dispose of waste, and an environment in which they can live in order to survive. Through the use of technology, scientists h ...
... 7.L.3A Cells are the most basic unit of any living organism. All organisms are composed of one (unicellular) or many cells (multicellular) and require food and water, a way to dispose of waste, and an environment in which they can live in order to survive. Through the use of technology, scientists h ...
CELLS, CELLS, CELLS
... the cell (e.g. proteins) 6. MITOCHONDRIA- supply energy for the cell . "powerhouse" of the cell . convert energy from food (Glucose) into a form the body can use (ATP) through a process called CELLULAR RESPIRATION Chemical formula for Cellular Respiration is (C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP) (T ...
... the cell (e.g. proteins) 6. MITOCHONDRIA- supply energy for the cell . "powerhouse" of the cell . convert energy from food (Glucose) into a form the body can use (ATP) through a process called CELLULAR RESPIRATION Chemical formula for Cellular Respiration is (C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP) (T ...
Cell Study Guide
... 17. The source of energy for photosynthesis is 18. Chloroplasts and mitochondria are organelles that are necessary for cells and organisms to function. Which type of organisms would have chloroplasts? 19. 6 C02 + 12 H20 ----------Light ------> C6H12O6+ 6 H20 + 6 O2 Chloroplasts This formula is for w ...
... 17. The source of energy for photosynthesis is 18. Chloroplasts and mitochondria are organelles that are necessary for cells and organisms to function. Which type of organisms would have chloroplasts? 19. 6 C02 + 12 H20 ----------Light ------> C6H12O6+ 6 H20 + 6 O2 Chloroplasts This formula is for w ...























