"A" and type "B".
... blood cells are produced by two different enzymes. These two enzymes are encoded by different versions, or alleles, of the same gene: A and B. ! The A and B alleles code for enzymes that produce the type A and B antigens respectively. A third version of this gene, the O allele, codes for a protein ...
... blood cells are produced by two different enzymes. These two enzymes are encoded by different versions, or alleles, of the same gene: A and B. ! The A and B alleles code for enzymes that produce the type A and B antigens respectively. A third version of this gene, the O allele, codes for a protein ...
Red Blood Cells of Patients with Celiac Disease
... A major area of blood cancer research is identifying the key genes and gene regulators that are involved in the development and growth of blood cancer cells. One such gene (called an “oncogene”) is BCL3, which when mutated or over-expressed, can turn a normal cell into a cancer cell and cause certai ...
... A major area of blood cancer research is identifying the key genes and gene regulators that are involved in the development and growth of blood cancer cells. One such gene (called an “oncogene”) is BCL3, which when mutated or over-expressed, can turn a normal cell into a cancer cell and cause certai ...
Leukaemia Section t(17;21)(q11.2;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Contains a Runt domain and, in the C-term, a transactivation domain; forms heterodimers; widely expressed; nuclear localisation; transcription factor (activator) for various hematopoietic-specific genes. ...
... Contains a Runt domain and, in the C-term, a transactivation domain; forms heterodimers; widely expressed; nuclear localisation; transcription factor (activator) for various hematopoietic-specific genes. ...
When Should We Request Blood Group DNA Testing?
... • Former medical director of LabCorp • On board of directors of Sequenom, Inc. • Vendor for fetal D typing from maternal blood ...
... • Former medical director of LabCorp • On board of directors of Sequenom, Inc. • Vendor for fetal D typing from maternal blood ...
Chapter 4: Modification of Mendelian Ratios
... carbohydrates that form the A and B antigens, called the H substance. Results in an O phenotype, although they do not have O blood; they will still have A and/or B antigens on their red cell surface. Issues arise at the time of transfusion; if they test RBC’s only in the patient, they could receive ...
... carbohydrates that form the A and B antigens, called the H substance. Results in an O phenotype, although they do not have O blood; they will still have A and/or B antigens on their red cell surface. Issues arise at the time of transfusion; if they test RBC’s only in the patient, they could receive ...
Blood Type Class Notes
... Specialized body fluid Four main components: red blood cells (carry oxygen), white blood cells (fight infection), platelets (clotting), plasma (90% water, also various proteins, sugar, vitamins, hormones, etc.) ...
... Specialized body fluid Four main components: red blood cells (carry oxygen), white blood cells (fight infection), platelets (clotting), plasma (90% water, also various proteins, sugar, vitamins, hormones, etc.) ...
Blood - Canyon ISD
... Losses of 15-30% lead to pallor and weakness Losses of over 30% cause severe shock which can be fatal Blood can be stored for up to 35 days in a refrigerator. ...
... Losses of 15-30% lead to pallor and weakness Losses of over 30% cause severe shock which can be fatal Blood can be stored for up to 35 days in a refrigerator. ...
Human Anatomy & Physiology II
... donate to any other ABO type called Universal donors • Misleading because of many other blood groups that must be matched ...
... donate to any other ABO type called Universal donors • Misleading because of many other blood groups that must be matched ...
transfusion medicine update - The Institute for Transfusion Medicine
... these patients should not wait excessively for the blood bank to complete the serological work up or to find antigen-negative units, in order to avoid irreversible damage due to tissue hypoxia. Patients should be transfused before the ...
... these patients should not wait excessively for the blood bank to complete the serological work up or to find antigen-negative units, in order to avoid irreversible damage due to tissue hypoxia. Patients should be transfused before the ...
Blood Typing
... she carries that has Rh + (positive) blood. In subsequent pregnancies, if the fetus is Rh +, Rh antibodies produced in maternal blood may cross the placenta and destroy fetal cells, causing erythroblastosis fetalis. ...
... she carries that has Rh + (positive) blood. In subsequent pregnancies, if the fetus is Rh +, Rh antibodies produced in maternal blood may cross the placenta and destroy fetal cells, causing erythroblastosis fetalis. ...
Training - Powerpoint
... Sanderson’s samples to the first two wells in column A. Add 5 drops of anti-A (blue) to the first well in column A (A-1). Observe whether a precipitate (or cloudiness) occurs - record a “+” if it does, or a “-” if it does not. Add 5 drops of anti-B (yellow) to the 2nd well in column A (A-2) and reco ...
... Sanderson’s samples to the first two wells in column A. Add 5 drops of anti-A (blue) to the first well in column A (A-1). Observe whether a precipitate (or cloudiness) occurs - record a “+” if it does, or a “-” if it does not. Add 5 drops of anti-B (yellow) to the 2nd well in column A (A-2) and reco ...
DCE
... epitope of the D antigen. The problem is that Patient B can make an antibody to Patient A even though both appear to have the entire D antigen present on their red blood cell’s using routine antiD typing reagents.. ...
... epitope of the D antigen. The problem is that Patient B can make an antibody to Patient A even though both appear to have the entire D antigen present on their red blood cell’s using routine antiD typing reagents.. ...
blood type - studentorg
... Sanderson’s samples to the first two wells in column 1. Add a 2-3 drops of anti-A (blue) to the first well in 1A. Observe whether a precipitate (or cloudiness) occurs - record a “+” if it does, or a “-” if it does not. Add a 2-3 drops of anti-B (yellow) to the 2nd well in column 1 (1B) and record th ...
... Sanderson’s samples to the first two wells in column 1. Add a 2-3 drops of anti-A (blue) to the first well in 1A. Observe whether a precipitate (or cloudiness) occurs - record a “+” if it does, or a “-” if it does not. Add a 2-3 drops of anti-B (yellow) to the 2nd well in column 1 (1B) and record th ...
Chapter 4: Modification of Mendelian Ratios
... carbohydrates that form the A and B antigens, called the H substance. Results in an O phenotype, although they do not have O blood; they will still have A and/or B antigens on their red cell surface. Issues arise at the time of transfusion; if they test RBC’s only in the patient, they could receive ...
... carbohydrates that form the A and B antigens, called the H substance. Results in an O phenotype, although they do not have O blood; they will still have A and/or B antigens on their red cell surface. Issues arise at the time of transfusion; if they test RBC’s only in the patient, they could receive ...
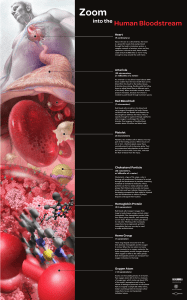
Zoom into the Human Bloodstream Annotated
... blood clots and heart attacks. Researchers are developing nanoparticles that might be injected into the bloodstream to collect at plaque deposits and signal their location. ...
... blood clots and heart attacks. Researchers are developing nanoparticles that might be injected into the bloodstream to collect at plaque deposits and signal their location. ...
Blood Types
... iden=fy types • Many different an=gens = many different blood group systems • Red Cross uses ABO system and Rh system to determine compa=bility ...
... iden=fy types • Many different an=gens = many different blood group systems • Red Cross uses ABO system and Rh system to determine compa=bility ...
CH 37-com - college of ayurved and research centre
... the P. G. degree M.D. (KayaChikitsa) in the year 1998. Her guide was Dr. B. M. Kulkarni & Research center was Tilak Ayurved Mahavidyalaya, Pune, (M.S.) India. ...
... the P. G. degree M.D. (KayaChikitsa) in the year 1998. Her guide was Dr. B. M. Kulkarni & Research center was Tilak Ayurved Mahavidyalaya, Pune, (M.S.) India. ...
The Genetics of Codominance
... Background: In humans the ABO blood types are inherited in a codominant fashion. There are four phenotypes: Type A, Type B, Type AB, and Type O. There are controlled by three alleles: the codominant alleles A and B and the recessive allele O. Blood types can be determined with a simple test that use ...
... Background: In humans the ABO blood types are inherited in a codominant fashion. There are four phenotypes: Type A, Type B, Type AB, and Type O. There are controlled by three alleles: the codominant alleles A and B and the recessive allele O. Blood types can be determined with a simple test that use ...
Unit 5 Objectives:Genetics 1. Define and relate the following terms
... Define the following terms used to describe dominant and recessive traits: trait dominant recessive codominant autosomal dominant autosomal recessive sex linked dominant sex linked recessive ...
... Define the following terms used to describe dominant and recessive traits: trait dominant recessive codominant autosomal dominant autosomal recessive sex linked dominant sex linked recessive ...
(Blood Typing).
... If Rh- blood mixed with Rh+ blood, then person with Rh- blood makes anti-Rh+ against Rh+ blood!...leads to agglutination When can this occur? Transfusions and pregnancy ...
... If Rh- blood mixed with Rh+ blood, then person with Rh- blood makes anti-Rh+ against Rh+ blood!...leads to agglutination When can this occur? Transfusions and pregnancy ...
The Rh factor
... O : type O individuals can donate blood to anyone ( because their blood has no antigens ) , but can receive blood only from other type O individual . ( because blood with any antigens is seen as foreign ) A : type A individuals can donate to other type A individuals and type AB individuals type ...
... O : type O individuals can donate blood to anyone ( because their blood has no antigens ) , but can receive blood only from other type O individual . ( because blood with any antigens is seen as foreign ) A : type A individuals can donate to other type A individuals and type AB individuals type ...
ANTI-H LECTIN
... The H antigen is a basic blood group antigen present in human beings. There is considerable variation in the H antigen content in different individuals of the same ABO group but the general pattern indicates their strength as O>A2>A2B>B>A1>A1B. Water soluble H substance can also be demonstrated in s ...
... The H antigen is a basic blood group antigen present in human beings. There is considerable variation in the H antigen content in different individuals of the same ABO group but the general pattern indicates their strength as O>A2>A2B>B>A1>A1B. Water soluble H substance can also be demonstrated in s ...
How to donate blood - Greater Madison Chamber of Commerce
... The Madison Holiday Blood Drive is the largest day-long drive within the American Red Cross Badger-Hawkeye Blood Services Region. All presenting donors at the Alliant Energy Center will receive a Red Cross T-shirt, while supplies last, and raffle prizes will be donated by local businesses. Free park ...
... The Madison Holiday Blood Drive is the largest day-long drive within the American Red Cross Badger-Hawkeye Blood Services Region. All presenting donors at the Alliant Energy Center will receive a Red Cross T-shirt, while supplies last, and raffle prizes will be donated by local businesses. Free park ...