Answers to Even-numbered Exercises
... A utility (program), sometimes referred to as a command, performs a task that is frequently related to the operating system. A utility is simpler than an application program, although there is no clear line separating the two. Linux distributions include many utilities. You can also download many ut ...
... A utility (program), sometimes referred to as a command, performs a task that is frequently related to the operating system. A utility is simpler than an application program, although there is no clear line separating the two. Linux distributions include many utilities. You can also download many ut ...
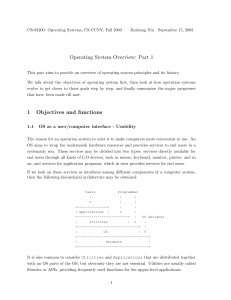
Operating System Overview: Part 1 1 Objectives and functions
... systematic way. These services may be divided into two types: services directly available for end users through all kinds of I/O devices, such as mouse, keyboard, monitor, printer, and so on; and services for application programs, which in turn provides services for end users. If we look on these se ...
... systematic way. These services may be divided into two types: services directly available for end users through all kinds of I/O devices, such as mouse, keyboard, monitor, printer, and so on; and services for application programs, which in turn provides services for end users. If we look on these se ...
PPT - Surendar Chandra
... details and perform resource allocation. They are designed to be portable. Hence, they define interfaces (e.g. system calls). Abstractions add overhead and so the OS is general purpose but not optimized for a specific scenario – Data bases - need access to hard drive – Movie player – need access to ...
... details and perform resource allocation. They are designed to be portable. Hence, they define interfaces (e.g. system calls). Abstractions add overhead and so the OS is general purpose but not optimized for a specific scenario – Data bases - need access to hard drive – Movie player – need access to ...
CTE214 Operating Systems Syllabus
... On successful completion of this course: • Students should apply key operating system design concepts (e.g. processes, threads, paging, etc.) to develop successful software systems. • Students should understand and discriminate the strengths and weaknesses of scheduling policies, interprocess commun ...
... On successful completion of this course: • Students should apply key operating system design concepts (e.g. processes, threads, paging, etc.) to develop successful software systems. • Students should understand and discriminate the strengths and weaknesses of scheduling policies, interprocess commun ...
Chapter 1: A Tour of Computer Systems
... (local disks) Local disks hold files retrieved from disks on remote network servers. ...
... (local disks) Local disks hold files retrieved from disks on remote network servers. ...
Test1_soln
... a. ULTs are cheaper to create and run than processes. b. Communication overhead between two ULTs is much smaller than between processes. c. ULTs are transparent to Kernel. Ans. (a) ULTs pertain to a single process, and therefore they share the same address space. Consequently, the overhead to create ...
... a. ULTs are cheaper to create and run than processes. b. Communication overhead between two ULTs is much smaller than between processes. c. ULTs are transparent to Kernel. Ans. (a) ULTs pertain to a single process, and therefore they share the same address space. Consequently, the overhead to create ...
Operating Systems Overview
... • Under an OS such as Windows, you see a familiar interface no matter what programs you use. • In a GUI, each program opens and runs in a separate window—a frame that presents the program and its ...
... • Under an OS such as Windows, you see a familiar interface no matter what programs you use. • In a GUI, each program opens and runs in a separate window—a frame that presents the program and its ...
COS 318: Operating Systems OS Structures and System Calls
... Jump to kernel, execute handler 0 in interrupt vector l Handler 0 sends SIGFPE to process l Kernel returns control to process l Process has outstanding signal l Did process register SIGFPE handler? l ...
... Jump to kernel, execute handler 0 in interrupt vector l Handler 0 sends SIGFPE to process l Kernel returns control to process l Process has outstanding signal l Did process register SIGFPE handler? l ...
Operating Systems
... A program that is loaded into memory and is 程序 executing is commonly referred to as a process. When a process executes, it typically executes for only a short time before it either finishes or needs to perform I/O. Rather than let the CPU sit idle when I/O takes place, the OS will rapidly switch the ...
... A program that is loaded into memory and is 程序 executing is commonly referred to as a process. When a process executes, it typically executes for only a short time before it either finishes or needs to perform I/O. Rather than let the CPU sit idle when I/O takes place, the OS will rapidly switch the ...
BAB 8 SISTEM PENGOPERASIAN
... The act of managing computer memory. The management of main memory is critical to the computer system. Virtual memory systems separate the memory addresses used by a process from actual physical addresses, allowing separation of processes and increasing the effectively available amount of RAM ...
... The act of managing computer memory. The management of main memory is critical to the computer system. Virtual memory systems separate the memory addresses used by a process from actual physical addresses, allowing separation of processes and increasing the effectively available amount of RAM ...
OPERATING SYSTEMS 2015-16 1 OPERATING SYSTEM
... Timesharing (multitasking) is logical extension in which CPU switches jobs so frequently that users can interact with each job while it is running, creating interactive computing Response time should be < 1 second Each user has at least one program executing in memory [process If several jobs ...
... Timesharing (multitasking) is logical extension in which CPU switches jobs so frequently that users can interact with each job while it is running, creating interactive computing Response time should be < 1 second Each user has at least one program executing in memory [process If several jobs ...
1.1 What is an Operating System?
... operating system. It starts out by typing the prompt, a character such as a dollar sign, which tells the user that it is waiting to accept a command. Some operating systems, especially those on microcomputers such as MS-DOS and Apple’s Macintosh system, include the command interpreter in the kernel ...
... operating system. It starts out by typing the prompt, a character such as a dollar sign, which tells the user that it is waiting to accept a command. Some operating systems, especially those on microcomputers such as MS-DOS and Apple’s Macintosh system, include the command interpreter in the kernel ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... – Hardware: processors, memory, disks, printers, keyboard, display, network interfaces, … – Software: office tools, multimedia players, … ...
... – Hardware: processors, memory, disks, printers, keyboard, display, network interfaces, … – Software: office tools, multimedia players, … ...
Dennis Ritchie and Brian Kernighan - Rose
... V4 (1973): Rewritten in C, Kernighan’s brainchild, in probably the most significant event in this OS's history: It meant Unix could be ported to a new hardware in months, and changes would be easy. The C language was originally designed for the Unix operating system, and hence there has always been ...
... V4 (1973): Rewritten in C, Kernighan’s brainchild, in probably the most significant event in this OS's history: It meant Unix could be ported to a new hardware in months, and changes would be easy. The C language was originally designed for the Unix operating system, and hence there has always been ...
11.4 Software Operating Systems
... the OS has to switch between different processes thousands of times a second making sure that each process and application receives enough of the processor's time to function properly. ...
... the OS has to switch between different processes thousands of times a second making sure that each process and application receives enough of the processor's time to function properly. ...
Operating Systems
... time. Functions that were originally part of the operating system have migrated to the hardware. On the other side, programmed functions extraneous to the problems being solved by the application programs are included in the operating system. ...
... time. Functions that were originally part of the operating system have migrated to the hardware. On the other side, programmed functions extraneous to the problems being solved by the application programs are included in the operating system. ...
Introduction to Distributed Systems
... and having the kernel return the desired result to the user process. Many distributed systems that are extensions of UNIX® use this approach because UNIX® itself has a large, monolithic kernel. Most distributed systems that have been designed from scratch use microkernel method. The microkernel is m ...
... and having the kernel return the desired result to the user process. Many distributed systems that are extensions of UNIX® use this approach because UNIX® itself has a large, monolithic kernel. Most distributed systems that have been designed from scratch use microkernel method. The microkernel is m ...
Operating Systems Design
... You submit a job, you twiddle your thumbs for a while, you get the output, see a bug, try to figure out what went wrong, resubmit the job, etc. Even running production programs was difficult in this environment ...
... You submit a job, you twiddle your thumbs for a while, you get the output, see a bug, try to figure out what went wrong, resubmit the job, etc. Even running production programs was difficult in this environment ...
Operating Systems CIS 250
... • Layered - broken down into smaller parts; allows for greater control over each part – less efficient (overhead between layers) – modularity - break the O/S into layers on top of one another; each module communicates with the one below it; simplifies debugging – information hiding-system programmer ...
... • Layered - broken down into smaller parts; allows for greater control over each part – less efficient (overhead between layers) – modularity - break the O/S into layers on top of one another; each module communicates with the one below it; simplifies debugging – information hiding-system programmer ...
Chapter 1 Introduction to Operating Systems
... First version of MS DOS shipped in August1981 It was the underlying basic OS on which early versions of MS Windows ran ...
... First version of MS DOS shipped in August1981 It was the underlying basic OS on which early versions of MS Windows ran ...