Lecture3-os-support
... Bad thing: crossing protection domains is expensive. Why? • So is this the best solution? ...
... Bad thing: crossing protection domains is expensive. Why? • So is this the best solution? ...
The Nachos Instructional Operating System
... of its predecessor systems, applications, the operating system kernel, and the hardware simulator run together in a normal UNIX process.2 In this UNIX process, at the lowest level, Nachos simulates the behavior of a standard uniprocessor workstation, including CPU instruction execution, address tran ...
... of its predecessor systems, applications, the operating system kernel, and the hardware simulator run together in a normal UNIX process.2 In this UNIX process, at the lowest level, Nachos simulates the behavior of a standard uniprocessor workstation, including CPU instruction execution, address tran ...
operating systems - Dhoto-Pens
... The goal is protecting the Operating System and others from malicious or ignorant users. The User/Supervisor Mode and privileged instructions. Concurrent threads might interfere with others. This leads to protection of resources by user/supervisor mode. These resources include: I/O Define I/O instru ...
... The goal is protecting the Operating System and others from malicious or ignorant users. The User/Supervisor Mode and privileged instructions. Concurrent threads might interfere with others. This leads to protection of resources by user/supervisor mode. These resources include: I/O Define I/O instru ...
a login shell
... • The .cshrc file is read any time a C shell starts • If you write a csh script, you should probably use the -f option to keep C shell scripts from reading .cshrc. • The .login file is read when you start a login shell. In this file you can set: – Environment variables (which UNIX will pass to subsh ...
... • The .cshrc file is read any time a C shell starts • If you write a csh script, you should probably use the -f option to keep C shell scripts from reading .cshrc. • The .login file is read when you start a login shell. In this file you can set: – Environment variables (which UNIX will pass to subsh ...
Solution to Lab Project 2.1
... professionals with advanced knowledge of DOS. Depends on HIMEM.SYS being loaded. ...
... professionals with advanced knowledge of DOS. Depends on HIMEM.SYS being loaded. ...
NP11_IM_Chapter04
... about operating systems. What operating systems are available? Can they find good descriptions of how operating systems work? 2. Quick Quiz: _________ provides process and memory management services that allow two or more tasks, jobs, or programs to run simultaneously. (Answer: Multitasking.) Wi ...
... about operating systems. What operating systems are available? Can they find good descriptions of how operating systems work? 2. Quick Quiz: _________ provides process and memory management services that allow two or more tasks, jobs, or programs to run simultaneously. (Answer: Multitasking.) Wi ...
Solaris Operating Systems
... Each user account must be assigned a name. This name is used to identify the account for purposes such as electronic mail and logging into a machine Male it easy for people to recognize a user’s account name when sending e-mail, transferring files, and so on. ...
... Each user account must be assigned a name. This name is used to identify the account for purposes such as electronic mail and logging into a machine Male it easy for people to recognize a user’s account name when sending e-mail, transferring files, and so on. ...
ICS 143 - Introduction to Operating Systems
... Separate user from computer User submits card deck cards put on tape tape processed by operator output written to tape tape printed on printer ...
... Separate user from computer User submits card deck cards put on tape tape processed by operator output written to tape tape printed on printer ...
Test Bank Chapter Three (Operating Systems)
... 1. Explain the difference between application software and system software. ANSWER: System software provides the infrastructure required by the application software. It includes the operating system and utilities. Application software provides the unique functionality required to perform the particu ...
... 1. Explain the difference between application software and system software. ANSWER: System software provides the infrastructure required by the application software. It includes the operating system and utilities. Application software provides the unique functionality required to perform the particu ...
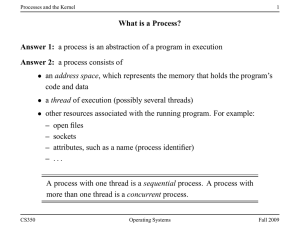
What is a Process? Answer 1: a process is an abstraction of a
... • multiprogramming means having multiple processes existing at the same time • most modern, general purpose operating systems support multiprogramming • all processes share the available hardware resources, with the sharing coordinated by the operating system: – Each process uses some of the availab ...
... • multiprogramming means having multiple processes existing at the same time • most modern, general purpose operating systems support multiprogramming • all processes share the available hardware resources, with the sharing coordinated by the operating system: – Each process uses some of the availab ...
Chapter 2: OS structure
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program Interface ...
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program Interface ...
Microsoft Office 2003
... operating system, which are not a threat to computers running UNIX or Linux. CLASSROOM ACTIVITIES 1. Class Discussion: Ask students to discuss their experiences with Microsoft Windows. Why do they think Windows is so popular? What are the strengths and weaknesses of Windows in their opinions? What a ...
... operating system, which are not a threat to computers running UNIX or Linux. CLASSROOM ACTIVITIES 1. Class Discussion: Ask students to discuss their experiences with Microsoft Windows. Why do they think Windows is so popular? What are the strengths and weaknesses of Windows in their opinions? What a ...
Operating-System Structures
... concurrently, resources must be allocated to each of them Many types of resources - Some (such as CPU cycles, main memory, and file storage) may have special allocation code, others (such as I/O devices) may have general request and release code Accounting - To keep track of which users use how ...
... concurrently, resources must be allocated to each of them Many types of resources - Some (such as CPU cycles, main memory, and file storage) may have special allocation code, others (such as I/O devices) may have general request and release code Accounting - To keep track of which users use how ...
Specialized Execution Environments
... features required of a general purpose OS. (As demonstrated by user-space device drivers.) Writing the code for such dedicated “OS”es or programs does not necessarily require recreating device drivers. Most de- ...
... features required of a general purpose OS. (As demonstrated by user-space device drivers.) Writing the code for such dedicated “OS”es or programs does not necessarily require recreating device drivers. Most de- ...
6up-pdf - ETH Systems Group
... Create a C stack frame on the kernel stack Look up the syscall number in a jump table Call the function (e.g. read(), getpid(), open(), etc.) ...
... Create a C stack frame on the kernel stack Look up the syscall number in a jump table Call the function (e.g. read(), getpid(), open(), etc.) ...
PPT - UNL CSE
... Tom is deploying a new server program for his client. During the field test, he notices that its performance is below his expectation. How would he identify the main causes? A company is planning to upgrade the server systems. You are asked to analyze which systems and which configurations will ...
... Tom is deploying a new server program for his client. During the field test, he notices that its performance is below his expectation. How would he identify the main causes? A company is planning to upgrade the server systems. You are asked to analyze which systems and which configurations will ...
Introduction
... The Program Status Word (PSW) contains the collection of code bits which are set by comparison instructions, the CPU priority and mode (user or kernel), and other control bits. The PSW is called flags register on Intel 8086 processor. Instructions that use registers to store their data execute much ...
... The Program Status Word (PSW) contains the collection of code bits which are set by comparison instructions, the CPU priority and mode (user or kernel), and other control bits. The PSW is called flags register on Intel 8086 processor. Instructions that use registers to store their data execute much ...
ErgoSoft RIP recommended System configuration
... Raster performance of the ErgoSoft RIP-Server mainly depends on the Processor. To achieve high raster speeds, it is recommended to have a high tact frequency on the individual processor cores rather than a large amount of cores, as the RIP-Server process profits most from a high performing individua ...
... Raster performance of the ErgoSoft RIP-Server mainly depends on the Processor. To achieve high raster speeds, it is recommended to have a high tact frequency on the individual processor cores rather than a large amount of cores, as the RIP-Server process profits most from a high performing individua ...
Operating Systems
... • File Compression is the shrinking of a file into a smaller file • In order to use a compressed file, it must be decompressed back to its original size • The file size is controlled by setting a file compression ratio. A file compression ratio determines how small the compressed file will be • WinZ ...
... • File Compression is the shrinking of a file into a smaller file • In order to use a compressed file, it must be decompressed back to its original size • The file size is controlled by setting a file compression ratio. A file compression ratio determines how small the compressed file will be • WinZ ...