ETEE3211 Fall 2003
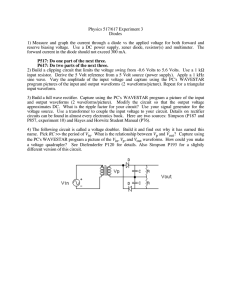
... EXTRA CREDIT (20 points max): An integrated circuit requires plus and minus voltages for their operation. Using the circuit to the right, determine the transformer winding ratio and the capacitor size needed to get a maximum of 14V and a minimum of 12V at the output when the input is 120Vrms 60Hz, V ...
... EXTRA CREDIT (20 points max): An integrated circuit requires plus and minus voltages for their operation. Using the circuit to the right, determine the transformer winding ratio and the capacitor size needed to get a maximum of 14V and a minimum of 12V at the output when the input is 120Vrms 60Hz, V ...
EI010 304 Electronic Devices and Circuits
... Band theory of solids: Energy band structure of Metals, Semi conductors and Insulators. Intrinsic material - Electron Hole pair- Fermi level- Doping- Extrinsic material- Effect of temperature. Semi conductor diodes: Theory of PN junction diode- Energy band structure- Diode equation. Space charge and ...
... Band theory of solids: Energy band structure of Metals, Semi conductors and Insulators. Intrinsic material - Electron Hole pair- Fermi level- Doping- Extrinsic material- Effect of temperature. Semi conductor diodes: Theory of PN junction diode- Energy band structure- Diode equation. Space charge and ...
Physics 517/617 Experiment 3 Diodes
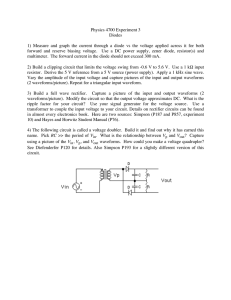
... input resistor. Derive the 5 Volt reference from a 5 Volt source (power supply). Apply a 1 kHz sine wave. Vary the amplitude of the input voltage and capture using the PC's WAVESTAR program pictures of the input and output waveforms (2 waveforms/picture). Repeat for a triangular input waveform. 3) B ...
... input resistor. Derive the 5 Volt reference from a 5 Volt source (power supply). Apply a 1 kHz sine wave. Vary the amplitude of the input voltage and capture using the PC's WAVESTAR program pictures of the input and output waveforms (2 waveforms/picture). Repeat for a triangular input waveform. 3) B ...
Physics 4700 Experiment 3 Diodes
... Vary the amplitude of the input voltage and capture pictures of the input and output waveforms (2 waveforms/picture). Repeat for a triangular input waveform. 3) Build a full wave rectifier. Capture a picture of the input and output waveforms (2 waveforms/picture). Modify the circuit so that the outp ...
... Vary the amplitude of the input voltage and capture pictures of the input and output waveforms (2 waveforms/picture). Repeat for a triangular input waveform. 3) Build a full wave rectifier. Capture a picture of the input and output waveforms (2 waveforms/picture). Modify the circuit so that the outp ...
rectifier report - Kaushik Science Projects
... A P-n junction is said to be reverse biased if the positive terminal of the external battery B is connected to n-side and the negative terminal to p-side of the p-n junction. In reverse biasing, the reverse bias voltage supports the potential barrier VB. (Now the majority carriers are pulled away fr ...
... A P-n junction is said to be reverse biased if the positive terminal of the external battery B is connected to n-side and the negative terminal to p-side of the p-n junction. In reverse biasing, the reverse bias voltage supports the potential barrier VB. (Now the majority carriers are pulled away fr ...
Precision Rectifiers
... • Since the (—) input is at ground potential, diode D1 is reverse biased. • Input current is set by E/Ri and gain by ─Rf/Ri. • Remember that this gain equation applies only for negative inputs, and Vo can only be positive or zero. ...
... • Since the (—) input is at ground potential, diode D1 is reverse biased. • Input current is set by E/Ri and gain by ─Rf/Ri. • Remember that this gain equation applies only for negative inputs, and Vo can only be positive or zero. ...
ZXM66P03N8 30V P-CHANNEL ENHANCEMENT MODE MOSFET
... For international sales offices visit www.zetex.com/offices Zetex products are distributed worldwide. For details, see www.zetex.com/salesnetwork This publication is issued to provide outline information only which (unless agreed by the Company in writing) may not be used, applied or reproduced for ...
... For international sales offices visit www.zetex.com/offices Zetex products are distributed worldwide. For details, see www.zetex.com/salesnetwork This publication is issued to provide outline information only which (unless agreed by the Company in writing) may not be used, applied or reproduced for ...
Electronics - Mill Creek High School
... Do not produce heat (wasted energy) so they are more efficient than incandescent bulbs ...
... Do not produce heat (wasted energy) so they are more efficient than incandescent bulbs ...
EE362L, Fall 2006
... Question – so if a power line wire isn’t insulated, why can a bird safely sit on the wire? Answer – because the bird is insulated from ground and not near wires of other phases. However, it is possible for large birds with long wing spans to make a phase-to-phase connection. ...
... Question – so if a power line wire isn’t insulated, why can a bird safely sit on the wire? Answer – because the bird is insulated from ground and not near wires of other phases. However, it is possible for large birds with long wing spans to make a phase-to-phase connection. ...
Electronics Engineering (NEC-101)
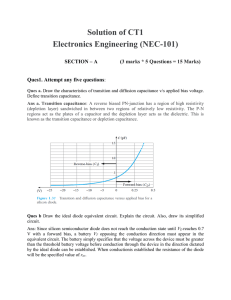
... Extrinsic Semiconductor: Where as an extrinsic semiconductor is an improved intrinsic semiconductor with a small amount of impurities added by a process, known as doping, which alters the electrical properties of the semiconductor and improves its conductivity. Introducing impurities into the semico ...
... Extrinsic Semiconductor: Where as an extrinsic semiconductor is an improved intrinsic semiconductor with a small amount of impurities added by a process, known as doping, which alters the electrical properties of the semiconductor and improves its conductivity. Introducing impurities into the semico ...
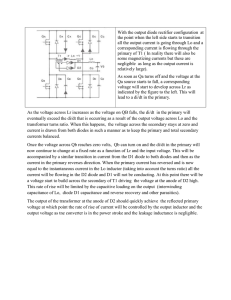
With the output diode rectifier configuration at the point when the left
... With the output diode rectifier configuration at the point when the left side starts to transition all the output current is going through Lo and a corresponding current is flowing through the primary of T1 ( In reality there will also be some magnetizing currents but these are negligible as long as ...
... With the output diode rectifier configuration at the point when the left side starts to transition all the output current is going through Lo and a corresponding current is flowing through the primary of T1 ( In reality there will also be some magnetizing currents but these are negligible as long as ...
Section B3: The Practical Diode
... with a slope close to zero. This results in a near zero conductance (g=i/v) or an infinite resistance (r=v/i). 2. For the reverse bias situation, vD < 0 and the exponential term is less than one. If the reverse bias magnitude is greater than a few VT, the exponential term becomes negligible and iD≅- ...
... with a slope close to zero. This results in a near zero conductance (g=i/v) or an infinite resistance (r=v/i). 2. For the reverse bias situation, vD < 0 and the exponential term is less than one. If the reverse bias magnitude is greater than a few VT, the exponential term becomes negligible and iD≅- ...
EE 101 Lab 4 Digital Signals
... A diode is a two-terminal semiconductor circuit element that allows electrical current to pass in only one direction. In effect it functions as a “flow valve” – current is allowed to pass in one direction through the diode, but is prevented from passing through in the opposite direction. Diodes are ...
... A diode is a two-terminal semiconductor circuit element that allows electrical current to pass in only one direction. In effect it functions as a “flow valve” – current is allowed to pass in one direction through the diode, but is prevented from passing through in the opposite direction. Diodes are ...
Diodes
... Next use LabView to measure the V-I characteristic for a Zener diode, the 1N4734, which has a Zener voltage of 5.6 V. (Note: In the forward condition, current flows out of the cathode which is the terminal labeled with the band.) Plot the V-I characteristic using the LabView program and note the dra ...
... Next use LabView to measure the V-I characteristic for a Zener diode, the 1N4734, which has a Zener voltage of 5.6 V. (Note: In the forward condition, current flows out of the cathode which is the terminal labeled with the band.) Plot the V-I characteristic using the LabView program and note the dra ...
Physics of a BJT
... Depletion region shrinks due to charges from the battery. The electric field is weaker. Majority carrier can cross via diffusion; Greater diffusion current. Current flows from P side to N side ...
... Depletion region shrinks due to charges from the battery. The electric field is weaker. Majority carrier can cross via diffusion; Greater diffusion current. Current flows from P side to N side ...
Charge
... Semiconductor materials doped to contain excess free electrons are considered n-type semiconductors. Even though the added impurity created excess free electrons, the material is still neutral in charge. It has been found that in n-type materials the free electron concentration is approximately equa ...
... Semiconductor materials doped to contain excess free electrons are considered n-type semiconductors. Even though the added impurity created excess free electrons, the material is still neutral in charge. It has been found that in n-type materials the free electron concentration is approximately equa ...
Introduction and Digital Images
... they are reverse biased. This is called the peak inverse voltage (PIV). The PIV depends on the type of rectifier circuit and the maximum secondary voltage. For example, in a full-wave circuit, if one diode is conducting (assuming 0 V drop), the other diode has the secondary voltage across it as you ...
... they are reverse biased. This is called the peak inverse voltage (PIV). The PIV depends on the type of rectifier circuit and the maximum secondary voltage. For example, in a full-wave circuit, if one diode is conducting (assuming 0 V drop), the other diode has the secondary voltage across it as you ...
Chapter 24: Electronics
... current and voltage. 2. Explain the difference between a p-type and an n-type semiconductor. 3. Construct a half-wave rectifier circuit with a diode. 4. Construct a transistor switch. 5. Describe the relationship between inputs and outputs of the four basic logic gates. 6. Construct an adding circui ...
... current and voltage. 2. Explain the difference between a p-type and an n-type semiconductor. 3. Construct a half-wave rectifier circuit with a diode. 4. Construct a transistor switch. 5. Describe the relationship between inputs and outputs of the four basic logic gates. 6. Construct an adding circui ...
Physics First Ch 24 ppt
... current and voltage. 2. Explain the difference between a p-type and an n-type semiconductor. 3. Construct a half-wave rectifier circuit with a diode. 4. Construct a transistor switch. 5. Describe the relationship between inputs and outputs of the four basic logic gates. 6. Construct an adding circui ...
... current and voltage. 2. Explain the difference between a p-type and an n-type semiconductor. 3. Construct a half-wave rectifier circuit with a diode. 4. Construct a transistor switch. 5. Describe the relationship between inputs and outputs of the four basic logic gates. 6. Construct an adding circui ...
NTUST-EE-2013S
... • When a pn junction is formed, electrons in the n-material diffuse across the junction and recombine with holes in the pmaterial. This action continues until the voltage of the barrier repels further diffusion. Further diffusion across the barrier requires the application of a voltage. • The pn jun ...
... • When a pn junction is formed, electrons in the n-material diffuse across the junction and recombine with holes in the pmaterial. This action continues until the voltage of the barrier repels further diffusion. Further diffusion across the barrier requires the application of a voltage. • The pn jun ...
Diodes
... V-I characteristics of diodes using LabView Repeat the measurement of I vs. V for a standard signal diode using the LabView program, I_vs_v, employing a 1kΩ resistor for the standard within the measurements. To find instructions on connecting the LabView board to your circuit, make selections within ...
... V-I characteristics of diodes using LabView Repeat the measurement of I vs. V for a standard signal diode using the LabView program, I_vs_v, employing a 1kΩ resistor for the standard within the measurements. To find instructions on connecting the LabView board to your circuit, make selections within ...
Ch 5 Homework - ECM
... 20. A(n) ____ is an electrical component that converts AC to DC by allowing voltage and current to move in only one direction. ...
... 20. A(n) ____ is an electrical component that converts AC to DC by allowing voltage and current to move in only one direction. ...
Basic Electrical Circuits
... Current is a flow of electricity that is not constant. In fact the direction of current flow periodically switches direction. Examples of AC are: ...
... Current is a flow of electricity that is not constant. In fact the direction of current flow periodically switches direction. Examples of AC are: ...
expt8
... drop of about 0.6 V across the junction when a current of about 5 mA is flowing through the junction. Similarly all forward biased Ge p-n junctions have a voltage drop of about 0.25 V at 1 mA. If an ordinary diode is reverse biased, only a very small current (106 - 1010A) flows until the peak inve ...
... drop of about 0.6 V across the junction when a current of about 5 mA is flowing through the junction. Similarly all forward biased Ge p-n junctions have a voltage drop of about 0.25 V at 1 mA. If an ordinary diode is reverse biased, only a very small current (106 - 1010A) flows until the peak inve ...
Diode

In electronics, a diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance to the flow of current in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. A vacuum tube diode has two electrodes, a plate (anode) and a heated cathode. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of crystals' rectifying abilities was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. The first semiconductor diodes, called cat's whisker diodes, developed around 1906, were made of mineral crystals such as galena. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconductors such as selenium or germanium are sometimes used.