Advanced Operating Systems
... Introduction to Real-Time1 Systems and Applications The second part of these notes provides introductory material on real-time systems and programming. Real-time systems have two parts: a real-time operating system and one or more real-time applications. It is common for such systems to be dedicated ...
... Introduction to Real-Time1 Systems and Applications The second part of these notes provides introductory material on real-time systems and programming. Real-time systems have two parts: a real-time operating system and one or more real-time applications. It is common for such systems to be dedicated ...
Microkernels Meet Recursive Virtual Machines
... full speed on the bare hardware, and only “special” instructions such as privileged instructions and accesses to I/O registers need to be emulated in software. Since the “upper” and “lower” interfaces of a hypervisor are the same, a sufficiently complete hypervisor can even run additional copies of ...
... full speed on the bare hardware, and only “special” instructions such as privileged instructions and accesses to I/O registers need to be emulated in software. Since the “upper” and “lower” interfaces of a hypervisor are the same, a sufficiently complete hypervisor can even run additional copies of ...
Concurrency (January 10)
... environment and context including scheduling parameters and the file descriptor table. The parent and children share the same files that are opened by the parent prior to the fork. When a program closes a file, the entry in the file descriptor table is freed. To be safer, children and parent p ...
... environment and context including scheduling parameters and the file descriptor table. The parent and children share the same files that are opened by the parent prior to the fork. When a program closes a file, the entry in the file descriptor table is freed. To be safer, children and parent p ...
Module 4: Processes
... process running at all times, to maximize CPU utilization. The objective of time sharing is to switch the CPU among processes so frequently that users can interact with each program while it is running. To meet these objectives, the process scheduler selects an available process for program exec ...
... process running at all times, to maximize CPU utilization. The objective of time sharing is to switch the CPU among processes so frequently that users can interact with each program while it is running. To meet these objectives, the process scheduler selects an available process for program exec ...
Solaris Operating Systems
... User Names Each user account must be assigned a name. This name is used to identify the account for purposes such as electronic mail and logging into a machine Male it easy for people to recognize a user’s account name when sending e-mail, transferring files, and so on. ...
... User Names Each user account must be assigned a name. This name is used to identify the account for purposes such as electronic mail and logging into a machine Male it easy for people to recognize a user’s account name when sending e-mail, transferring files, and so on. ...
CPU Scheduling - McMaster Computing and Software
... SJF algorithm can either be preemptive or nonpreemptive Preemptive version of SJF is called shortest-remaining-time- ...
... SJF algorithm can either be preemptive or nonpreemptive Preemptive version of SJF is called shortest-remaining-time- ...
Memory Management – Thrashing, Segmentation and Paging
... Another pair of segments for kernel virtual addresses (3GB ... 4GB) ...
... Another pair of segments for kernel virtual addresses (3GB ... 4GB) ...
OPERATING SYSTEMS UNIT I Syllabus: Operating Systems
... Assignments: 1. Explain the various types of computer systems. 2. Explain how protection is provided for the hardware resources by the operating system. 3. What are the system components of an operating system and explain them? 4. What are the various process scheduling concepts? 5. List five servic ...
... Assignments: 1. Explain the various types of computer systems. 2. Explain how protection is provided for the hardware resources by the operating system. 3. What are the system components of an operating system and explain them? 4. What are the various process scheduling concepts? 5. List five servic ...
Document
... Exokernel-Based Operating System Two components: exokernel and library operating system (libOS). LibOS resides outside the kernel. Exokernel protects hardware resources (CPU, memory, disk, network, etc). Applications link to libOSes and manage resources through the libOS. Applications can also mana ...
... Exokernel-Based Operating System Two components: exokernel and library operating system (libOS). LibOS resides outside the kernel. Exokernel protects hardware resources (CPU, memory, disk, network, etc). Applications link to libOSes and manage resources through the libOS. Applications can also mana ...
ppt
... – Prohibits outgoing invocations when incoming invocations are disabled. (to avoid deadlock) • Limiting for accessing data on two different processors ...
... – Prohibits outgoing invocations when incoming invocations are disabled. (to avoid deadlock) • Limiting for accessing data on two different processors ...
Operating System Concepts
... If several jobs ready to run at the same time CPU scheduling If processes don’t fit in memory, swapping moves them in and out to run Virtual memory allows execution of processes not completely in memory ...
... If several jobs ready to run at the same time CPU scheduling If processes don’t fit in memory, swapping moves them in and out to run Virtual memory allows execution of processes not completely in memory ...
Linux Introduction - Personal Web Pages
... Even versions based on the licensed UNIX source code – May be so “Unix-like” they are certified to bear the “UNIX” trademark ...
... Even versions based on the licensed UNIX source code – May be so “Unix-like” they are certified to bear the “UNIX” trademark ...
No Slide Title
... three main bodies of code; the most important distinction between the kernel and all other components. The kernel is responsible for maintaining the important ...
... three main bodies of code; the most important distinction between the kernel and all other components. The kernel is responsible for maintaining the important ...
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 7th Edition
... 9) The earliest computers employed __________ processing, a name derived by the way the users have access to the systems. Answer: serial 10) __________ was designed to keep the processor and I/O devices, including storage devices, simultaneously busy to achieve maximum efficiency. Answer: Multiprogr ...
... 9) The earliest computers employed __________ processing, a name derived by the way the users have access to the systems. Answer: serial 10) __________ was designed to keep the processor and I/O devices, including storage devices, simultaneously busy to achieve maximum efficiency. Answer: Multiprogr ...
Module 1: Introduction What is an Operating System?
... Time-Sharing Systems– Interactive Computing ...
... Time-Sharing Systems– Interactive Computing ...
IV. Parallel Operating Systems
... positions. Most major hardware vendors sell UMA machines in the form of symmetric multiprocessors with write-through caches. This means that writes to cache are immediately written to main memory. In the alternative policy of write-back caching, writes to the cache are only written to main memory wh ...
... positions. Most major hardware vendors sell UMA machines in the form of symmetric multiprocessors with write-through caches. This means that writes to cache are immediately written to main memory. In the alternative policy of write-back caching, writes to the cache are only written to main memory wh ...
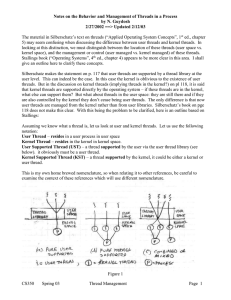
Notes by Guydosh on Thread managment
... 5) may seem confusing when discussing the difference between user threads and kernel threads. In looking at this distinction, we must distinguish between the location of these threads (user space vs. kernel space), and the management or control (user managed vs. kernel managed) of these threads. Sta ...
... 5) may seem confusing when discussing the difference between user threads and kernel threads. In looking at this distinction, we must distinguish between the location of these threads (user space vs. kernel space), and the management or control (user managed vs. kernel managed) of these threads. Sta ...
Document
... instructions for “flushing” the cache can be used to maintain consistency of main memory Movement of data among lower levels of the memory hierarchy is under direct control of the OS virtual memory page faults file system calls ...
... instructions for “flushing” the cache can be used to maintain consistency of main memory Movement of data among lower levels of the memory hierarchy is under direct control of the OS virtual memory page faults file system calls ...
A Survey of Embedded Operating System
... wait object allow a thread to block its own execution until the specified object changes. Windows CE queues mutex, critical section and event requests in "FIFO-by-priority" order: a different FIFO queue is defined for each of the 8 priority levels. Real-time application use interrupts as a way of e ...
... wait object allow a thread to block its own execution until the specified object changes. Windows CE queues mutex, critical section and event requests in "FIFO-by-priority" order: a different FIFO queue is defined for each of the 8 priority levels. Real-time application use interrupts as a way of e ...
Chapter 4-1
... were the OS Early OS was just a utility called an executive and only handled a single user - system resources managed by user Multiprogrammed OS allowed for more than one user – system resources managed by the monitor Early day protection was easy – you protected the user from themselves but t ...
... were the OS Early OS was just a utility called an executive and only handled a single user - system resources managed by user Multiprogrammed OS allowed for more than one user – system resources managed by the monitor Early day protection was easy – you protected the user from themselves but t ...
OPERATING SYSTEMS STRUCTURES
... Generic device driver code Drivers for each device - translate read/write requests into disk position commands. ...
... Generic device driver code Drivers for each device - translate read/write requests into disk position commands. ...
DOS - InfoShare.tk
... In the 1980s or early 1990s, the operating system that shipped with most PCs was a version of the Disk Operating System (DOS) created by Microsoft: MSDOS. ...
... In the 1980s or early 1990s, the operating system that shipped with most PCs was a version of the Disk Operating System (DOS) created by Microsoft: MSDOS. ...
PPT Chapter 09
... Direct and Indirect Naming • In direct naming, sender and receiver processes mention each other’s name – In symmetric naming, both sender and receiver processes specify each other’s name – In asymmetric naming, receiver does not name process from which it wishes to receive a message; kernel gives i ...
... Direct and Indirect Naming • In direct naming, sender and receiver processes mention each other’s name – In symmetric naming, both sender and receiver processes specify each other’s name – In asymmetric naming, receiver does not name process from which it wishes to receive a message; kernel gives i ...