The Optimal Mechanism for Selling to a Budget
... ``conditional'' case. Now, the seller can costlessly prevent the buyer from overstating his budget through the use of a cash bond or financial disclosure requirement, so prices can be conditioned on the buyer's budget. The optimal mechanism is now implemented by a two-dimensional pricing function th ...
... ``conditional'' case. Now, the seller can costlessly prevent the buyer from overstating his budget through the use of a cash bond or financial disclosure requirement, so prices can be conditioned on the buyer's budget. The optimal mechanism is now implemented by a two-dimensional pricing function th ...
Tetris Game-playing Agents in Python
... agent and whether we consider it a failure or a success. First for the reflex agent. The reflex agent performed better than expected, and with more hand tuning of the weights, it could be expected to perform even better. Although 13 lines is not an especially large number per game, in some games it ...
... agent and whether we consider it a failure or a success. First for the reflex agent. The reflex agent performed better than expected, and with more hand tuning of the weights, it could be expected to perform even better. Although 13 lines is not an especially large number per game, in some games it ...
39 Learning the Prior in Minimal Peer Prediction
... prior to agents but does not insist on the mechanism knowing the prior. Unlike Prelec’s mechanism, RBTS achieves strict incentive compatibility for every number of agents n ≥ 3. The mechanism is based on the observation that a particularity of the quadratic scoring rule can be used to truthfully eli ...
... prior to agents but does not insist on the mechanism knowing the prior. Unlike Prelec’s mechanism, RBTS achieves strict incentive compatibility for every number of agents n ≥ 3. The mechanism is based on the observation that a particularity of the quadratic scoring rule can be used to truthfully eli ...
http://cep.lse.ac.uk/seminarpapers/10-03-16-PM.pdf
... examples—and in our model—there are many agents relative to the number of object types (also referred to as objects), each object type is represented by one or more indivisible copies, and each agent consumes at most one object copy.1 Agents are indifferent among copies of the same object and have st ...
... examples—and in our model—there are many agents relative to the number of object types (also referred to as objects), each object type is represented by one or more indivisible copies, and each agent consumes at most one object copy.1 Agents are indifferent among copies of the same object and have st ...
Reinforcement learning to play an optimal Nash equilibrium in team
... on extending reinforcement learning (RL) to multiagent settings [11, 15, 5, 17]. Markov games (aka. stochastic games) [16] have emerged as the prevalent model of multiagent RL. An approach called Nash-Q [9, 6, 8] has been proposed for learning the game structure and the agents’ strategies (to a fixe ...
... on extending reinforcement learning (RL) to multiagent settings [11, 15, 5, 17]. Markov games (aka. stochastic games) [16] have emerged as the prevalent model of multiagent RL. An approach called Nash-Q [9, 6, 8] has been proposed for learning the game structure and the agents’ strategies (to a fixe ...
Reinforcement Learning to Play an Optimal Nash Equilibrium in
... on extending reinforcement learning (RL) to multiagent settings [11, 15, 5, 17]. Markov games (aka. stochastic games) [16] have emerged as the prevalent model of multiagent RL. An approach called Nash-Q [9, 6, 8] has been proposed for learning the game structure and the agents’ strategies (to a fixe ...
... on extending reinforcement learning (RL) to multiagent settings [11, 15, 5, 17]. Markov games (aka. stochastic games) [16] have emerged as the prevalent model of multiagent RL. An approach called Nash-Q [9, 6, 8] has been proposed for learning the game structure and the agents’ strategies (to a fixe ...
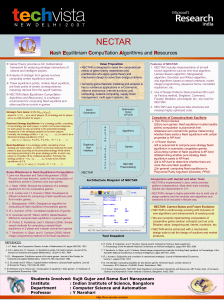
NECTAR: Nash Equilibrium Computation Algorithms
... irrespective of the strategies played by the other players. Formally, the strategy profile s∗ = (s1∗, s2∗ , . . . , sn∗) is said to be a dominant strategy equilibrium of G if, ui(si∗,s-i∗) ≥ ui(si,s-i), ∀si∈Si, ∀s-i∈S-i , ∀i = 1, 2, . . . , n ...
... irrespective of the strategies played by the other players. Formally, the strategy profile s∗ = (s1∗, s2∗ , . . . , sn∗) is said to be a dominant strategy equilibrium of G if, ui(si∗,s-i∗) ≥ ui(si,s-i), ∀si∈Si, ∀s-i∈S-i , ∀i = 1, 2, . . . , n ...
Game Theory Zero
... More formally, we can define the "equilibrium pair" of strategy under Nash equilibrium as (x*, y*), where x* is the strategy chosen by A y* is the strategy chosen by B. Then Nash equilibrium is a state where ...
... More formally, we can define the "equilibrium pair" of strategy under Nash equilibrium as (x*, y*), where x* is the strategy chosen by A y* is the strategy chosen by B. Then Nash equilibrium is a state where ...
NEER WORKING PAPER SERIES Robert Feenstra
... with initial endowments of x greater than è will be sellers in equilibrium, and all individuals with endowments less than Ô will be buyers or x in equilibrium. The boundary ...
... with initial endowments of x greater than è will be sellers in equilibrium, and all individuals with endowments less than Ô will be buyers or x in equilibrium. The boundary ...
Contracts for Experimentation
... Proof. It suffices to show that in each of the menus, each of the contracts would induce the agent (of either type) to reveal project success immediately when it is obtained. Consider first the menus of Theorem 3 and Theorem 5: for each ✓ 2 {L, H}, the contract for type ✓, C✓ , is a penalty contract ...
... Proof. It suffices to show that in each of the menus, each of the contracts would induce the agent (of either type) to reveal project success immediately when it is obtained. Consider first the menus of Theorem 3 and Theorem 5: for each ✓ 2 {L, H}, the contract for type ✓, C✓ , is a penalty contract ...
Comparative Statics - Oregon State University
... equations that must be solved simultaneously to find the optimal values of the choice variables. When these functions are implicit and include many variables, it becomes convenient to differentiate the first-order conditions and solve the resulting system using matrix algebra and Cramer’s rule (Simo ...
... equations that must be solved simultaneously to find the optimal values of the choice variables. When these functions are implicit and include many variables, it becomes convenient to differentiate the first-order conditions and solve the resulting system using matrix algebra and Cramer’s rule (Simo ...
The theory of implementation in Nash equilibrium : a survey
... society might have; the set consists of the "welfare optima" relative to the ...
... society might have; the set consists of the "welfare optima" relative to the ...
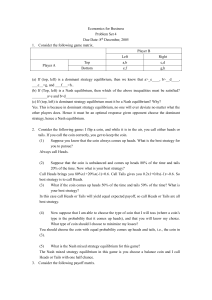
Economics for Business
... Now suppose that I am able to choose the type of coin that I will toss (where a coin’s type is the probability that it comes up heads), and that you will know my choice. What type of coin should I choose to minimize my losses? You should choose the coin with equal probability comes up heads and tail ...
... Now suppose that I am able to choose the type of coin that I will toss (where a coin’s type is the probability that it comes up heads), and that you will know my choice. What type of coin should I choose to minimize my losses? You should choose the coin with equal probability comes up heads and tail ...
Rational expectation can preclude trades
... The set Θ is interpreted as the set of payoff-relevant events; endowments and utility functions may depend on θ. The set X is interpreted as consisting of payoff-irrelevant events; these events do not affect endowments or taste directly. It is assumed here that the contingent commodities are ex-ante Pa ...
... The set Θ is interpreted as the set of payoff-relevant events; endowments and utility functions may depend on θ. The set X is interpreted as consisting of payoff-irrelevant events; these events do not affect endowments or taste directly. It is assumed here that the contingent commodities are ex-ante Pa ...
PDF Download
... net-of-tax income every period. Instead, they use financial markets to allocate their resources over time. For instance, a mortgage contract enables agents to live in a house that reflects their life-time income rather than in a rental unit that reflects their present disposable income every period. ...
... net-of-tax income every period. Instead, they use financial markets to allocate their resources over time. For instance, a mortgage contract enables agents to live in a house that reflects their life-time income rather than in a rental unit that reflects their present disposable income every period. ...
Income Smoothing as Rational Equilibrium Behavior? A Second Look
... ings management is that of income smoothing provided by Lambert (1984). In a multi-period setting where the optimal …rst-best strategy is to implement the same expected earnings (i.e., “action”) in every sub-period, the deviation in equilibrium behavior under the optimal second-best multi-period con ...
... ings management is that of income smoothing provided by Lambert (1984). In a multi-period setting where the optimal …rst-best strategy is to implement the same expected earnings (i.e., “action”) in every sub-period, the deviation in equilibrium behavior under the optimal second-best multi-period con ...
30. TYPE OF THE RETAILER PROBLEM WITH COMPLETE INFORMATION WITH NASH EQUALIBRIA REPEATEDLY
... proves the existence and the uniqueness of the Nash solution under certain conditions. In this paper, we organized the profit function with some conditions under which the optimal solution of the competitive retailer problem with two players and the leader-follower type ordering problem have the sam ...
... proves the existence and the uniqueness of the Nash solution under certain conditions. In this paper, we organized the profit function with some conditions under which the optimal solution of the competitive retailer problem with two players and the leader-follower type ordering problem have the sam ...
Coordination and Higher Order Uncertainty
... an equilibrium of all nearby games of incomplete information. Some games have no robust equilibria, but Kajii and Morris show that some interesting classes of games do have robust equilibria. 4. (Generalizations) It is quite easy to duplicate the above analysis to more general 2 × 2 games with strat ...
... an equilibrium of all nearby games of incomplete information. Some games have no robust equilibria, but Kajii and Morris show that some interesting classes of games do have robust equilibria. 4. (Generalizations) It is quite easy to duplicate the above analysis to more general 2 × 2 games with strat ...
On the Interaction between Computer Science and Economics
... Suppose that we fix a social situation involving the agents A. How should we represent the knowledge of each agent? A natural assumption is that no agent can have all the information about a situation. For one thing agents are computationally limited and can only process a bounded amount of informat ...
... Suppose that we fix a social situation involving the agents A. How should we represent the knowledge of each agent? A natural assumption is that no agent can have all the information about a situation. For one thing agents are computationally limited and can only process a bounded amount of informat ...
... We establish existence without imposing the restrictive conditions (e.g., one-dimensional signals and rewards, monotone likelihood ratio conditions, additively separable utility in rewards and actions, etc.) that are typical for the validity of the FOA. Similar to Holmström and Milgrom (1987, 1991) ...
On extensive form implementation of contracts in differential
... do not retain this property under free disposal. In particular, not only free disposal destroys incentive compatibility but a problem also appears in verifying that an agent has actually destroyed part of his initial endowment. Secondly, we provide examples which demonstrate that with free disposal ...
... do not retain this property under free disposal. In particular, not only free disposal destroys incentive compatibility but a problem also appears in verifying that an agent has actually destroyed part of his initial endowment. Secondly, we provide examples which demonstrate that with free disposal ...
after Nash eqm, Subgame Perfect Nash eqm, and Bayesi
... • Educational signaling: (i) a student finds out whether he low or high productivity, (ii) the student chooses to get a high school or college degree, and (iii) a firm decides what wage to offer. • Lawsuits: (i) a client finds out whether he has a genuine or spurious lawsuit against a firm, (ii) the ...
... • Educational signaling: (i) a student finds out whether he low or high productivity, (ii) the student chooses to get a high school or college degree, and (iii) a firm decides what wage to offer. • Lawsuits: (i) a client finds out whether he has a genuine or spurious lawsuit against a firm, (ii) the ...
Is the Media Sensationalizing Processed Formulas?
... 1980’s and then Gerber in 2007, Nestle has heavily invested and promoted these partially hydrolyzed whey proteins in its infant formulas. Following Nestlé’s marketing efforts, other infant formula companies began to add whey proteins to some of their infant formulas. These formulas are usually marke ...
... 1980’s and then Gerber in 2007, Nestle has heavily invested and promoted these partially hydrolyzed whey proteins in its infant formulas. Following Nestlé’s marketing efforts, other infant formula companies began to add whey proteins to some of their infant formulas. These formulas are usually marke ...
Lecture 23 1 Proper Scoring Rules
... r2 + (1 − r)2 . Compute the associated proper scoring rule S. Plot e.g. S(0.3; ·) and S(0.7; ·) and check that they act as the proof of the theorem says they should. ...
... r2 + (1 − r)2 . Compute the associated proper scoring rule S. Plot e.g. S(0.3; ·) and S(0.7; ·) and check that they act as the proof of the theorem says they should. ...
PDF
... the satisfaction value of specifications. The multi-valued setting arises directly in systems in which the designer can give to the atomic propositions rich values, expressing, for example, energy consumption, waiting time, or different levels of confidence [5, 1], and arises indirectly in probabil ...
... the satisfaction value of specifications. The multi-valued setting arises directly in systems in which the designer can give to the atomic propositions rich values, expressing, for example, energy consumption, waiting time, or different levels of confidence [5, 1], and arises indirectly in probabil ...