Post-Operative Time Effects after Sciatic Nerve Crush on the
... most conspicuous phenomena that occur in response to injuries. In this research, the effects of postoperative time following sciatic nerve crush on the number of spinal motoneurons were investigated. Twelve adult male Wistar rats, whose left sciatic nerves were highly compressed for 30 s, assigned t ...
... most conspicuous phenomena that occur in response to injuries. In this research, the effects of postoperative time following sciatic nerve crush on the number of spinal motoneurons were investigated. Twelve adult male Wistar rats, whose left sciatic nerves were highly compressed for 30 s, assigned t ...
Document
... CHAPTER 13 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: Brain and Spinal Cord CHAPTER OVERVIEW: This chapter provides an overview of the embryological development of the nervous system and detailed descriptions of the structure and function of the adult brain and spinal cord. Brain functions that are identified with a p ...
... CHAPTER 13 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: Brain and Spinal Cord CHAPTER OVERVIEW: This chapter provides an overview of the embryological development of the nervous system and detailed descriptions of the structure and function of the adult brain and spinal cord. Brain functions that are identified with a p ...
PowerPoint to accompany Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... •What is an Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP) and what happens to the postsynaptic neuron? •What is an Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP) and what happens to the postsynaptic neuron? ...
... •What is an Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP) and what happens to the postsynaptic neuron? •What is an Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP) and what happens to the postsynaptic neuron? ...
Experimental spinal cord transplantation as a mechanism of
... mine and many others, which can be used in cell therapy to replace missing factors in the damaged spinal cord. The grafted cells can also function in wound repair in the host nervous system by myelinating nerve fibers and contributing astrocytes. The grafts appear to be functional but the animals ar ...
... mine and many others, which can be used in cell therapy to replace missing factors in the damaged spinal cord. The grafted cells can also function in wound repair in the host nervous system by myelinating nerve fibers and contributing astrocytes. The grafts appear to be functional but the animals ar ...
a needle into the sub- and the dorsal funiculi. Preganglionic
... Lamina Ml is the largest cytoarchitectonic region of the spinal gray matter, occupying the intermediate zone between the dorsal and ven_ tral horns as well ...
... Lamina Ml is the largest cytoarchitectonic region of the spinal gray matter, occupying the intermediate zone between the dorsal and ven_ tral horns as well ...
Somatosensory Systems: Pain and Temperature - Dr
... of the lateral spinothalamic tract. These are axonal branches that come from the main axonal branch that is ascending towards thalamus. These axonal branches are given off throuhout the brainstem and midbrain and synapse in the reticular formation in these structures, as well as in the superior coll ...
... of the lateral spinothalamic tract. These are axonal branches that come from the main axonal branch that is ascending towards thalamus. These axonal branches are given off throuhout the brainstem and midbrain and synapse in the reticular formation in these structures, as well as in the superior coll ...
The Emergence of the Ectoderm: Central Nervous System and
... Atlas of the Human Brain in Section, 2nd ed., Melville Roberts, Joseph Hanaway, and D. Kent ...
... Atlas of the Human Brain in Section, 2nd ed., Melville Roberts, Joseph Hanaway, and D. Kent ...
Nervous Syst ppt
... proximal portion may survive if the cell body is not damaged. C. The distal portion will die (degenerate). Macrophages move into the area and remove debris. D. Neuron cell body reorganizes its Nissl bodies to provide proteins necessary for axon growth. E. The Schwann cells form a regeneration tube t ...
... proximal portion may survive if the cell body is not damaged. C. The distal portion will die (degenerate). Macrophages move into the area and remove debris. D. Neuron cell body reorganizes its Nissl bodies to provide proteins necessary for axon growth. E. The Schwann cells form a regeneration tube t ...
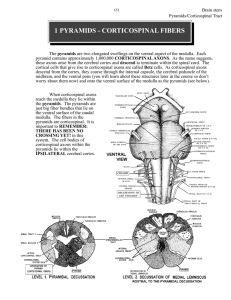
1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS
... At the most caudal pole of the pyramids the corticospinal axons cross over the midline and now continue their descent on the contralateral (to the cell of origin) side. This crossover point is called the PYRAMIDAL DECUSSATION. The crossing fibers enter the lateral funiculus of the spinal cord where ...
... At the most caudal pole of the pyramids the corticospinal axons cross over the midline and now continue their descent on the contralateral (to the cell of origin) side. This crossover point is called the PYRAMIDAL DECUSSATION. The crossing fibers enter the lateral funiculus of the spinal cord where ...
Brain Anatomy - Seattle Central College
... • Relay stations (Pyramids): Sensory & Motor nerves – conscious control of skeletal muscle ...
... • Relay stations (Pyramids): Sensory & Motor nerves – conscious control of skeletal muscle ...
lateral horns of gray matter
... Dural sinuses: function as veins, collecting blood from brain tissues for return to the heart Superior sagittal sinus—one of several dural sinuses • Falx cerebelli: separates the two hemispheres of the ...
... Dural sinuses: function as veins, collecting blood from brain tissues for return to the heart Superior sagittal sinus—one of several dural sinuses • Falx cerebelli: separates the two hemispheres of the ...
Blue Box Notes Back Strain, Sprains and Spasms (p. 495) · Warm up
... Problem when arteriosclerosis (hardening of arteries) – reduces blood flow Symptoms – prolonged turning of the head such as trying to back up in car causes lightheadedness, dizziness, and other symptoms caused by blood supply to brainstem. Compression of Lumbar Spinal Nerve Roots (p. 505) ↑ in ...
... Problem when arteriosclerosis (hardening of arteries) – reduces blood flow Symptoms – prolonged turning of the head such as trying to back up in car causes lightheadedness, dizziness, and other symptoms caused by blood supply to brainstem. Compression of Lumbar Spinal Nerve Roots (p. 505) ↑ in ...
Blue Box Notes Back Strain, Sprains and Spasms (p. 495) · Warm up
... Problem when arteriosclerosis (hardening of arteries) – reduces blood flow Symptoms – prolonged turning of the head such as trying to back up in car causes lightheadedness, dizziness, and other symptoms caused by blood supply to brainstem. Compression of Lumbar Spinal Nerve Roots (p. 505) ↑ in ...
... Problem when arteriosclerosis (hardening of arteries) – reduces blood flow Symptoms – prolonged turning of the head such as trying to back up in car causes lightheadedness, dizziness, and other symptoms caused by blood supply to brainstem. Compression of Lumbar Spinal Nerve Roots (p. 505) ↑ in ...
Spinal and Cranial Nerves
... Cranial Nerves XI and XII Accessory (XI) • primarily motor • motor to muscles of soft palate, pharynx, larynx, neck, and back ...
... Cranial Nerves XI and XII Accessory (XI) • primarily motor • motor to muscles of soft palate, pharynx, larynx, neck, and back ...
13 Anatomy of the Metencephalon and Mesencephalon
... Olivary nuclei relay info from the spinal cord, cerebral cortex, and the brainstem to the cerebellar cortex. ...
... Olivary nuclei relay info from the spinal cord, cerebral cortex, and the brainstem to the cerebellar cortex. ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... • Sensory (afferent) nerves convey sensory information to the CNS. • Motor (efferent) nerves convey motor impulses from the CNS to the muscles and glands. • Mixed nerves: both sensory and motor • Axons terminate as they contact other neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells. • An axon transmits a nerve ...
... • Sensory (afferent) nerves convey sensory information to the CNS. • Motor (efferent) nerves convey motor impulses from the CNS to the muscles and glands. • Mixed nerves: both sensory and motor • Axons terminate as they contact other neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells. • An axon transmits a nerve ...
INTERNAL CAPSULE
... both the spinal cord and cerebellum – Two reticulospinal tracts originate in the rostral pontine and medullary reticular formation • Major alternate route by which spinal neurons are controlled • Regulate sensitivity of spinal reflex arcs • Inhibition of flexor reflexes • Mediates some complex “beha ...
... both the spinal cord and cerebellum – Two reticulospinal tracts originate in the rostral pontine and medullary reticular formation • Major alternate route by which spinal neurons are controlled • Regulate sensitivity of spinal reflex arcs • Inhibition of flexor reflexes • Mediates some complex “beha ...
MODULE 4: MOTOR AND SOMATOSENSORY PATHWAYS
... spinothalamic tract and other anterolateral pathways, somatosensory cortex, central modulation of pain, and the thalamus. The key clinical concepts will include paresthesias, spinal cord lesions, sensory loss, patterns and localization, spinal cord syndromes. The book will provide the details of the ...
... spinothalamic tract and other anterolateral pathways, somatosensory cortex, central modulation of pain, and the thalamus. The key clinical concepts will include paresthesias, spinal cord lesions, sensory loss, patterns and localization, spinal cord syndromes. The book will provide the details of the ...
repair of avulsed cervical nerve roots
... to the cord itself. Recent work has raised the possibility of the repair of nerve roots avulsed from the spinal cord (Carlstedt 1991; Hems and Glasby ...
... to the cord itself. Recent work has raised the possibility of the repair of nerve roots avulsed from the spinal cord (Carlstedt 1991; Hems and Glasby ...
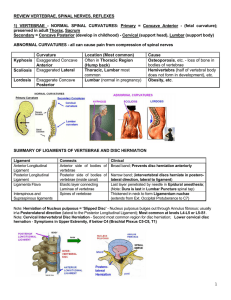
REVIEW VERTEBRAE, SPINAL NERVES, REFLEXES 1
... major lateral; IVC and Abdominal aorta anterior to bodies ...
... major lateral; IVC and Abdominal aorta anterior to bodies ...
Neural Grafting: Repairing the Brain and Spinal Cord (Part 5 of 18)
... of the synaptic contacts of a neuron can occur within a few millimeters of the cell. The ultimate wiring of the brain, made up of billions of synapses and connections, is extremely complex. Although in humans most axons reach their target sites before birth, the final configuration of the synaptic c ...
... of the synaptic contacts of a neuron can occur within a few millimeters of the cell. The ultimate wiring of the brain, made up of billions of synapses and connections, is extremely complex. Although in humans most axons reach their target sites before birth, the final configuration of the synaptic c ...
Endogenous Stem Cells in the Adult Murine Spinal Cord
... An organotypic culture of spinal cord would facilitate the rapid testing of agonists and antagonists of pro-glial and anti-neuronal factors in a three dimensionally intact, cytoarchitecturally appropriate environment. As inhibition of neurogenesis is likely to involve local cell communication, prese ...
... An organotypic culture of spinal cord would facilitate the rapid testing of agonists and antagonists of pro-glial and anti-neuronal factors in a three dimensionally intact, cytoarchitecturally appropriate environment. As inhibition of neurogenesis is likely to involve local cell communication, prese ...
Chapter 14 - MDC Faculty Home Pages
... 14.2 Protection and Support of the Spinal Cord • Spinal cord meninges – Pia mater: delicate layer adhering to spinal cord o Made of elastic and collagen fibers o Denticulate ligaments: lateral extensions of pia; help suspend spinal cord o Filum terminale: pia anchoring inferior end of spinal cord to ...
... 14.2 Protection and Support of the Spinal Cord • Spinal cord meninges – Pia mater: delicate layer adhering to spinal cord o Made of elastic and collagen fibers o Denticulate ligaments: lateral extensions of pia; help suspend spinal cord o Filum terminale: pia anchoring inferior end of spinal cord to ...
Descending Tracts
... These tracts are originated from the motor, premotor, supplementary motor and somatic sensory areas of the cerebral cortex. COURSE AND DESTINATIONS: Fibers descend in the corona radiata, then through the anterior two-thirds of the posterior limb of the internal capsule down to the brainstem. In the ...
... These tracts are originated from the motor, premotor, supplementary motor and somatic sensory areas of the cerebral cortex. COURSE AND DESTINATIONS: Fibers descend in the corona radiata, then through the anterior two-thirds of the posterior limb of the internal capsule down to the brainstem. In the ...
Investigating pain networks in the spinal cord using functional MRI
... alternatively, that ‘pain is in the brain’. However, these two statements do not mean the same thing. Regions outside of the brain, including the brainstem region, such as periaqueductal gray (PAG) matter and the rostral ventromedial medulla (RVM), have been known for decades to play an important ro ...
... alternatively, that ‘pain is in the brain’. However, these two statements do not mean the same thing. Regions outside of the brain, including the brainstem region, such as periaqueductal gray (PAG) matter and the rostral ventromedial medulla (RVM), have been known for decades to play an important ro ...
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). The spinal cord begins at the occipital bone and extends down to the space between the first and second lumbar vertebrae; it does not extend the entire length of the vertebral column. It is around 45 cm (18 in) in men and around 43 cm (17 in) long in women. Also, the spinal cord has a varying width, ranging from 13 mm (1⁄2 in) thick in the cervical and lumbar regions to 6.4 mm (1⁄4 in) thick in the thoracic area. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of neural signals between the brain and the rest of the body but also contains neural circuits that can independently control numerous reflexes and central pattern generators.The spinal cord has three major functions:as a conduit for motor information, which travels down the spinal cord, as a conduit for sensory information in the reverse direction, and finally as a center for coordinating certain reflexes.