Operating Systems
... ⇒ require a special (unprivileged) instruction to allow transition from user to kernel mode. • Generally called a software interrupt since operates similarly to a real (hardware) interrupt. . . • Set of OS services accessible via software interrupt mechanism called system calls. Operating Systems — ...
... ⇒ require a special (unprivileged) instruction to allow transition from user to kernel mode. • Generally called a software interrupt since operates similarly to a real (hardware) interrupt. . . • Set of OS services accessible via software interrupt mechanism called system calls. Operating Systems — ...
lec10
... • The responsibility of the OS arise from three characteristics of I/O systems: – The I/O system is shared by multiple programs using the processor. ...
... • The responsibility of the OS arise from three characteristics of I/O systems: – The I/O system is shared by multiple programs using the processor. ...
Introduction to the Process
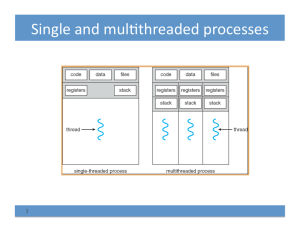
... – Protected from each other! – OS protected from them – Processes provides memory protection – Threads more efficient than processes (later) • Fundamental tradeoff between protection and efficiency ...
... – Protected from each other! – OS protected from them – Processes provides memory protection – Threads more efficient than processes (later) • Fundamental tradeoff between protection and efficiency ...
Operating System Tutorial
... An Operating System (OS) is an interface between a computer user and computer hardware. An operating system is a software which performs all the basic tasks like file management, memory management, process management, handling input and output, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives ...
... An Operating System (OS) is an interface between a computer user and computer hardware. An operating system is a software which performs all the basic tasks like file management, memory management, process management, handling input and output, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives ...
Introduction
... Mainframe operating systems Server operating systems Multiprocessor operating systems Personal computer operating systems Real-time operating systems Embedded operating systems Smart card operating systems ...
... Mainframe operating systems Server operating systems Multiprocessor operating systems Personal computer operating systems Real-time operating systems Embedded operating systems Smart card operating systems ...
Module 6: CPU Scheduling
... process (LWP - a mean of achieving multitasking. In contrast to a regular (full-blown) process, an LWP shares all (or most of) its logical address space and system resources with other process(es); in contrast to a thread, a lightweight process has its own private process identifier and parenthood r ...
... process (LWP - a mean of achieving multitasking. In contrast to a regular (full-blown) process, an LWP shares all (or most of) its logical address space and system resources with other process(es); in contrast to a thread, a lightweight process has its own private process identifier and parenthood r ...
Operating System Support for Virtual Machines
... • When the guest machine process switches between guest kernel mode to guest user mode, the access mode of guest kernel’s portion address space must be changed appropriately. • The access mode alternation is invoked by making host system calls – mmap, munmap and mprotect that incur significant overh ...
... • When the guest machine process switches between guest kernel mode to guest user mode, the access mode of guest kernel’s portion address space must be changed appropriately. • The access mode alternation is invoked by making host system calls – mmap, munmap and mprotect that incur significant overh ...
Interrupts - Matthew L. Wright
... – Loads memory bus as data are copied between controllers, buffers, and memory locations • To improve I/O efficiency, we can: – Reduce the number of context switches. – Reduce the number of times that data must be copied in memory while passing between device and application. – Reduce the frequency ...
... – Loads memory bus as data are copied between controllers, buffers, and memory locations • To improve I/O efficiency, we can: – Reduce the number of context switches. – Reduce the number of times that data must be copied in memory while passing between device and application. – Reduce the frequency ...
Presentation
... Must guarantee that no two processes can execute wait () and signal () on the same semaphore at the same time Thus, implementation becomes the critical section problem where the wait and signal code are placed in the critical section. Could now have busy waiting in critical section implementation ...
... Must guarantee that no two processes can execute wait () and signal () on the same semaphore at the same time Thus, implementation becomes the critical section problem where the wait and signal code are placed in the critical section. Could now have busy waiting in critical section implementation ...
11. Kernel Design
... Old-Fashioned Alternative Old interface for x86 and IBM PC architecture Rarely supported by modern processor instruction sets Low-performance (ordered memory accesses, no DMA) ...
... Old-Fashioned Alternative Old interface for x86 and IBM PC architecture Rarely supported by modern processor instruction sets Low-performance (ordered memory accesses, no DMA) ...
Chapter 1: Introduction
... System call – request to the operating system to allow user to wait for I/O completion. ...
... System call – request to the operating system to allow user to wait for I/O completion. ...
Development of Dependable Real
... read values from the port and write these values to the environment. The execution of the sensor and actor functions is also performed time-triggered. The execution frequency has to be specified by the developer. The sensor execution takes thereby place at the begin of each interval, the actor execu ...
... read values from the port and write these values to the environment. The execution of the sensor and actor functions is also performed time-triggered. The execution frequency has to be specified by the developer. The sensor execution takes thereby place at the begin of each interval, the actor execu ...
Chapter 3: Processes (6th edition chap 4)
... state of the old process and load the saved state for the new process" Context-switch time is overhead; the system does no useful work ...
... state of the old process and load the saved state for the new process" Context-switch time is overhead; the system does no useful work ...
Module 4: Processes
... Stubs – client-side proxy for the actual procedure on the server The client-side stub locates the server and marshalls the parameters The server-side stub receives this message, unpacks the marshalled ...
... Stubs – client-side proxy for the actual procedure on the server The client-side stub locates the server and marshalls the parameters The server-side stub receives this message, unpacks the marshalled ...
Memory manager
... Multiprogramming, virtual memory, well-designed file and directory systems, and short commands. ...
... Multiprogramming, virtual memory, well-designed file and directory systems, and short commands. ...
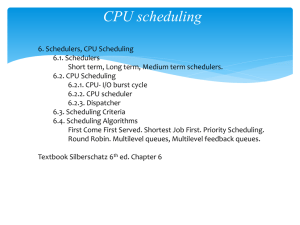
CPU scheduler
... CPU scheduling CPU-I/O Burst Cycle Scheduling is a fundamental operatingsystem function. Almost all computer resources are scheduled before use. The CPU is, of course, one of the primary computer resources. Thus, its scheduling is central to operatingsystem design. The success of CPU scheduling dep ...
... CPU scheduling CPU-I/O Burst Cycle Scheduling is a fundamental operatingsystem function. Almost all computer resources are scheduled before use. The CPU is, of course, one of the primary computer resources. Thus, its scheduling is central to operatingsystem design. The success of CPU scheduling dep ...
Trusted Operating Systems
... • Everything in the trusted OS necessary to enforce security policy • System element on which security enforcement depends: – Hardware • processors, memory, registers, and I/O devices ...
... • Everything in the trusted OS necessary to enforce security policy • System element on which security enforcement depends: – Hardware • processors, memory, registers, and I/O devices ...
Answers to Even-Numbered Exercises
... Linux is portable, is based on standards, is written in C, has a kernel programming interface, can support many users, and can run multiple tasks simultaneously. For more information refer to “What Is So Good About Linux?” on page 6. The source code for the operating system is readily available so s ...
... Linux is portable, is based on standards, is written in C, has a kernel programming interface, can support many users, and can run multiple tasks simultaneously. For more information refer to “What Is So Good About Linux?” on page 6. The source code for the operating system is readily available so s ...
Operating system structures
... Mode bit provided by hardware Provides ability to distinguish when system is running user code or kernel code Some instructions designated as privileged, only executable in kernel mode ...
... Mode bit provided by hardware Provides ability to distinguish when system is running user code or kernel code Some instructions designated as privileged, only executable in kernel mode ...
Operating System Layer
... parent’s region. When parent and child share a region, the page frames (units of physical memory corresponding to virtual memory pages) belonging to the parent’s region are mapped simultaneously into the corresponding child region. ...
... parent’s region. When parent and child share a region, the page frames (units of physical memory corresponding to virtual memory pages) belonging to the parent’s region are mapped simultaneously into the corresponding child region. ...
Osprey: Operating System for Predictable Clouds
... Each application in Osprey runs in a resource container that controls resource consumption by the application. We distinguish between two types of resources: preemptive and non-preemptive. Preemptive resources, such as CPU time or network interface bandwidth, can be freely given to the application a ...
... Each application in Osprey runs in a resource container that controls resource consumption by the application. We distinguish between two types of resources: preemptive and non-preemptive. Preemptive resources, such as CPU time or network interface bandwidth, can be freely given to the application a ...
Chapter 1 – 8 Essay Question Review
... Ans: In the first approach, upon the user issuing a command, the interpreter jumps to the appropriate section of code, executes the command, and returns control back to the user. In the second approach, the interpreter loads the appropriate program into memory along with the appropriate arguments. T ...
... Ans: In the first approach, upon the user issuing a command, the interpreter jumps to the appropriate section of code, executes the command, and returns control back to the user. In the second approach, the interpreter loads the appropriate program into memory along with the appropriate arguments. T ...