output - Innovetech
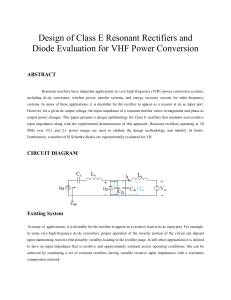
... systems. In many of these applications, it is desirable for the rectifier to appear as a resistor at its ac input port. However, for a given dc output voltage, the input impedance of a resonant rectifier varies in magnitude and phase as output power changes. This paper presents a design methodology ...
... systems. In many of these applications, it is desirable for the rectifier to appear as a resistor at its ac input port. However, for a given dc output voltage, the input impedance of a resonant rectifier varies in magnitude and phase as output power changes. This paper presents a design methodology ...
classes/2014/electronics/Lecture 3
... • The maximum reverse-bias potential that can be applied before entering the Zener region is called the peak inverse voltage (referred to simply as the PIV rating) or the peak reverse voltage (denoted by PRV rating). ...
... • The maximum reverse-bias potential that can be applied before entering the Zener region is called the peak inverse voltage (referred to simply as the PIV rating) or the peak reverse voltage (denoted by PRV rating). ...
experiment no 4
... (200 Hz) as input to the circuit. Connect the diode voltage VD to CH-2 and the Difference amplifier output VA to CH-1. Make sure that you are getting waveforms on these channels. (ii) Put the CRO into XY mode and adjust the beam such that the origin is at the centre of the CRO display. (iii) See the ...
... (200 Hz) as input to the circuit. Connect the diode voltage VD to CH-2 and the Difference amplifier output VA to CH-1. Make sure that you are getting waveforms on these channels. (ii) Put the CRO into XY mode and adjust the beam such that the origin is at the centre of the CRO display. (iii) See the ...
microwave solid state devices
... A main advantage is their high power capability. These diodes are used in a variety of applications from low power radar systems to alarms. Nevertheless these diodes make excellent microwave generators for many applications. An alternating signal is generated simply by applying a DC supply when a su ...
... A main advantage is their high power capability. These diodes are used in a variety of applications from low power radar systems to alarms. Nevertheless these diodes make excellent microwave generators for many applications. An alternating signal is generated simply by applying a DC supply when a su ...
College of Micronesia – FSM
... General Objectives: This introductory course is designed for students to investigate the operation of semiconductors. Student will discover how semiconductor components such as diodes, ...
... General Objectives: This introductory course is designed for students to investigate the operation of semiconductors. Student will discover how semiconductor components such as diodes, ...
Slide 1
... at kHz to MHz rates – this high frequency modulation is useful for improving the signal-to-noise ratio in many experiments. For example, detecting gases based on their rotational vibrational ...
... at kHz to MHz rates – this high frequency modulation is useful for improving the signal-to-noise ratio in many experiments. For example, detecting gases based on their rotational vibrational ...
diodelab
... exponential term depends on Vbi + V, but when V = 0 this term must cancel Io, so the Vbi can just be absorbed into a coefficient Io. Together, all this leads to an ideal equation. In forward bias Shockley's derivation assumed that the electrons and holes cross the depletion region associated with Vb ...
... exponential term depends on Vbi + V, but when V = 0 this term must cancel Io, so the Vbi can just be absorbed into a coefficient Io. Together, all this leads to an ideal equation. In forward bias Shockley's derivation assumed that the electrons and holes cross the depletion region associated with Vb ...
The Power Diode
... (resistor R), the current flowing in the load resistor is therefore proportional to the voltage (Ohm´s Law), and the voltage across the load resistor is the same as the supply voltage, Vs (minus Vf), that is the "DC" voltage across the load is sinusoidal for the first half cycle only. Then Vout = V ...
... (resistor R), the current flowing in the load resistor is therefore proportional to the voltage (Ohm´s Law), and the voltage across the load resistor is the same as the supply voltage, Vs (minus Vf), that is the "DC" voltage across the load is sinusoidal for the first half cycle only. Then Vout = V ...
For reverse bias
... For silicon diodes, the typical forward voltage is 0.7 volts, nominal. For germanium diodes, the forward voltage is only 0.3 volts. Voltage drop across a conducting, semiconductor diode remains constant at 0.7 volts for silicon and 0.3 volts for germanium. ...
... For silicon diodes, the typical forward voltage is 0.7 volts, nominal. For germanium diodes, the forward voltage is only 0.3 volts. Voltage drop across a conducting, semiconductor diode remains constant at 0.7 volts for silicon and 0.3 volts for germanium. ...
Alloys and elements
... first of these, the light-emitting diode (LED), was developed to replace the fragile, short-life incandescent light bulbs used to indicate on/off conditions on panels. A LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE is a diode which, when forward biased, produces visible light. The light may be red, green, or amber, dependi ...
... first of these, the light-emitting diode (LED), was developed to replace the fragile, short-life incandescent light bulbs used to indicate on/off conditions on panels. A LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE is a diode which, when forward biased, produces visible light. The light may be red, green, or amber, dependi ...
hH Schottky Diode Voltage Doubler Application Note 956-4
... Interchanging the chips does not affect performance. The circuit may also be assembled using ...
... Interchanging the chips does not affect performance. The circuit may also be assembled using ...
LDP-CW 20-50
... The capability ranges from continuous output current to analog modulated waveforms like sinusoidal, rectangular or triangular. The modulation is limited usually by the load inductance. Intended field of application are laser soldering and welding as well as generic surface treatment and show lasers. ...
... The capability ranges from continuous output current to analog modulated waveforms like sinusoidal, rectangular or triangular. The modulation is limited usually by the load inductance. Intended field of application are laser soldering and welding as well as generic surface treatment and show lasers. ...
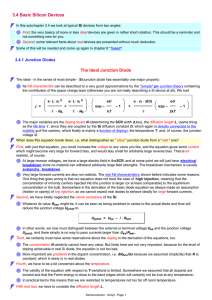
3.4 Basic Silicon Devices
... In other words, we equate some relevant length dCon of the device with the average distance that minority carriers travel before they disappear, and ttran is the time they move around. This makes not only immediate sense but has far-reaching consequences, as we will see, e.g. in chapter 8. Some majo ...
... In other words, we equate some relevant length dCon of the device with the average distance that minority carriers travel before they disappear, and ttran is the time they move around. This makes not only immediate sense but has far-reaching consequences, as we will see, e.g. in chapter 8. Some majo ...
BJT-definitions and models
... 1 – The collector must be positive than the emitter. 2 – The base-emitter and base-collector circuits behave like diodes. Normally the baseemitter diode is conducting and the base-collector diode is reverse-biased 3 – When 1 and 2 are obeyed Ic is proportional to Ib (Ic = beta . Ib) Both Ib and Ic f ...
... 1 – The collector must be positive than the emitter. 2 – The base-emitter and base-collector circuits behave like diodes. Normally the baseemitter diode is conducting and the base-collector diode is reverse-biased 3 – When 1 and 2 are obeyed Ic is proportional to Ib (Ic = beta . Ib) Both Ib and Ic f ...
Schottky diode I-V Characteristics
... (mobile electrons) play a significant role in normal operation of the device. The majority carriers are quickly injected into the conduction band of the metal contact on the other side of the diode to become free moving electrons. Therefore no slow, random recombination of n- and p- type carriers is ...
... (mobile electrons) play a significant role in normal operation of the device. The majority carriers are quickly injected into the conduction band of the metal contact on the other side of the diode to become free moving electrons. Therefore no slow, random recombination of n- and p- type carriers is ...
Power Diodes - Dr. Imtiaz Hussain
... • The diode current does not stop at zero, instead it grows in the negative direction to Irr called “peak reverse recovery current” which can be comparable to IF. • Voltage drop across the diode does not change appreciably from its steady state value till the diode current reaches reverse recovery l ...
... • The diode current does not stop at zero, instead it grows in the negative direction to Irr called “peak reverse recovery current” which can be comparable to IF. • Voltage drop across the diode does not change appreciably from its steady state value till the diode current reaches reverse recovery l ...
EEE 531--Semiconductor Device Theory I
... EEE 531--Semiconductor Device Theory I Catalog Description: Transport and recombination theory, pn and Schottky barrier diodes, bipolar and junction field-effect transistors, and MOS capacitors and transistors. ...
... EEE 531--Semiconductor Device Theory I Catalog Description: Transport and recombination theory, pn and Schottky barrier diodes, bipolar and junction field-effect transistors, and MOS capacitors and transistors. ...
971 Quiz 01
... (d) When a transistor is used as a switch it must be either OFF or fully ON. In the fully ON state the voltage VBE across the transistor is almost zero and the transistor is said to be saturated. In this case the both junction of transistor should be under the forward bias and the collector current ...
... (d) When a transistor is used as a switch it must be either OFF or fully ON. In the fully ON state the voltage VBE across the transistor is almost zero and the transistor is said to be saturated. In this case the both junction of transistor should be under the forward bias and the collector current ...
tunnel diode - UniMAP Portal
... • typical device lengths L range: few to several hundreds • Fig (a) & (b): energy band diagram at thermal equilibrium & electric-field distribution when V=3VT • VT: product of threshold field ET & device length L • To improve performance: use 2-zone cathode contact (consists of high-field zone & ...
... • typical device lengths L range: few to several hundreds • Fig (a) & (b): energy band diagram at thermal equilibrium & electric-field distribution when V=3VT • VT: product of threshold field ET & device length L • To improve performance: use 2-zone cathode contact (consists of high-field zone & ...
Diodes, Transistors and Mixers
... • Electrostatic barrier can be created by junctions Conductivity when charge carriers have enough energy to overcome barrier (usually thermionic emission) PN Junctions ...
... • Electrostatic barrier can be created by junctions Conductivity when charge carriers have enough energy to overcome barrier (usually thermionic emission) PN Junctions ...
Diodes, Transistors and Mixers
... • Electrostatic barrier can be created by junctions Conductivity when charge carriers have enough energy to overcome barrier (usually thermionic emission) PN Junctions ...
... • Electrostatic barrier can be created by junctions Conductivity when charge carriers have enough energy to overcome barrier (usually thermionic emission) PN Junctions ...
Electrical and Electronic Principles P3 Task 1 Electrical and
... Diodes are semiconducting devices. For a semiconductor to allow current to flow, certain conditions have to be met. In the case of the diode connecting 0.6 volts between the positve and negative terminals will cause the diode to begin conducting. This is called forward biasing the diode. Connecting ...
... Diodes are semiconducting devices. For a semiconductor to allow current to flow, certain conditions have to be met. In the case of the diode connecting 0.6 volts between the positve and negative terminals will cause the diode to begin conducting. This is called forward biasing the diode. Connecting ...
university of california - Berkeley Robotics and Intelligent Machines
... the diode voltage has a temperature coefficient of -1.5mV/K. You are using copies of this diode to make a bandgap reference as in Lab 4 (where D1 is Q2), with D2 composed of n=144 copies of D1. You can use the approximation that ln(144) ~= 5. Assuming that the current in both diodes is maintained at ...
... the diode voltage has a temperature coefficient of -1.5mV/K. You are using copies of this diode to make a bandgap reference as in Lab 4 (where D1 is Q2), with D2 composed of n=144 copies of D1. You can use the approximation that ln(144) ~= 5. Assuming that the current in both diodes is maintained at ...
Diode

In electronics, a diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance to the flow of current in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. A vacuum tube diode has two electrodes, a plate (anode) and a heated cathode. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of crystals' rectifying abilities was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. The first semiconductor diodes, called cat's whisker diodes, developed around 1906, were made of mineral crystals such as galena. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconductors such as selenium or germanium are sometimes used.