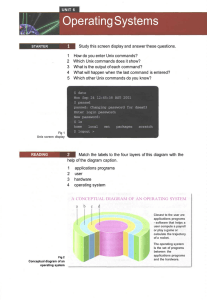
View - LAD
... the operating system. – Usually takes the form of a trap to a specific location in the interrupt vector. – Control passes through the interrupt vector to a service routine in the OS, and the mode bit is set to monitor mode. – The monitor verifies that the parameters are correct and legal, executes t ...
... the operating system. – Usually takes the form of a trap to a specific location in the interrupt vector. – Control passes through the interrupt vector to a service routine in the OS, and the mode bit is set to monitor mode. – The monitor verifies that the parameters are correct and legal, executes t ...
RTOS Acceleration by Reducing Overhead due to Context
... hard real-time and soft real-time systems. In a hard realtime or immediate real-time system, the completion of an operating after its deadline is considered useless, and this may cause a critical failure of the complete system and can lead to an accident (e.g. Engine Control Unit of a car, Computer ...
... hard real-time and soft real-time systems. In a hard realtime or immediate real-time system, the completion of an operating after its deadline is considered useless, and this may cause a critical failure of the complete system and can lead to an accident (e.g. Engine Control Unit of a car, Computer ...
slides - Simon Fraser University
... Interrupt transfers control to the interrupt service routine generally, ...
... Interrupt transfers control to the interrupt service routine generally, ...
History of OS - EECG Toronto
... Read the first job from the tape Run it Write the output to another tape Read the next job and repeat the process ...
... Read the first job from the tape Run it Write the output to another tape Read the next job and repeat the process ...
Course Intro
... will as well be introduced. Special emphasis will be assigned to Unix/Linux. Participant of the course will be required to carry out lab explorations, practical work in terms of assignments and small projects. ...
... will as well be introduced. Special emphasis will be assigned to Unix/Linux. Participant of the course will be required to carry out lab explorations, practical work in terms of assignments and small projects. ...
modelpaper
... System? Describe in detail. 6.Describe the differences among short-term, medium-term, and long-term scheduling. 7. Explain Multiple-Processor Scheduling in detail. Put some light on the architecture of multiple-processor organization. 8.What do you understand by starvation? Why Priority Algorithm su ...
... System? Describe in detail. 6.Describe the differences among short-term, medium-term, and long-term scheduling. 7. Explain Multiple-Processor Scheduling in detail. Put some light on the architecture of multiple-processor organization. 8.What do you understand by starvation? Why Priority Algorithm su ...
ppt - METU
... Hold and wait: a process holding at least one resource is waiting to acquire additional resources held by other processes. No preemption: a resource can be released only voluntarily by the process holding it, after that process has completed its task. Circular wait: there exists a set {P0, P1, …, P0 ...
... Hold and wait: a process holding at least one resource is waiting to acquire additional resources held by other processes. No preemption: a resource can be released only voluntarily by the process holding it, after that process has completed its task. Circular wait: there exists a set {P0, P1, …, P0 ...
Chapter 2: Computer Systems Structures ("Computer Architecture")
... Asynchronous(2 modes: current user proc goes on vs some other process goes on): After I/O starts, control returns to user program without waiting for I/O completion – if user cannot continue w/o results, OS can switch to another user process. This action is generally accomplished using a System ca ...
... Asynchronous(2 modes: current user proc goes on vs some other process goes on): After I/O starts, control returns to user program without waiting for I/O completion – if user cannot continue w/o results, OS can switch to another user process. This action is generally accomplished using a System ca ...
bit8_DC_Lecture_2
... System Architectures: Peer-to-Peer Model • P2P architecture is to exploit the resources in a large number of participating computers for the fulfillment of a given task ...
... System Architectures: Peer-to-Peer Model • P2P architecture is to exploit the resources in a large number of participating computers for the fulfillment of a given task ...
THE MACH SYSTEM
... Execution environment Contains one or more threads Provides a protection domain, a protected access to system resources via ports Thread: unit of computation (execution) must run in the context of a task all threads in a task share ports, memory, etc. process = task + thread ...
... Execution environment Contains one or more threads Provides a protection domain, a protected access to system resources via ports Thread: unit of computation (execution) must run in the context of a task all threads in a task share ports, memory, etc. process = task + thread ...
What is an Operating System?
... Usually disks used to store data that does not fit in main memory or data that must be kept for a “long” period of time. ...
... Usually disks used to store data that does not fit in main memory or data that must be kept for a “long” period of time. ...
Computer Network and Infrastructure
... Interrupts increase the efficiency of the processor by allowing multiple tasks which may not be sequential in order However if the time required for I/O operations is longer than the user operation (this is the true case) the processor will be idle for a long time. Multiprogramming which has more th ...
... Interrupts increase the efficiency of the processor by allowing multiple tasks which may not be sequential in order However if the time required for I/O operations is longer than the user operation (this is the true case) the processor will be idle for a long time. Multiprogramming which has more th ...
Operating Systems
... acts as an interface between applications and the computer hardware. Answer: operating system (OS) 2) The portion of the monitor that is always in main memory and available for execution is referred to as the _________ . Answer: resident monitor 3) __________ is a technique in which a process, execu ...
... acts as an interface between applications and the computer hardware. Answer: operating system (OS) 2) The portion of the monitor that is always in main memory and available for execution is referred to as the _________ . Answer: resident monitor 3) __________ is a technique in which a process, execu ...
OS_Intro - SIUE Computer Science
... (3) OS is the government in your computer (the agent that allocate resources) OS provides “resource management” in your computer ...
... (3) OS is the government in your computer (the agent that allocate resources) OS provides “resource management” in your computer ...
CUSTOMER_CODE SMUDE DIVISION_CODE SMUDE
... in the relocation register to generate the corresponding address (See figure 7.4). Since an address generated by the CPU is checked against these two registers, both the operating system and other user programs and data are protected and are not accessible by the running process. ...
... in the relocation register to generate the corresponding address (See figure 7.4). Since an address generated by the CPU is checked against these two registers, both the operating system and other user programs and data are protected and are not accessible by the running process. ...
What is an Operating System?
... Time-Sharing Systems Personal-Computer Systems Parallel Systems Distributed Systems Real -Time Systems ...
... Time-Sharing Systems Personal-Computer Systems Parallel Systems Distributed Systems Real -Time Systems ...
Chapter 3: Processes
... Execution of program started via GUI mouse clicks, command line entry of its name, etc." ...
... Execution of program started via GUI mouse clicks, command line entry of its name, etc." ...
EET-225 Homework #1
... 10. Log into a Linux operating system and explore the filesystem. a) Linux is available on all computers in Lab 138. Boot the system and choose the correct operating system when the selection screen appears. b) Login as "student" with a password of "kcdevry". This is case-sensitive. c) Using the av ...
... 10. Log into a Linux operating system and explore the filesystem. a) Linux is available on all computers in Lab 138. Boot the system and choose the correct operating system when the selection screen appears. b) Login as "student" with a password of "kcdevry". This is case-sensitive. c) Using the av ...
ch2-OS-Structure
... layers. The bottom layer (layer 0), is the hardware; the highest (layer N) is the user interface. With modularity, layers are ...
... layers. The bottom layer (layer 0), is the hardware; the highest (layer N) is the user interface. With modularity, layers are ...
operating system
... incredibly slow for computers. Rather than let the CPU sit idle as this interactive input takes place, the operating system will rapidly switch the CPU to the program of some other user. OPERATING SYSTEM SERVICES: An operating system provides an environment for the execution of programs. It provides ...
... incredibly slow for computers. Rather than let the CPU sit idle as this interactive input takes place, the operating system will rapidly switch the CPU to the program of some other user. OPERATING SYSTEM SERVICES: An operating system provides an environment for the execution of programs. It provides ...
Operating Systems
... Efficiency (why?) Evolvability (why?) Abstraction is the key to managing the complexity ...
... Efficiency (why?) Evolvability (why?) Abstraction is the key to managing the complexity ...
Chapter 6 An Introduction to System Software
... In most OS, access control is handled by requiring a user to enter a legal user name and password before any other requests are accepted . The password file is maintained by superuser. ...
... In most OS, access control is handled by requiring a user to enter a legal user name and password before any other requests are accepted . The password file is maintained by superuser. ...
Chapter 6 An Introduction to System Software and
... In most OS, access control is handled by requiring a user to enter a legal user name and password before any other requests are accepted . The password file is maintained by superuser. ...
... In most OS, access control is handled by requiring a user to enter a legal user name and password before any other requests are accepted . The password file is maintained by superuser. ...