Introduction
... 1.2 History of operating systems 1.3 The operating system zoo 1.4 Computer hardware review 1.5 Operating system concepts 1.6 System calls 1.7 Operating system structure ...
... 1.2 History of operating systems 1.3 The operating system zoo 1.4 Computer hardware review 1.5 Operating system concepts 1.6 System calls 1.7 Operating system structure ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... 1.5 Operating system concepts 1.6 System calls 1.7 Operating system structure ...
... 1.5 Operating system concepts 1.6 System calls 1.7 Operating system structure ...
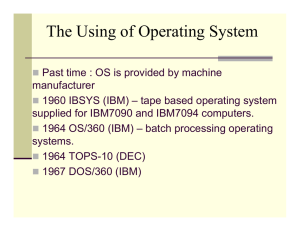
Introduction Chapter 1 Introduction What is an Operating System
... (a) Two directories before linking /usr/jim/memo to ast's directory (b) The same directories after linking ...
... (a) Two directories before linking /usr/jim/memo to ast's directory (b) The same directories after linking ...
Operating Systems I Supervision Exercises
... (ii ) For two concurrently-running instances of the same program, each with code, data, heap and stack segments, which segments might benefit from copy-on-write? In what circumstances, if any, could these instead be shared read-only? ...
... (ii ) For two concurrently-running instances of the same program, each with code, data, heap and stack segments, which segments might benefit from copy-on-write? In what circumstances, if any, could these instead be shared read-only? ...
Architectural Support for Operating Systems
... • In the idle loop: – OS executes an infinite loop (UNIX) – OS performs some system management & profiling – OS halts the processor and enter in low-power mode (notebooks) – OS computes some function (DEC’s VMS on VAX computed Pi) • OS wakes up on: – interrupts from hardware devices – traps from use ...
... • In the idle loop: – OS executes an infinite loop (UNIX) – OS performs some system management & profiling – OS halts the processor and enter in low-power mode (notebooks) – OS computes some function (DEC’s VMS on VAX computed Pi) • OS wakes up on: – interrupts from hardware devices – traps from use ...
Operating System Organization Purpose of an OS
... use of resources •Processor Modes - hardware mode bit is used to distinguish between OS and user instructions •Kernels - most critical part of OS placed in kernel (trusted software module) •Method of invoking system service - calling a system function or sending a message to a system process ...
... use of resources •Processor Modes - hardware mode bit is used to distinguish between OS and user instructions •Kernels - most critical part of OS placed in kernel (trusted software module) •Method of invoking system service - calling a system function or sending a message to a system process ...
UNICOS, FORTRAN 90, NQS
... between the user and the kernel. The shell interprets commands and command options entered at the command-line prompt and initiates the appropriate actions in the kernel. – UNICOS supports two shells: • The Korn shell (default) • The C shell ...
... between the user and the kernel. The shell interprets commands and command options entered at the command-line prompt and initiates the appropriate actions in the kernel. – UNICOS supports two shells: • The Korn shell (default) • The C shell ...
BAB 8 SISTEM PENGOPERASIAN
... programs known as memory managers when PC main memories started to be routinely larger than 640 KB in the late 1980s. These move portions of the operating system outside their normal locations in order to increase the amount of conventional or quasi-conventional memory available to other applicati ...
... programs known as memory managers when PC main memories started to be routinely larger than 640 KB in the late 1980s. These move portions of the operating system outside their normal locations in order to increase the amount of conventional or quasi-conventional memory available to other applicati ...
The SAS System for the UNIX Environment
... Many members of /usr/group felt that not all standards issues had been addressed. Thus, in 1985/usr/group Standards Committee merged with the newly formed IEEE P1 003 Committee and adopted Draft 1 as the new IEEE standard called POSIX (Portable Operating System Interface for Computer Environments). ...
... Many members of /usr/group felt that not all standards issues had been addressed. Thus, in 1985/usr/group Standards Committee merged with the newly formed IEEE P1 003 Committee and adopted Draft 1 as the new IEEE standard called POSIX (Portable Operating System Interface for Computer Environments). ...
Allowable Process States - Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia
... – In the blocked state, the process cannot run until some external events have taken place. (Dagunduro) – A blocked process requests a resource that is not available at the moment, so it remains blocked until the resource it needs becomes available. (Nutt, 220). ...
... – In the blocked state, the process cannot run until some external events have taken place. (Dagunduro) – A blocked process requests a resource that is not available at the moment, so it remains blocked until the resource it needs becomes available. (Nutt, 220). ...
MS-DOS-&-PC-DOS-by-Lindsey-Buranych-Alan-Crouch
... – In the blocked state, the process cannot run until some external events have taken place. (Dagunduro) – A blocked process requests a resource that is not available at the moment, so it remains blocked until the resource it needs becomes available. (Nutt, 220). ...
... – In the blocked state, the process cannot run until some external events have taken place. (Dagunduro) – A blocked process requests a resource that is not available at the moment, so it remains blocked until the resource it needs becomes available. (Nutt, 220). ...
ppt
... of a process (program counter, call stack) from its other aspects (address space, open files, owner, etc.). And we will allow each {process / address space} to have multiple threads of control. • But for now – for simplicity and for historical reasons – consider each {process / address space} to hav ...
... of a process (program counter, call stack) from its other aspects (address space, open files, owner, etc.). And we will allow each {process / address space} to have multiple threads of control. • But for now – for simplicity and for historical reasons – consider each {process / address space} to hav ...
ISA_673-android_presentation_(1) - eee
... Operating Systems Security Exploring the Android Platform ...
... Operating Systems Security Exploring the Android Platform ...
Operating Systems
... Operating system must do some basic file operations: Create a file : Allocate space, record name and location Writing a file: Data entry Reading a file Deleting a file: Release file space Truncate a file: Erase user content data in a file ...
... Operating system must do some basic file operations: Create a file : Allocate space, record name and location Writing a file: Data entry Reading a file Deleting a file: Release file space Truncate a file: Erase user content data in a file ...
Introduction to Linux/Unix
... Permissions are set at three user levels: owner, u (u from user) group member, g and World, o (All Others outside owner and owner’s group). ALL, a i.e u+g+o ...
... Permissions are set at three user levels: owner, u (u from user) group member, g and World, o (All Others outside owner and owner’s group). ALL, a i.e u+g+o ...
Layer 1 Process Management
... •All the user processes in the whole system are part of a single tree with init at the root. •During the initialization phase, the kernel starts the task, and then the memory manager, the file system, and any other servers that run in layer. When all of these have run and initialized themselves, the ...
... •All the user processes in the whole system are part of a single tree with init at the root. •During the initialization phase, the kernel starts the task, and then the memory manager, the file system, and any other servers that run in layer. When all of these have run and initialized themselves, the ...
BBA IInd SEMESTER EXAMINATION 2008-09
... First-come, First-served (run in order 10,6, 2, 4, 8) iv) Shortest job first For (i) assume that the system is multi-programmed, and to each job gets share of the CPU. For (ii) through (iv) assume that only one job at a time runs, until finishes. All jobs are completely CPU bound. ...
... First-come, First-served (run in order 10,6, 2, 4, 8) iv) Shortest job first For (i) assume that the system is multi-programmed, and to each job gets share of the CPU. For (ii) through (iv) assume that only one job at a time runs, until finishes. All jobs are completely CPU bound. ...
Os 2marks - Erode Sengunthar Engineering College
... If a process does not have enough memory for its working set, it will thrash. Providing enough frames to each process to avoid thrashing may require process swapping and scheduling 6. What Are The File Attributes? Name, type, location, size, protection, time, date and user identification these are t ...
... If a process does not have enough memory for its working set, it will thrash. Providing enough frames to each process to avoid thrashing may require process swapping and scheduling 6. What Are The File Attributes? Name, type, location, size, protection, time, date and user identification these are t ...
Chapter 2 Operating
... writing a simple program to read data from one file and copy them to another file. The first input that the program will need is the names of the two files: the input file and the output file. These names can be specified in many ways, depending on the operating-system design. Once the two file name ...
... writing a simple program to read data from one file and copy them to another file. The first input that the program will need is the names of the two files: the input file and the output file. These names can be specified in many ways, depending on the operating-system design. Once the two file name ...
XOberon Operating System
... managed differently based on its characteristics and is tuned for optimal performance. Many of the memory related problems are now solved by this memory management scheme, bringing reliability and more functionality to the system. ...
... managed differently based on its characteristics and is tuned for optimal performance. Many of the memory related problems are now solved by this memory management scheme, bringing reliability and more functionality to the system. ...
after_introduction
... • All the runnable software on a computer, including the OS, is organized into a number of sequential processes (or processes in short) ...
... • All the runnable software on a computer, including the OS, is organized into a number of sequential processes (or processes in short) ...
PPTX - Duke Computer Science
... architecture—is nearly universal. Although aspects of this architecture, such as dynamic code loading and shared memory, were not in Multics’ immediate successors (early versions of UNIX [35] or early PC operating systems), today’s systems, such as FreeBSD, Linux, Solaris, and Windows, embrace …the ...
... architecture—is nearly universal. Although aspects of this architecture, such as dynamic code loading and shared memory, were not in Multics’ immediate successors (early versions of UNIX [35] or early PC operating systems), today’s systems, such as FreeBSD, Linux, Solaris, and Windows, embrace …the ...
IES VILLABLANCA TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT Name
... 3.When the computer has to react within a guaranteed time to an input, which type of operating system is the best? multi-tasking real-time processing batch processing 4.Which type of operating system allows multiple tasks to run at the same time, each taking turns using the resources of the computer ...
... 3.When the computer has to react within a guaranteed time to an input, which type of operating system is the best? multi-tasking real-time processing batch processing 4.Which type of operating system allows multiple tasks to run at the same time, each taking turns using the resources of the computer ...