Fields of Science
... Describe the differences between dome mountains and fault-block mountains in terms of how they are formed. Dome mountains are formed by uplifting forces, either igneous intrusions of forces that arch rocks upward. They are round and usually appear alone. Fault block mountains are whole blocks of cru ...
... Describe the differences between dome mountains and fault-block mountains in terms of how they are formed. Dome mountains are formed by uplifting forces, either igneous intrusions of forces that arch rocks upward. They are round and usually appear alone. Fault block mountains are whole blocks of cru ...
Homework for Faults Folds Mtns from Intro Geology
... 1. The general term for the change in shape of a rock when sufficient stress is applied is strain. True or False? 2. A rock that undergoes sufficient stress to change its original shape has exceeded its elastic limit. True or False? 3. Rocks in which plastic deformation occurs remain in their deform ...
... 1. The general term for the change in shape of a rock when sufficient stress is applied is strain. True or False? 2. A rock that undergoes sufficient stress to change its original shape has exceeded its elastic limit. True or False? 3. Rocks in which plastic deformation occurs remain in their deform ...
Digital Image Correlation Strain Analysis of Geometric Stress
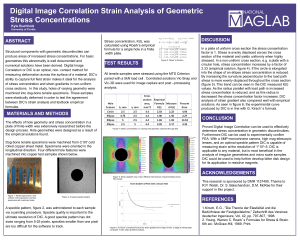
... Proved Digital Image Correlation can be used to effectively determine stress concentration in geometric discontinuities. Furthermore DIC can be used to experimentally confirm FEA. With a 5MP monochrome camera, high mag telescopic lenses, and an optimal speckle pattern DIC is capable of measuring str ...
... Proved Digital Image Correlation can be used to effectively determine stress concentration in geometric discontinuities. Furthermore DIC can be used to experimentally confirm FEA. With a 5MP monochrome camera, high mag telescopic lenses, and an optimal speckle pattern DIC is capable of measuring str ...
Sedimentary Textures
... Derivation • what were the original rocks? • Lots of different rock particles mean the HINTERLAND was a big area and very diverse ...
... Derivation • what were the original rocks? • Lots of different rock particles mean the HINTERLAND was a big area and very diverse ...
A reassessment of the brittle deformation history, age and attribute
... related to Devonian ENE-WSW transtension associated with sinistral shear along the Great Glen Fault (GGF) during Orcadian and proto-West Orkney basin formation. Group 2 structures are closely associated systems of metre- to kilometre-scale N-S trending folds and thrusts related to a highly heterogen ...
... related to Devonian ENE-WSW transtension associated with sinistral shear along the Great Glen Fault (GGF) during Orcadian and proto-West Orkney basin formation. Group 2 structures are closely associated systems of metre- to kilometre-scale N-S trending folds and thrusts related to a highly heterogen ...
Introduction
... Tectonics: Study of the origin and geologic evolution (history of motion and deformation) of large areas (regional to global) of the Earth’s lithosphere (e.g., origin of continents; building of mountain belts; formation of ocean floor) Structural Geology: Study of deformation in rocks at scales rang ...
... Tectonics: Study of the origin and geologic evolution (history of motion and deformation) of large areas (regional to global) of the Earth’s lithosphere (e.g., origin of continents; building of mountain belts; formation of ocean floor) Structural Geology: Study of deformation in rocks at scales rang ...
Section 3 Deforming Earth`s Crust
... break. The surface along which rocks break and slide past each other is called a fault. The blocks of crust on each side of the fault are called fault blocks. When a fault is not vertical, there are two kinds of fault blocks—the hanging wall and the footwall. The illustration at the far left of Figu ...
... break. The surface along which rocks break and slide past each other is called a fault. The blocks of crust on each side of the fault are called fault blocks. When a fault is not vertical, there are two kinds of fault blocks—the hanging wall and the footwall. The illustration at the far left of Figu ...
Lecture 1 Plate Tectonics
... Special kind of reverse Thrust fault: reverse with dip less than ...
... Special kind of reverse Thrust fault: reverse with dip less than ...
Types of Faulting
... Earthquakes occur when there is a sudden movement on the Earth’s crust. Most movement on the Earth’s crust takes place along plate boundaries. There are three main types of plate boundaries; they include converging (moving together), diverging (moving apart), and sliding or transform plate boundarie ...
... Earthquakes occur when there is a sudden movement on the Earth’s crust. Most movement on the Earth’s crust takes place along plate boundaries. There are three main types of plate boundaries; they include converging (moving together), diverging (moving apart), and sliding or transform plate boundarie ...
Deforming the Earth`s Crust
... Monoclines are rock layers that are folded so that both ________ of the fold are horizontal. Faults • Some rock layers __________ when stress is applied to them. • The surface along which rocks break is called a ___________. • The ________ of crust on each side of the fault are called fault ________ ...
... Monoclines are rock layers that are folded so that both ________ of the fold are horizontal. Faults • Some rock layers __________ when stress is applied to them. • The surface along which rocks break is called a ___________. • The ________ of crust on each side of the fault are called fault ________ ...
File
... Primary (P) Waves - travel the fastest of the three waves and can pass through solids, liquids, and gases. They cause slight vibrations (compression) that would rattle dishes on shelves, which provides a warning to people of the earthquake movement to come. Secondary (S) Waves - travel more slowly t ...
... Primary (P) Waves - travel the fastest of the three waves and can pass through solids, liquids, and gases. They cause slight vibrations (compression) that would rattle dishes on shelves, which provides a warning to people of the earthquake movement to come. Secondary (S) Waves - travel more slowly t ...
GEOL_15_mid_term_I_s..
... Origin of the Earth and Time: What is the age of the Earth? What are the two types of time that geologists use? What is the law of superposition? What is a radioactive half‐life? Can we use radiocarbon ages to evaluate the age of the earth? Why or why not? Earth’s Structure: What are the two ways ...
... Origin of the Earth and Time: What is the age of the Earth? What are the two types of time that geologists use? What is the law of superposition? What is a radioactive half‐life? Can we use radiocarbon ages to evaluate the age of the earth? Why or why not? Earth’s Structure: What are the two ways ...
Chapter 2 Earthquakes
... the tiltmeter will move from one ________ to the other. 4. Satellite monitors- These satellites have ___________ that make images of _________. The satellite determines the __________ it takes for the radio waves to make their trip to give accurate measurements of the __________ to the ground. B. Mo ...
... the tiltmeter will move from one ________ to the other. 4. Satellite monitors- These satellites have ___________ that make images of _________. The satellite determines the __________ it takes for the radio waves to make their trip to give accurate measurements of the __________ to the ground. B. Mo ...
Chapter 11 2004.ppt
... The brittle-ductile transition is at 10-15 km depth. Above = brittle; below = ductile. Continental crust earthquakes occur above this transition zone.Both kinds of deformation can occur in the same outcrop depending on whether the deformation circumstances were fast or slow. Force = mass x accelerat ...
... The brittle-ductile transition is at 10-15 km depth. Above = brittle; below = ductile. Continental crust earthquakes occur above this transition zone.Both kinds of deformation can occur in the same outcrop depending on whether the deformation circumstances were fast or slow. Force = mass x accelerat ...
Strike-Slip Faults
... Along a strike-slip fault, blocks of rock move sideways on either side of the fault plane. Stresses that push blocks of rock horizontally cause earthquakes along strike-slip faults. These faults can occur where plates scrape past each other. The San Andreas Fault is a strike-slip fault. ...
... Along a strike-slip fault, blocks of rock move sideways on either side of the fault plane. Stresses that push blocks of rock horizontally cause earthquakes along strike-slip faults. These faults can occur where plates scrape past each other. The San Andreas Fault is a strike-slip fault. ...
... areas have previously been associatedwith asperities. Based on the structure of the overriding plate, former publications have proposed a mechanical modelfor the origin of asperities along the Chilean convergent margin, in which the dense igneous material in the forearc ofthe overriding plate above ...
Practice for Chapter 9
... 1. The general term for the change in shape of a rock when sufficient stress is applied is strain. True or False? 2. A rock that undergoes sufficient stress to change its original shape has exceeded its elastic limit. True or False? 3. Rocks in which plastic deformation occurs remain in their deform ...
... 1. The general term for the change in shape of a rock when sufficient stress is applied is strain. True or False? 2. A rock that undergoes sufficient stress to change its original shape has exceeded its elastic limit. True or False? 3. Rocks in which plastic deformation occurs remain in their deform ...
Journal of Babylon University/Pure and Applied Sciences/ No.(4
... led to the upcoming overburden and active extensional faulting. According to Mastin and Pollard (Mastin and Pollard, 1988), the fissures and faults along the area might have formed above a shallow intrusion of magma. 2) Most fissures in the sedimentary section result from the reactivation of basemen ...
... led to the upcoming overburden and active extensional faulting. According to Mastin and Pollard (Mastin and Pollard, 1988), the fissures and faults along the area might have formed above a shallow intrusion of magma. 2) Most fissures in the sedimentary section result from the reactivation of basemen ...
Obj. 2.1.1 Layers of the Earth A
... 1. Which of the following is NOT a type of stress seen in rocks? a. shear stress c. compressional stress b. tensional stress d. transitional stress 2. Tensional stresses commonly cause which of the following? a. strike-slip faults c. thrust faults b. reverse faults d. normal faults 3. Compressional ...
... 1. Which of the following is NOT a type of stress seen in rocks? a. shear stress c. compressional stress b. tensional stress d. transitional stress 2. Tensional stresses commonly cause which of the following? a. strike-slip faults c. thrust faults b. reverse faults d. normal faults 3. Compressional ...
Stress, Strain, and Viscosity
... Are all materials either a solid or a fluid, all the time ? Applied heat can cause solid materials to behave like a fluid Some material may be elastic when small forces are applied but deform permanently with larger applied forces ...
... Are all materials either a solid or a fluid, all the time ? Applied heat can cause solid materials to behave like a fluid Some material may be elastic when small forces are applied but deform permanently with larger applied forces ...
A Model of Three Faults
... 1. Color the paper fault model handout according to the color key provided. 2. Glue the fault model onto a piece of construction paper. 3. Cut out the fault model and fold each side down to form a box with the drawn features on top. 4. Glue the corners together. The box is a three dimensional model ...
... 1. Color the paper fault model handout according to the color key provided. 2. Glue the fault model onto a piece of construction paper. 3. Cut out the fault model and fold each side down to form a box with the drawn features on top. 4. Glue the corners together. The box is a three dimensional model ...
(pages 162-165) PART 1 Chapter 6
... 1. In places where rock of the crust is pushed together, _____________________ causes _________________ faults to form. 2. A reverse fault has the same structure as a normal fault, but the blocks move in the opposite direction. 3. The rock forming the ______________ _____________ of a reverse fault ...
... 1. In places where rock of the crust is pushed together, _____________________ causes _________________ faults to form. 2. A reverse fault has the same structure as a normal fault, but the blocks move in the opposite direction. 3. The rock forming the ______________ _____________ of a reverse fault ...
Normal Fault Associated Plate Boundary
... the motions of plates compress, pull or shear the crust so much that the crust breaks. • 3 Types of Faults – Strike Slip Fault – Normal Fault – Reverse Fault ...
... the motions of plates compress, pull or shear the crust so much that the crust breaks. • 3 Types of Faults – Strike Slip Fault – Normal Fault – Reverse Fault ...