Q: Roll a fair die. (a) What is the expected number of different faces
... six faces when the die is tossed 6 times. If we don’t use the above formula, we can directly calculate ...
... six faces when the die is tossed 6 times. If we don’t use the above formula, we can directly calculate ...
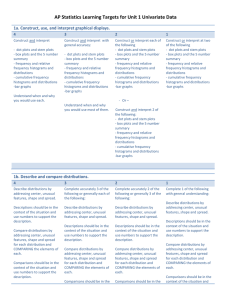
Descriptive Statistics
... of the negative deviations above it and the sum of the positive deviations about it. 3. (Y - )2 is minimal – the mean is the point that makes the sum of squared deviations about it as small as possible. This definition of the mean will be very important later. ...
... of the negative deviations above it and the sum of the positive deviations about it. 3. (Y - )2 is minimal – the mean is the point that makes the sum of squared deviations about it as small as possible. This definition of the mean will be very important later. ...
Bayesian networks – exercises
... Conclusion: Both the sampling methods are consistent and shall converge to the target probability value .5161. The number of samples must be much larger anyway. Rejection sampling suffers from a large portion of generated and further unemployed samples (see s2 and s6 ). Their proportion grows for un ...
... Conclusion: Both the sampling methods are consistent and shall converge to the target probability value .5161. The number of samples must be much larger anyway. Rejection sampling suffers from a large portion of generated and further unemployed samples (see s2 and s6 ). Their proportion grows for un ...
Research Methods I
... options n, mean, stderr, t, and prt These statistics will be computed for the difference variable T will give the t-value and its probability, testing the null hypothesis that the variable DISS comes from a population whose mean is zero. The mean gives the average difference score. If p<.05 we can s ...
... options n, mean, stderr, t, and prt These statistics will be computed for the difference variable T will give the t-value and its probability, testing the null hypothesis that the variable DISS comes from a population whose mean is zero. The mean gives the average difference score. If p<.05 we can s ...
Statistics
... using it to summarise a data set: • It is heavily influenced by any extreme/outlying points within the data set, and when calculated incorporating these points the mean value could be misleading with reference to the rest of the data set. • It gives no information as to how the data within the set i ...
... using it to summarise a data set: • It is heavily influenced by any extreme/outlying points within the data set, and when calculated incorporating these points the mean value could be misleading with reference to the rest of the data set. • It gives no information as to how the data within the set i ...
CHAPTER SEVEN Hypothesis Testing with z Tests NOTE TO
... Make It Your Own: Short-Term Memory Use Miller’s classic paper as the basis for this class demonstration. See Miller, G. A. (March 1956). The magical number seven, plus or minus two: some limits on our capacity for processing information. Psychological Review, 63(2), 81–97. To view or purchase this ...
... Make It Your Own: Short-Term Memory Use Miller’s classic paper as the basis for this class demonstration. See Miller, G. A. (March 1956). The magical number seven, plus or minus two: some limits on our capacity for processing information. Psychological Review, 63(2), 81–97. To view or purchase this ...
A ∩ B
... person is a high school graduate? There are a total of 340 people in the sample that own a home. Because there are 221 high school graduates among the 340 home owners, the desired probability is P(is a high school graduate given owns a home) = 2. If we know that a person is a high school graduate, w ...
... person is a high school graduate? There are a total of 340 people in the sample that own a home. Because there are 221 high school graduates among the 340 home owners, the desired probability is P(is a high school graduate given owns a home) = 2. If we know that a person is a high school graduate, w ...
4.2 powerpoint
... or a computer. For instance, you can find binomial probabilities by using your TI-83, TI-84 or Excel on the computer. Go to 2nd VARS on your calculator. Arrow down to binompdf which is choice A. Click Enter. Trials = 6, P (Probability = .5, x values: 3 ENTER You should get : .3125. Please practice t ...
... or a computer. For instance, you can find binomial probabilities by using your TI-83, TI-84 or Excel on the computer. Go to 2nd VARS on your calculator. Arrow down to binompdf which is choice A. Click Enter. Trials = 6, P (Probability = .5, x values: 3 ENTER You should get : .3125. Please practice t ...
X - Erwin Sitompul
... Joint Probability Distributions If X and Y are two discrete random variables, the probability distribution for their simultaneous occurrence can be represented by a function with values f(x, y) for any pair of values (x, y) within the range of the random variables X and Y. Such function is refer ...
... Joint Probability Distributions If X and Y are two discrete random variables, the probability distribution for their simultaneous occurrence can be represented by a function with values f(x, y) for any pair of values (x, y) within the range of the random variables X and Y. Such function is refer ...