Slide 1
... reproduction, defense, and structure. Nitrogen makes up 78% of atmosphere as N2 Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are very important N2 needs to be “fixed” before it can be used by most living things. ...
... reproduction, defense, and structure. Nitrogen makes up 78% of atmosphere as N2 Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are very important N2 needs to be “fixed” before it can be used by most living things. ...
Chapter 5: Marine Sediments
... - filters (sugar refinement, brewing, and swimming pool filters) - mild abrasives (in such products as toothpaste, facial scrubs, and household cleaning and polishing compounds) - absorbent (chemical spills and as pest control) - chemical carrier (in paint and dynamite) - optical quality glass (beca ...
... - filters (sugar refinement, brewing, and swimming pool filters) - mild abrasives (in such products as toothpaste, facial scrubs, and household cleaning and polishing compounds) - absorbent (chemical spills and as pest control) - chemical carrier (in paint and dynamite) - optical quality glass (beca ...
report - Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
... experiments, in situ observations and modeling studies. Modeling activities range from small-scale studies within the sea ice and sediment compartments to local coastal regions of strategic importance and the large-scale systems of the Arctic Ocean and neighboring seas. 5.3. CERC in Ocean Science an ...
... experiments, in situ observations and modeling studies. Modeling activities range from small-scale studies within the sea ice and sediment compartments to local coastal regions of strategic importance and the large-scale systems of the Arctic Ocean and neighboring seas. 5.3. CERC in Ocean Science an ...
The Assessment of the Forestry Carbon Sinks and the Effect... Global Climate Change
... classified into three categories: Absorbing carbon directly by the forests; Absorbing carbon indirectly by timbers and other wood products; The mitigation caused by wood substitution. Therefore, we should increase the carbon stocks in both aspects: the interior and the extensive. The activities are ...
... classified into three categories: Absorbing carbon directly by the forests; Absorbing carbon indirectly by timbers and other wood products; The mitigation caused by wood substitution. Therefore, we should increase the carbon stocks in both aspects: the interior and the extensive. The activities are ...
Estuarine Environments
... • Despite long-term storage of OM, salt marshes are a source of N and P to estuaries ...
... • Despite long-term storage of OM, salt marshes are a source of N and P to estuaries ...
Organic Naming Notes
... - In this example there is a chain with 9 (nonane) 2. Number the chain starting with one that will give the attached groups (substituent group) the lowest number. 3. Add numbers of the parent chain carbon bonded to the names of the substituent group ...
... - In this example there is a chain with 9 (nonane) 2. Number the chain starting with one that will give the attached groups (substituent group) the lowest number. 3. Add numbers of the parent chain carbon bonded to the names of the substituent group ...
Carbon cycle dice game
... leaves its source rocks because it is more buoyant than the surrounding water, and it rises to the surface at the future site of Los Angeles, where it traps unwary mammoths, ground sloths, and dire wolves. In the sun and air, the oil gets gummy and becomes tar, and is eventually oxidized to carbon d ...
... leaves its source rocks because it is more buoyant than the surrounding water, and it rises to the surface at the future site of Los Angeles, where it traps unwary mammoths, ground sloths, and dire wolves. In the sun and air, the oil gets gummy and becomes tar, and is eventually oxidized to carbon d ...
Coastal Marine Ecology - Artifact2
... “propagules” that drop from the tree and either take root where they fall, or drift away on the tide. As they grow, they build up more land as the roots trap sediment that otherwise would have choked out coral reefs. ...
... “propagules” that drop from the tree and either take root where they fall, or drift away on the tide. As they grow, they build up more land as the roots trap sediment that otherwise would have choked out coral reefs. ...
Chapter 8 Review
... • Rocky and sandy shores hot different types of organisms • The area of shoreline between low and high tide is called the intertidal zone. Organisms who live here must deal with changes in salinity, heavy crashing waves during high tide, and loss of water and increase in heat during low tide. • On ...
... • Rocky and sandy shores hot different types of organisms • The area of shoreline between low and high tide is called the intertidal zone. Organisms who live here must deal with changes in salinity, heavy crashing waves during high tide, and loss of water and increase in heat during low tide. • On ...
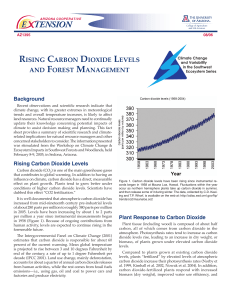
Rising Carbon Dioxide Levels and Forest Management
... storing it in plants, at least until a stand-replacing fire occurs. Not only does a stand-replacing fire release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere as it burns plants and wood, it arguably may cause a reduction in the disturbed stand’s ability to sequester carbon until a full tree canopy is reestablis ...
... storing it in plants, at least until a stand-replacing fire occurs. Not only does a stand-replacing fire release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere as it burns plants and wood, it arguably may cause a reduction in the disturbed stand’s ability to sequester carbon until a full tree canopy is reestablis ...
Ecology Independent Study
... 39. Why does the amount of energy present in the primary producer level represent the TOTAL amount of energy available for higher trophic levels? Why does only 10% get passed forward from each level? ...
... 39. Why does the amount of energy present in the primary producer level represent the TOTAL amount of energy available for higher trophic levels? Why does only 10% get passed forward from each level? ...
Carbonate Chemistry of the Oceans
... amounts of nutrients remain in the water all year round because of a limited amount of iron. If they were taken up, then the pCO2 in the ocean, and subsequently the pCO2 in the atmosphere, could be drawn down further. There is evidence that this happened during glacial periods. Ice-core records show ...
... amounts of nutrients remain in the water all year round because of a limited amount of iron. If they were taken up, then the pCO2 in the ocean, and subsequently the pCO2 in the atmosphere, could be drawn down further. There is evidence that this happened during glacial periods. Ice-core records show ...
Ocean Waters and the Ocean Floor
... salt. This can be expressed as 35 ppt (parts per thousand). This is also called salinity, or the ratio of salts to pure water. • Salt is mainly sodium chloride, or common table salt. • 8 different elements make up the 5 types of salt. • In areas of heavy precipitation, the salt concentration is less ...
... salt. This can be expressed as 35 ppt (parts per thousand). This is also called salinity, or the ratio of salts to pure water. • Salt is mainly sodium chloride, or common table salt. • 8 different elements make up the 5 types of salt. • In areas of heavy precipitation, the salt concentration is less ...
Organic Geochemistry - DISL Sharepoint Site
... Burial will be a small fraction of the carbon delivered to the sediments. Most will be respired to CO2 and diffuse back to water column. ...
... Burial will be a small fraction of the carbon delivered to the sediments. Most will be respired to CO2 and diffuse back to water column. ...
Biogeochemical Cycles Note Slides File
... • Photosynthesis = movement of CO2 from air into food/sugar found in biomass of autotrophs • Decomposition = release of carbon gases into atmosphere by decay of biomass by decomposers (like bacteria) • Cellular Respiration = release of CO2 into atmosphere from breakdown of food/sugar • Combustion = ...
... • Photosynthesis = movement of CO2 from air into food/sugar found in biomass of autotrophs • Decomposition = release of carbon gases into atmosphere by decay of biomass by decomposers (like bacteria) • Cellular Respiration = release of CO2 into atmosphere from breakdown of food/sugar • Combustion = ...
GoConqr - Editing: limestone to plate tectonics
... earthquakes and volcanic eruptions will occur ...
... earthquakes and volcanic eruptions will occur ...
Prescott`s Microbiology, 9th Edition 30 Microorganisms in Marine
... a. Aquatic environments are low-oxygen diffusion environments; this can lead to the formation of hypoxic or anoxic zones, which are inhabited by anaerobic microbes b. At higher temperatures and with lower pressure the solubility of oxygen in water is further decreased 2. Carbon dioxide a. Important ...
... a. Aquatic environments are low-oxygen diffusion environments; this can lead to the formation of hypoxic or anoxic zones, which are inhabited by anaerobic microbes b. At higher temperatures and with lower pressure the solubility of oxygen in water is further decreased 2. Carbon dioxide a. Important ...
Study Questions - Geocycles, communities, populations
... 7. What is carrying capacity? What role does it play in logistic growth? 8. What are examples of factors that can limit population size? 9. What does r represent in these two growth models? What factors can affect r? 10. What type of growth is shown by human populations? What are the limiting factor ...
... 7. What is carrying capacity? What role does it play in logistic growth? 8. What are examples of factors that can limit population size? 9. What does r represent in these two growth models? What factors can affect r? 10. What type of growth is shown by human populations? What are the limiting factor ...
Chapter 3: Feedbacks in the Carbon Cycle
... organic matter in soils. Enhanced storage would serve as a sink for excess CO2 and thus act as a negative feedback, decreasing the rate of atmospheric CO2 increase. Whether enhanced fertilization can be sustained, and whether enhanced photosynthesis will translate to increased carbon storage, are cu ...
... organic matter in soils. Enhanced storage would serve as a sink for excess CO2 and thus act as a negative feedback, decreasing the rate of atmospheric CO2 increase. Whether enhanced fertilization can be sustained, and whether enhanced photosynthesis will translate to increased carbon storage, are cu ...
Long-term grazing exclusion did not provide adequate soil carbon
... in northern Kenyan rangelands for climate change mitigation and local livelihoods diversification. However, to qualify for carbon credits, carbon markets are requiring additional carbon storage beyond what is existing under normal-land use practices. Grazing exclusion is often thought to improve ran ...
... in northern Kenyan rangelands for climate change mitigation and local livelihoods diversification. However, to qualify for carbon credits, carbon markets are requiring additional carbon storage beyond what is existing under normal-land use practices. Grazing exclusion is often thought to improve ran ...
background project results - California Sea Grant
... generally predict shifts in the timing of snowmelt off the Sierras. Reduced freshwater flows, along with continued water diversions, are expected to lead to higher overall salinities in the delta, as well. The dominant plants in the low-salinity and freshwater marshes of the estuary were Schoenopl ...
... generally predict shifts in the timing of snowmelt off the Sierras. Reduced freshwater flows, along with continued water diversions, are expected to lead to higher overall salinities in the delta, as well. The dominant plants in the low-salinity and freshwater marshes of the estuary were Schoenopl ...
Strategic Framework for Fisheries, Aquaculture and Climate Change
... forests and oceans to absorb and bury CO2 is a crucial aspect of mitigation. The contribution of forests in sequestering carbon is well known while, in contrast, the critical role of the oceans and waters has been overlooked. It is important to highlight the vital contribution of the oceans in reduc ...
... forests and oceans to absorb and bury CO2 is a crucial aspect of mitigation. The contribution of forests in sequestering carbon is well known while, in contrast, the critical role of the oceans and waters has been overlooked. It is important to highlight the vital contribution of the oceans in reduc ...
Earth`s Life-Support Systems pp
... The greenhouse effect occurs when certain gases in the atmosphere trap infrared radiation (heat). This effect makes the planet warmer, in the same way a greenhouse keeps its inside temperature warmer. The greenhouse effect is caused by greenhouse gases; the most important in Earth's atmosphere are: ...
... The greenhouse effect occurs when certain gases in the atmosphere trap infrared radiation (heat). This effect makes the planet warmer, in the same way a greenhouse keeps its inside temperature warmer. The greenhouse effect is caused by greenhouse gases; the most important in Earth's atmosphere are: ...
Species Loss and Aboveground Carbon Storage in a Tropical Forest
... Tropical forest biodiversity is declining, but the resulting effects on key ecosystem services, such as carbon storage and sequestration, remain unknown. We assessed the influence of the loss of tropical tree species on carbon storage by simulating 18 possible extinction scenarios within a well-stud ...
... Tropical forest biodiversity is declining, but the resulting effects on key ecosystem services, such as carbon storage and sequestration, remain unknown. We assessed the influence of the loss of tropical tree species on carbon storage by simulating 18 possible extinction scenarios within a well-stud ...