How to make Frequency plots with Pspice
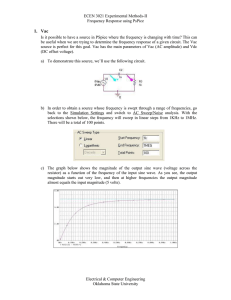
... In this particular figure, the top plot is the ratio of the amplitude of the output voltage to the amplitude of the source voltage (gain), while the bottom plot is the phase difference between the input voltage and the output voltage. ...
... In this particular figure, the top plot is the ratio of the amplitude of the output voltage to the amplitude of the source voltage (gain), while the bottom plot is the phase difference between the input voltage and the output voltage. ...
Three phase fully controlled converters are very popular in many
... Three phase fully controlled converters are very popular in many industrial applications particularly in situations where power regeneration from the dc side is essential. It can handle reasonably high power and has acceptable input and output harmonic distortion. The configuration also lends itself ...
... Three phase fully controlled converters are very popular in many industrial applications particularly in situations where power regeneration from the dc side is essential. It can handle reasonably high power and has acceptable input and output harmonic distortion. The configuration also lends itself ...
Voltage Amplifier
... OpAmp transfer characteristic is nonlinear, which causes clipping at output voltage if input signal goes out of linear range The range of output voltages before clipping occurs depends on the type of OpAmp, the load resistance and power supply voltage. Output current limit: real OpAmp has a maxi ...
... OpAmp transfer characteristic is nonlinear, which causes clipping at output voltage if input signal goes out of linear range The range of output voltages before clipping occurs depends on the type of OpAmp, the load resistance and power supply voltage. Output current limit: real OpAmp has a maxi ...
DN351 - Versatile Micropower Voltage Reference Provides Resistor Programmable Output from 0.4V to 18V
... signal level, or even provide a controlled negative signal conversion range within a positive-only input window. Figure 3 shows a single supply powered LT1990 difference amp sensing a bidirectional motor current. The LT6650 reference is configured to provide an optimal REF input level for the circui ...
... signal level, or even provide a controlled negative signal conversion range within a positive-only input window. Figure 3 shows a single supply powered LT1990 difference amp sensing a bidirectional motor current. The LT6650 reference is configured to provide an optimal REF input level for the circui ...
SP8716/8/9 520MHz LOW CURRENT TWO-MODULUS DIVIDERS
... *Tested as specified in table of Electrical Characteristics ...
... *Tested as specified in table of Electrical Characteristics ...
quick start guide for demonstration circuit 956 ltc2485 description
... IN+ to IN- and note the indicated voltage. Reverse the polarity; the indicated voltage will typically be within a few microvolts of the first reading multiplied by –1. INPUT NORMAL MODE REJECTION The LTC2485’s SINC4 digital filter is trimmed to reject 50 or 60Hz line noise when operated with the int ...
... IN+ to IN- and note the indicated voltage. Reverse the polarity; the indicated voltage will typically be within a few microvolts of the first reading multiplied by –1. INPUT NORMAL MODE REJECTION The LTC2485’s SINC4 digital filter is trimmed to reject 50 or 60Hz line noise when operated with the int ...
a-d conversion
... Analog to Digital Conversion • In this process, we convert an analog voltage into a number • Computers store numbers in “bits” • Typically use a 12 bit converter - converts each input voltage into some number between 0 and 4095 (212-1) • Maximum sample rate - if 100 kHz – takes 10 sec to perform t ...
... Analog to Digital Conversion • In this process, we convert an analog voltage into a number • Computers store numbers in “bits” • Typically use a 12 bit converter - converts each input voltage into some number between 0 and 4095 (212-1) • Maximum sample rate - if 100 kHz – takes 10 sec to perform t ...
Document
... on-off cycle, in the SC-buck topology there is a need to distribute the switching phases to satisfy the charge-balance of the flying capacitor. The new control method hybrids a voltage-mode small-signal controller for steady-state operation and a non-linear, state-plane based transient-mode control ...
... on-off cycle, in the SC-buck topology there is a need to distribute the switching phases to satisfy the charge-balance of the flying capacitor. The new control method hybrids a voltage-mode small-signal controller for steady-state operation and a non-linear, state-plane based transient-mode control ...
UniMasr.com_109
... Bulky inductors for low frequencies (not suitable for integration) RC filters cannot realize Q > 0.5 Filters parameters are coupled (changing one component can change different filter parameters) Cannot realize ideal integrator ...
... Bulky inductors for low frequencies (not suitable for integration) RC filters cannot realize Q > 0.5 Filters parameters are coupled (changing one component can change different filter parameters) Cannot realize ideal integrator ...
ECE1250F14_HW2_2p1soln
... Any network consisting of only resistors between two terminals may be replaced by a single equivalent resistor. ...
... Any network consisting of only resistors between two terminals may be replaced by a single equivalent resistor. ...
BDS-MF Generator
... The BDS-MF is a 40 kHz plasma generator with max power delivery of 5kW or10 kW is specifically designed for plasma excitation on PECVD or plasma cleaning applications. The unit is capable of delivery up to 10kW at 7000V RMS output. The output is balanced type, capable to drive 2 symmetrical electrode ...
... The BDS-MF is a 40 kHz plasma generator with max power delivery of 5kW or10 kW is specifically designed for plasma excitation on PECVD or plasma cleaning applications. The unit is capable of delivery up to 10kW at 7000V RMS output. The output is balanced type, capable to drive 2 symmetrical electrode ...
Integrating ADC
An integrating ADC is a type of analog-to-digital converter that converts an unknown input voltage into a digital representation through the use of an integrator. In its most basic implementation, the unknown input voltage is applied to the input of the integrator and allowed to ramp for a fixed time period (the run-up period). Then a known reference voltage of opposite polarity is applied to the integrator and is allowed to ramp until the integrator output returns to zero (the run-down period). The input voltage is computed as a function of the reference voltage, the constant run-up time period, and the measured run-down time period. The run-down time measurement is usually made in units of the converter's clock, so longer integration times allow for higher resolutions. Likewise, the speed of the converter can be improved by sacrificing resolution.Converters of this type can achieve high resolution, but often do so at the expense of speed. For this reason, these converters are not found in audio or signal processing applications. Their use is typically limited to digital voltmeters and other instruments requiring highly accurate measurements.























