Operating Systems Security
... more difficult to maintain, even in the developed world, but with the advent of the information age, our information and the infrastructure via which it is stored, processed and communicated, is increasingly important to control. The security of our information and its supporting infrastructure is t ...
... more difficult to maintain, even in the developed world, but with the advent of the information age, our information and the infrastructure via which it is stored, processed and communicated, is increasingly important to control. The security of our information and its supporting infrastructure is t ...
Memory Mapped Files
... The programmer returns a block to the Heap Manager free list by calling the “free” method on a pointer previously returned by malloc. When a block is freed, it is marked as available. It is erroneous for the application to ever use the pointer to that block again for any purpose. The freed blo ...
... The programmer returns a block to the Heap Manager free list by calling the “free” method on a pointer previously returned by malloc. When a block is freed, it is marked as available. It is erroneous for the application to ever use the pointer to that block again for any purpose. The freed blo ...
II. Fast Cell Site Selection - Communications and signal processing
... During FCSS decision, the mobile signals the present serving BSR and the future serving BSR for acknowledgement of switching decision. The mobile, the present and future BSRs then synchronize data and protocol states before the end of FCSS action so that the future BSR can properly resume transmissi ...
... During FCSS decision, the mobile signals the present serving BSR and the future serving BSR for acknowledgement of switching decision. The mobile, the present and future BSRs then synchronize data and protocol states before the end of FCSS action so that the future BSR can properly resume transmissi ...
Operating Systems 2230 Lecture 7: Uniprocessor scheduling
... • more judiciously based on the expected resource requirements (CPU time and memory) of the new processes. Supercomputing environments still employ batch scheduling in which longrunning tasks will be scheduled so as to minimise their impact (late at night). Some operating systems may also admit new ...
... • more judiciously based on the expected resource requirements (CPU time and memory) of the new processes. Supercomputing environments still employ batch scheduling in which longrunning tasks will be scheduled so as to minimise their impact (late at night). Some operating systems may also admit new ...
Processes - Kent State University
... an (almost) identical copy of parent (same code, same data, etc.) • parent – the original process parent can either wait for the child to complete, or continue executing in parallel (concurrently) with the child parent does not terminate until the child does In UNIX, a process creates a child ...
... an (almost) identical copy of parent (same code, same data, etc.) • parent – the original process parent can either wait for the child to complete, or continue executing in parallel (concurrently) with the child parent does not terminate until the child does In UNIX, a process creates a child ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE)
... days people like to stay connected with each other all over the world and also share resources of different places with help of wireless technology. Mobile Ad-Hoc NETwork(MANET) are rapidly expanding in area of Mobile mobility very importantly[1]. Mobile Ad-hoc NETwork as a rule has a dynamic behavi ...
... days people like to stay connected with each other all over the world and also share resources of different places with help of wireless technology. Mobile Ad-Hoc NETwork(MANET) are rapidly expanding in area of Mobile mobility very importantly[1]. Mobile Ad-hoc NETwork as a rule has a dynamic behavi ...
Introductory Guide to Z
... inclusion process is initiated on the Primary Controller first then activating the function button or command on the node itself. When an un-initialized node is activated, the Primary Controller will assign it the Home ID and Node ...
... inclusion process is initiated on the Primary Controller first then activating the function button or command on the node itself. When an un-initialized node is activated, the Primary Controller will assign it the Home ID and Node ...
Analysis of current and potential sensor network technologies and
... data is offering a broad range of possibilities in many different fields of applications, ranging from fire detection in wide forest areas, to surveillance systems, exchange of information in mobile networks, or infrastructures for medical care. This increasing intere ...
... data is offering a broad range of possibilities in many different fields of applications, ranging from fire detection in wide forest areas, to surveillance systems, exchange of information in mobile networks, or infrastructures for medical care. This increasing intere ...
Lecture 15 - Faculty Website Directory
... – Windows contains a hardware abstraction layer(HAL): • A dynamic-link library that provides isolation from hardware dependencies furnished by different venders. • The HAL abstracts hardware, such as caches, with a layer of low-level software so that higher-level code need not change when moving fro ...
... – Windows contains a hardware abstraction layer(HAL): • A dynamic-link library that provides isolation from hardware dependencies furnished by different venders. • The HAL abstracts hardware, such as caches, with a layer of low-level software so that higher-level code need not change when moving fro ...
No Slide Title
... Executive, which runs in protected mode, provides the basic system services. On top of the executive, several server subsystems operate in user mode. Modular structure allows additional environmental subsystems to be added without affecting the executive. Portability — 2000 can be moved from ...
... Executive, which runs in protected mode, provides the basic system services. On top of the executive, several server subsystems operate in user mode. Modular structure allows additional environmental subsystems to be added without affecting the executive. Portability — 2000 can be moved from ...
ch22
... Executive, which runs in protected mode, provides the basic system services. On top of the executive, several server subsystems operate in user mode. Modular structure allows additional environmental subsystems to be added without affecting the executive. Portability —XP can be moved from on ...
... Executive, which runs in protected mode, provides the basic system services. On top of the executive, several server subsystems operate in user mode. Modular structure allows additional environmental subsystems to be added without affecting the executive. Portability —XP can be moved from on ...
Low-Cost Driver Assistance Using ZigBee®/IEEE® 802.15.4
... monitored. Since these applications will require intensive data logging, fast, high-endurance, non-volatile memory with error correction capability should be included in the waypoint units. The solution could also be used to track stolen or fugitive ...
... monitored. Since these applications will require intensive data logging, fast, high-endurance, non-volatile memory with error correction capability should be included in the waypoint units. The solution could also be used to track stolen or fugitive ...
Omni-Kernel: An Operating System Architecture for Pervasive Monitoring and Scheduling
... between shared and core-specific state allows the framework to automate efficient multi-core scheduling of messages. Sharing typically occurs only when messages are sent by one core and queued for processing on another, or when a scheduler inspects shared state to select a core for an affinity label ...
... between shared and core-specific state allows the framework to automate efficient multi-core scheduling of messages. Sharing typically occurs only when messages are sent by one core and queued for processing on another, or when a scheduler inspects shared state to select a core for an affinity label ...
Multiprocessing with the Exokernel Operating System - PDOS
... hinder certain application’s performance. The exokernel operating system addresses this problem by applying the end-to-end argument to operating systems: the kernel only multiplexes hardware and protects resources, leaving all software abstractions and resource management policies for user-level app ...
... hinder certain application’s performance. The exokernel operating system addresses this problem by applying the end-to-end argument to operating systems: the kernel only multiplexes hardware and protects resources, leaving all software abstractions and resource management policies for user-level app ...
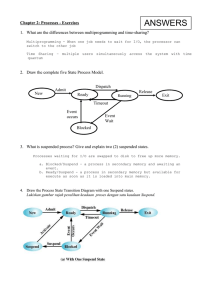
Chapter 2: Processes - Exercises
... within a process is called a thread. Threads within a single ...
... within a process is called a thread. Threads within a single ...
process management
... create and destroy than process. (100 times faster ) Performance: when there is substantial computing and also substantial I/O, having threads allows activities to overlap, thus speed up the application. Threads are useful on systems with multiple CPUs, where real parallelism is possible. ...
... create and destroy than process. (100 times faster ) Performance: when there is substantial computing and also substantial I/O, having threads allows activities to overlap, thus speed up the application. Threads are useful on systems with multiple CPUs, where real parallelism is possible. ...
Module 4: Processes
... So far, process has a single thread of execution Consider having multiple program counters per process ...
... So far, process has a single thread of execution Consider having multiple program counters per process ...
Brief Announcement: Atomic Consistency and Partition
... Impossible to accurately detect process failures ...
... Impossible to accurately detect process failures ...
ppt
... • General purpose operating systems handling diverse set of tasks – Conventional best-effort with low response time + Ex: word processor ...
... • General purpose operating systems handling diverse set of tasks – Conventional best-effort with low response time + Ex: word processor ...
Operating Systems for Reconfigurable Systems
... The challenges in developing an OS for reconfigurable systems ...
... The challenges in developing an OS for reconfigurable systems ...
Distributed operating system
A distributed operating system is a software over a collection of independent, networked, communicating, and physically separate computational nodes. Each individual node holds a specific software subset of the global aggregate operating system. Each subset is a composite of two distinct service provisioners. The first is a ubiquitous minimal kernel, or microkernel, that directly controls that node’s hardware. Second is a higher-level collection of system management components that coordinate the node's individual and collaborative activities. These components abstract microkernel functions and support user applications.The microkernel and the management components collection work together. They support the system’s goal of integrating multiple resources and processing functionality into an efficient and stable system. This seamless integration of individual nodes into a global system is referred to as transparency, or single system image; describing the illusion provided to users of the global system’s appearance as a single computational entity.