Electrical Current and Circuits
... Voltage • Depends on Potential Energy • Voltage: the number of electrons that are in an energy source Voltage can vary ...
... Voltage • Depends on Potential Energy • Voltage: the number of electrons that are in an energy source Voltage can vary ...
Chapter 8: Electrical Relationships
... Measure how current changes when resistance is increased. Describe how voltage, current, and resistance are related. Use Ohm’s law to solve circuit problems. Explain why resistors are used in a circuit. Define power as the rate at which energy flows. Describe relationships between work, energy, and ...
... Measure how current changes when resistance is increased. Describe how voltage, current, and resistance are related. Use Ohm’s law to solve circuit problems. Explain why resistors are used in a circuit. Define power as the rate at which energy flows. Describe relationships between work, energy, and ...
Tutorial 1
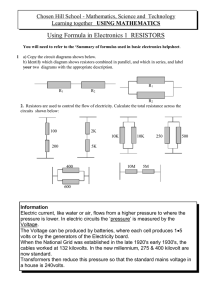
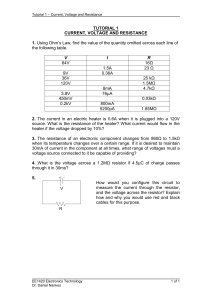
... heater if the voltage dropped by 10%? 3. The resistance of an electronic component changes from 860Ω to 1.5kΩ when its temperature changes over a certain range. If it is desired to maintain 30mA of current in the component at all times, what range of voltages must a voltage source connected to it be ...
... heater if the voltage dropped by 10%? 3. The resistance of an electronic component changes from 860Ω to 1.5kΩ when its temperature changes over a certain range. If it is desired to maintain 30mA of current in the component at all times, what range of voltages must a voltage source connected to it be ...
Measurement
... relates the voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) in an electrical circuit. The formula states that V IR where voltage is measured in volts, current is amperes, and resistance is ohms ( ). V V This equation can be rearranged into two other formulas. They are I and R . Each R I formula ...
... relates the voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) in an electrical circuit. The formula states that V IR where voltage is measured in volts, current is amperes, and resistance is ohms ( ). V V This equation can be rearranged into two other formulas. They are I and R . Each R I formula ...
Chapter-10 Electricity
... Georg Simon Ohm (1787-1854), a German physicist, discovered Ohm’s law in 1826. This is an experimental law, valid for both alternating current (ac) and direct current (dc) circuits. ...
... Georg Simon Ohm (1787-1854), a German physicist, discovered Ohm’s law in 1826. This is an experimental law, valid for both alternating current (ac) and direct current (dc) circuits. ...
Powerpoint Slides
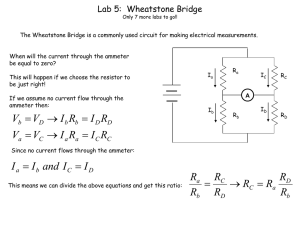
... The Wheatstone Bridge is a commonly used circuit for making electrical measurements. When will the current through the ammeter be equal to zero? This will happen if we choose the resistor to be just right! If we assume no current flow through the ammeter then: ...
... The Wheatstone Bridge is a commonly used circuit for making electrical measurements. When will the current through the ammeter be equal to zero? This will happen if we choose the resistor to be just right! If we assume no current flow through the ammeter then: ...
basic electricity: ohm`s law - Saint Leo University Faculty
... we can re-write this equation as: ...
... we can re-write this equation as: ...
Slide 1
... a charge of 2.50 C passes through it in 2.00 s? 2. How many electrons passed through? ...
... a charge of 2.50 C passes through it in 2.00 s? 2. How many electrons passed through? ...
Portable Appliance Testing Course Pre-Study Revision
... The candidate will need to understand basic numeric prefixes used with electrical symbols and measurement units i.e.… milli (m) a thousandth e.g. 3mA : three thousandths of an amp kilo (k) a thousand times e.g. 100k : one hundred thousand ohms mega (M) a million times e.g. 2M : two million ohms ...
... The candidate will need to understand basic numeric prefixes used with electrical symbols and measurement units i.e.… milli (m) a thousandth e.g. 3mA : three thousandths of an amp kilo (k) a thousand times e.g. 100k : one hundred thousand ohms mega (M) a million times e.g. 2M : two million ohms ...
Electric Current Synchronous Session
... • Voltage exists when there is an imbalance in charge • If two objects have different amount of charge, there is voltage between them • For example, standard battery has a voltage difference of 1.5 volts between its positive and negative terminals • Volts expressed in joules/coulomb ...
... • Voltage exists when there is an imbalance in charge • If two objects have different amount of charge, there is voltage between them • For example, standard battery has a voltage difference of 1.5 volts between its positive and negative terminals • Volts expressed in joules/coulomb ...
Slide 1
... Current- the movement of charge. Symbol is I, unit is the Ampere (A) I = q/t 1 A = 1 C/s Conventional current- from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. Drift velocity- the speed in which individual electrons move within the conductor, opposite the electric field. The drift velocity is re ...
... Current- the movement of charge. Symbol is I, unit is the Ampere (A) I = q/t 1 A = 1 C/s Conventional current- from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. Drift velocity- the speed in which individual electrons move within the conductor, opposite the electric field. The drift velocity is re ...
DELMAR`S Standard Textbook of Electricity – 5th Edition Unit 2
... 1 lb of water 1 degree Farenheit ...
... 1 lb of water 1 degree Farenheit ...
Electricity - Mr. Meserve`s Class
... is Ohm’s Law. Ohm’s law states that when electrical potential (voltage) creates a flow of electricity (current), the current and the electrical resistance of the circuit are proportional to the voltage. In mathematical terms, V = I x R where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance ...
... is Ohm’s Law. Ohm’s law states that when electrical potential (voltage) creates a flow of electricity (current), the current and the electrical resistance of the circuit are proportional to the voltage. In mathematical terms, V = I x R where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance ...
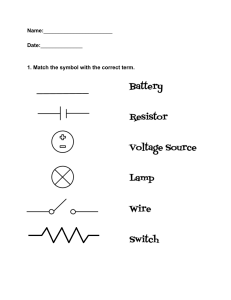
1. Match the symbol with the correct term.
... C. ___________ are positively charged particles. D. Atoms are made out of protons, electrons, and ____________. E. Batteries have two _____________. One is positive and one is negative. F. A ____________ circuit has multiple loops. G. ____________ is the flow of electrical charge in a circuit. ...
... C. ___________ are positively charged particles. D. Atoms are made out of protons, electrons, and ____________. E. Batteries have two _____________. One is positive and one is negative. F. A ____________ circuit has multiple loops. G. ____________ is the flow of electrical charge in a circuit. ...