Redox - slider-chemistry-12
... Review of some electrical terms 3 common terms to be familiar with: 1. Voltage (volts, V) – also known as potential difference, it is the work done in moving a unit charge from one point to another in joules per coulomb (known as volts). Or it is the difference in the electrical potential between tw ...
... Review of some electrical terms 3 common terms to be familiar with: 1. Voltage (volts, V) – also known as potential difference, it is the work done in moving a unit charge from one point to another in joules per coulomb (known as volts). Or it is the difference in the electrical potential between tw ...
8.3 * Resistance and Ohms Law - Mr Schmitt
... Resistance – is the property of any material that slows down the flow of electrons (i.e. a load) and converts electrical energy into other forms of energy (i.e. light or heat). ...
... Resistance – is the property of any material that slows down the flow of electrons (i.e. a load) and converts electrical energy into other forms of energy (i.e. light or heat). ...
Chapter 16
... • If it flows in one direction, it is direct current (DC). • If it flows in one direction and then another, it is alternating current (AC). • AC is used in our homes because it can be transmitted over long distances. ...
... • If it flows in one direction, it is direct current (DC). • If it flows in one direction and then another, it is alternating current (AC). • AC is used in our homes because it can be transmitted over long distances. ...
Quiz 6
... Ohm’s law relates the voltage with the current and resistance in circuit: V = iR The equation is only valid for components which are ohmic in nature; i.e. those whose resistivity is independent of the applied electric field: ...
... Ohm’s law relates the voltage with the current and resistance in circuit: V = iR The equation is only valid for components which are ohmic in nature; i.e. those whose resistivity is independent of the applied electric field: ...
Ohm`s law 2.08 - retremblay.net
... 7. What is the decimal equivalent of 6/8 ? ___________________________ ...
... 7. What is the decimal equivalent of 6/8 ? ___________________________ ...
SNC 1D
... referred to as the __________. ___________ is measured by an ammeter which is connected inside the circuit. __________ (potential difference) is the amount of energy per coulomb of charge between 2 different points in the circuit. It is measured by a voltmeter which is connected across two points in ...
... referred to as the __________. ___________ is measured by an ammeter which is connected inside the circuit. __________ (potential difference) is the amount of energy per coulomb of charge between 2 different points in the circuit. It is measured by a voltmeter which is connected across two points in ...
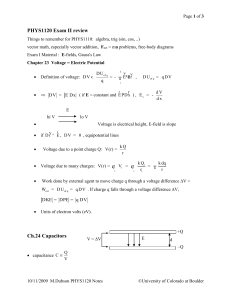
PHYS1120ExamIIReview.. - University of Colorado Boulder
... elements in parallel always have the same voltage: Ibig V same across both R's ...
... elements in parallel always have the same voltage: Ibig V same across both R's ...
Ohm`s Law Quiz Key Equations
... 9. A typical wall outlet in the United States provides a voltage of 120 V to your appliances. What current would be necessary for the electricity to pass through a 17-ohm resistor? ...
... 9. A typical wall outlet in the United States provides a voltage of 120 V to your appliances. What current would be necessary for the electricity to pass through a 17-ohm resistor? ...
Ohms Law Notes
... from a wall outlet changes direction 120 times per second Direct Current The flow of current in one consistent direction ...
... from a wall outlet changes direction 120 times per second Direct Current The flow of current in one consistent direction ...
Dec
... 50 Hz supply. A non-inductive resistor under the same conditions takes 12 amperes. If the two are connected in series and placed across the same supply, find the current taken. If now the frequency is reduced to 40 Hz, the voltage being maintained constant, find the current taken. 4. A heater is req ...
... 50 Hz supply. A non-inductive resistor under the same conditions takes 12 amperes. If the two are connected in series and placed across the same supply, find the current taken. If now the frequency is reduced to 40 Hz, the voltage being maintained constant, find the current taken. 4. A heater is req ...
Power Point
... nonohmic An ohmic device The resistance is constant over a wide range of voltages The relationship between current and voltage is linear The slope is related to the resistance ...
... nonohmic An ohmic device The resistance is constant over a wide range of voltages The relationship between current and voltage is linear The slope is related to the resistance ...
Basic Circuit Ideas
... potential” is required (voltage) . The Current (I) which flows in a conductor is proportional to this Voltage (V). The Resistance of the circuit also influences the flow of charge. Ohm’s Law: V = I R R = resistance = ohms Ω ...
... potential” is required (voltage) . The Current (I) which flows in a conductor is proportional to this Voltage (V). The Resistance of the circuit also influences the flow of charge. Ohm’s Law: V = I R R = resistance = ohms Ω ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... 1. What happens to current if resistance is decreased? 2. What happens to current if voltage is decreased? 3. What happens to resistance if wire diameter is decreased? 4. What happens to resistance if wire length is decreased? 5. What happens to power if current is decreased (but voltage is constant ...
... 1. What happens to current if resistance is decreased? 2. What happens to current if voltage is decreased? 3. What happens to resistance if wire diameter is decreased? 4. What happens to resistance if wire length is decreased? 5. What happens to power if current is decreased (but voltage is constant ...
s4rs-electrical-circuit-components
... • Capacitance is the ability of something to store an electrical charge • Charge is a property of matter that causes it to experience a force (attraction or repulsion) when near other electrically charged matter. There are two types of electric charges—positive and negative. • Capacitance = Charge / ...
... • Capacitance is the ability of something to store an electrical charge • Charge is a property of matter that causes it to experience a force (attraction or repulsion) when near other electrically charged matter. There are two types of electric charges—positive and negative. • Capacitance = Charge / ...