Chapter 8 slideshow.notebook
... Current Electricity Current electricity: is when the electrons are controlled by moving along a path together. What is voltage? ...
... Current Electricity Current electricity: is when the electrons are controlled by moving along a path together. What is voltage? ...
Basic Circuits Notes
... Note: When we say “current”, we are referring to conventional current (mythical positive charges moving in our wires or circuit elements). In reality, it is the negatively charged electrons that are loosely bound in metal atoms that make up our wires and move in the opposite direction of conven ...
... Note: When we say “current”, we are referring to conventional current (mythical positive charges moving in our wires or circuit elements). In reality, it is the negatively charged electrons that are loosely bound in metal atoms that make up our wires and move in the opposite direction of conven ...
Lec_18-Thyristors
... anode and cathode, are across the full four layers, and the control terminal, called the gate, is attached to p-type material near to the cathode. ...
... anode and cathode, are across the full four layers, and the control terminal, called the gate, is attached to p-type material near to the cathode. ...
OHM`S LAW Objectives: a. To find the unknown resistance of an
... Where, “A” is area of cross-section of the wire of length “l” Experiments: Part 1: Finding the value of R1 In this exercise you will apply different potential differences across an ohmic resistor and measure the corresponding currents. The different potential difference are created through the disch ...
... Where, “A” is area of cross-section of the wire of length “l” Experiments: Part 1: Finding the value of R1 In this exercise you will apply different potential differences across an ohmic resistor and measure the corresponding currents. The different potential difference are created through the disch ...
Thyristors Introduction & Characteristics
... anode and cathode, are across the full four layers, and the control terminal, called the gate, is attached to p-type material near to the cathode. ...
... anode and cathode, are across the full four layers, and the control terminal, called the gate, is attached to p-type material near to the cathode. ...
SPH 4A - mackenziekim
... 1. From where does the word magnet originate? 2. Draw domains in a highly magnetic bar of steel. Describe the domain theory and how it is used to explain what is created when a bar magnet is broken in half. 3. Sketch the pattern of the magnetic field around: a) a bar magnet b) an electromagnet 4. Wh ...
... 1. From where does the word magnet originate? 2. Draw domains in a highly magnetic bar of steel. Describe the domain theory and how it is used to explain what is created when a bar magnet is broken in half. 3. Sketch the pattern of the magnetic field around: a) a bar magnet b) an electromagnet 4. Wh ...
KidWind Kit Inventory List:
... Basic Electricity understandings and safety: • Electrons flow from negative to positive • Generally (in DC circuits) red is positive and black is negative • Some materials (insulators) do not share or release electrons easily – they have high resistance; Conductors easily share electrons and hav ...
... Basic Electricity understandings and safety: • Electrons flow from negative to positive • Generally (in DC circuits) red is positive and black is negative • Some materials (insulators) do not share or release electrons easily – they have high resistance; Conductors easily share electrons and hav ...
8.1 Reading Notes
... A waterwheel turns when a current of water exerts a force on it. _______________ ____________ is what makes an electric motor turn or an electric stove heat up. Electric current is measured in _____________ in honor of Andre-Marie Ampere. Electric current can carry a great deal of _____________. An ...
... A waterwheel turns when a current of water exerts a force on it. _______________ ____________ is what makes an electric motor turn or an electric stove heat up. Electric current is measured in _____________ in honor of Andre-Marie Ampere. Electric current can carry a great deal of _____________. An ...
Electromagnetism PowerPoint
... The metal which makes up a light bulb filament or stovetop eye has a high electrical resistance. This causes light and heat to be given off. ...
... The metal which makes up a light bulb filament or stovetop eye has a high electrical resistance. This causes light and heat to be given off. ...
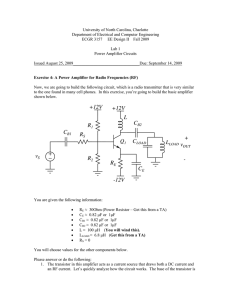
Signal Resistance of the Current Mirror
... 6.3 V; it would be much better if it were zero! Several methods exist of making the quiescent value zero. 1. Take the output via a capacitor. This is a good solution for an a.c. amplifier, but it will not work for d.c. or indeed slow a.c. Anyone who has tried to measure slow signals on an oscillosco ...
... 6.3 V; it would be much better if it were zero! Several methods exist of making the quiescent value zero. 1. Take the output via a capacitor. This is a good solution for an a.c. amplifier, but it will not work for d.c. or indeed slow a.c. Anyone who has tried to measure slow signals on an oscillosco ...
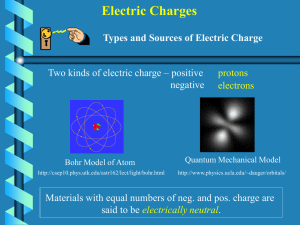
Physics 242 2 Electric Charges (1)
... RESISTIVITY RESISTIVITY: When electric charge flows through a circuit it encounters electrical RESISTANCE. The resistance of a metal conductor or this opposition property of a conductor is called as resistivity. ...
... RESISTIVITY RESISTIVITY: When electric charge flows through a circuit it encounters electrical RESISTANCE. The resistance of a metal conductor or this opposition property of a conductor is called as resistivity. ...
Electricity
... 1. _______________:the transfer of charge without contact between materials. 2. _________________:a property that causes subatomic particles such as protons and electrons to attract or repel each other. *An excess or shortage of electrons produces a net electric charge. 3. __________________: potent ...
... 1. _______________:the transfer of charge without contact between materials. 2. _________________:a property that causes subatomic particles such as protons and electrons to attract or repel each other. *An excess or shortage of electrons produces a net electric charge. 3. __________________: potent ...
Key for Spring Final Exam
... Current = total charge/time 9. What is the equation relating current, voltage, and resistance? Current = voltage/resistance 10. What are four factors that affect resistance of a wire? a. _______material it’s made of___________________________ b. ____length________ c. ____cross-sectional area (thickn ...
... Current = total charge/time 9. What is the equation relating current, voltage, and resistance? Current = voltage/resistance 10. What are four factors that affect resistance of a wire? a. _______material it’s made of___________________________ b. ____length________ c. ____cross-sectional area (thickn ...
electric current - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... A chemical reaction facilitated by an electrolyte causes electrons to move internally from one terminal of the battery (one type of metal) to the other (a different type of metal). This difference in charges produces voltage. Positive end (cathode) loses electrons Negative end (anode) gains electron ...
... A chemical reaction facilitated by an electrolyte causes electrons to move internally from one terminal of the battery (one type of metal) to the other (a different type of metal). This difference in charges produces voltage. Positive end (cathode) loses electrons Negative end (anode) gains electron ...
Chapter 16 Practice Test #2
... ____ 12. Resistance is caused by a. internal friction. c. proton charge. b. electron charge. d. a heat source. ____ 13. The SI unit of resistance is the a. volt. c. ohm. b. ampere. d. joule. ____ 14. Whether or not charges will move in a material depends partly on how tightly _____ are held in the ...
... ____ 12. Resistance is caused by a. internal friction. c. proton charge. b. electron charge. d. a heat source. ____ 13. The SI unit of resistance is the a. volt. c. ohm. b. ampere. d. joule. ____ 14. Whether or not charges will move in a material depends partly on how tightly _____ are held in the ...
Resistance Exercises
... windows. Each window has length L, width W, and thickness Δx. How can the architect reduce the heat flow rate through each window? (a) us a material with a higher thermal conductivity (b) increase L and /or W (c) increase Δx (d) all of the above 22. A wall has three layers with resistances of R1, R2 ...
... windows. Each window has length L, width W, and thickness Δx. How can the architect reduce the heat flow rate through each window? (a) us a material with a higher thermal conductivity (b) increase L and /or W (c) increase Δx (d) all of the above 22. A wall has three layers with resistances of R1, R2 ...
Slide 1
... Linear Circuit obeys Ohm’s Law (i.e. v α i or v = Ri) if the i or v in any part of the circuit is sinusoidal, the i and v in every other part of the circuit is sinusoidal and of the same frequency Non-linear circuits do not obey Ohm’s Law. Circuit Elements: Active – supply energy: voltage or ...
... Linear Circuit obeys Ohm’s Law (i.e. v α i or v = Ri) if the i or v in any part of the circuit is sinusoidal, the i and v in every other part of the circuit is sinusoidal and of the same frequency Non-linear circuits do not obey Ohm’s Law. Circuit Elements: Active – supply energy: voltage or ...
View File
... as that of a DC current of the same value The maximum current occurs for a small amount of time ...
... as that of a DC current of the same value The maximum current occurs for a small amount of time ...