Grade 8 Science - St. Paul's Intermediate School
... does not sink into the ground or evaporate. It flows across the Earth’s surface. Affected by ground material, amount of rain, length of time it rains, slope of the land, vegetation, and the amount of development. ...
... does not sink into the ground or evaporate. It flows across the Earth’s surface. Affected by ground material, amount of rain, length of time it rains, slope of the land, vegetation, and the amount of development. ...
Convection - Animated Science
... crust) is cracked into a number of large pieces (tectonic plates) which are constantly moving. This is as a result of convection currents within the Earth’s mantle driven by heat released by natural radioactive processes. ...
... crust) is cracked into a number of large pieces (tectonic plates) which are constantly moving. This is as a result of convection currents within the Earth’s mantle driven by heat released by natural radioactive processes. ...
Concept Review
... combine with the atmospheric oxygen to form ozone, which is a strong oxidizer, damaging materials and plants. Other Hazardous Air Pollutants (HAPs) are chemicals that pose a risk by bioaccumulation and/or persistence. Aesthetic degradation includes those things, such as noise and odors, that reduce ...
... combine with the atmospheric oxygen to form ozone, which is a strong oxidizer, damaging materials and plants. Other Hazardous Air Pollutants (HAPs) are chemicals that pose a risk by bioaccumulation and/or persistence. Aesthetic degradation includes those things, such as noise and odors, that reduce ...
Atmosphere and Weather Study Guide
... The atmosphere is a thin layer of gases that surround Earth. 2. Name the 2 major gasses in our atmosphere. How much of our atmosphere is made from each? Nitrogen makes up 78% of the earth’s atmosphere and oxygen makes up 21%. 3. Why is the atmosphere important to life on Earth? It traps energy from ...
... The atmosphere is a thin layer of gases that surround Earth. 2. Name the 2 major gasses in our atmosphere. How much of our atmosphere is made from each? Nitrogen makes up 78% of the earth’s atmosphere and oxygen makes up 21%. 3. Why is the atmosphere important to life on Earth? It traps energy from ...
final exam study guide KEY
... A sedimentary rock is a rock that forms when sediments (produced by weather, erosion, deposition) are compacted and cemented together. Sediments can be a variety of sizes and be organic or inorganic. What’s an intrusive igneous rock? How does it form? These rocks form from cooled magma below Earth ...
... A sedimentary rock is a rock that forms when sediments (produced by weather, erosion, deposition) are compacted and cemented together. Sediments can be a variety of sizes and be organic or inorganic. What’s an intrusive igneous rock? How does it form? These rocks form from cooled magma below Earth ...
How Green is My Building? Resource systems in buildings
... In conducting a “green audit” of a building, the following need to be considered • Resources & materials in the building structure and moving through the building • Lifecycle costs of those materials (e.g., new, recycled, energy inputs) & activities? • Broader ecological impacts of acquiring those ...
... In conducting a “green audit” of a building, the following need to be considered • Resources & materials in the building structure and moving through the building • Lifecycle costs of those materials (e.g., new, recycled, energy inputs) & activities? • Broader ecological impacts of acquiring those ...
dry adiabatic rate
... • The atmosphere is absolutely stable when the air at the surface is either cooler than the air aloft (an inversion), or the temperature difference between the warmer surface air and the air aloft is not very great, I.e., the environmental lapse rate is less than the moist adiabatic rate. ...
... • The atmosphere is absolutely stable when the air at the surface is either cooler than the air aloft (an inversion), or the temperature difference between the warmer surface air and the air aloft is not very great, I.e., the environmental lapse rate is less than the moist adiabatic rate. ...
air pollution - sabresocials.com
... soil is toxic to plants. It also causes the soil surface to compact, and crust over. ...
... soil is toxic to plants. It also causes the soil surface to compact, and crust over. ...
grade_8_chapter_2_and_part_of_3_study_guide_2015_answers
... A large “hole” in the Earth’s surface (usually greater than 2000 m) that holds ocean water. (b) How were the ocean basins’s first formed? According to some scientists, the Earth’s continents were thought to have been all together in a super continent called Pangea. The magma, in the Mantle, oozed up ...
... A large “hole” in the Earth’s surface (usually greater than 2000 m) that holds ocean water. (b) How were the ocean basins’s first formed? According to some scientists, the Earth’s continents were thought to have been all together in a super continent called Pangea. The magma, in the Mantle, oozed up ...
Document
... composition of rocks. Water is mixed with carbon dioxide from the air and dissolves certain rocks such as limestone. ...
... composition of rocks. Water is mixed with carbon dioxide from the air and dissolves certain rocks such as limestone. ...
Geothermal Energy: Natural heat energy produced by the Earth
... from geothermal reservoirs, is passed through heat exchanger, ...
... from geothermal reservoirs, is passed through heat exchanger, ...
Geothermal Energy: Natural heat energy produced by the Earth
... from geothermal reservoirs, is passed through heat exchanger, ...
... from geothermal reservoirs, is passed through heat exchanger, ...
Chapter 11 Water Water Resources Water Use and Management
... Power-plant cooling systems: pump water from rivers or lakes, carry it in a cooling tower, then pumping it back into the source. ...
... Power-plant cooling systems: pump water from rivers or lakes, carry it in a cooling tower, then pumping it back into the source. ...
A-Cubed - Building Products Index
... offers efficiency figures of up to 144% (Air 7°C, Water 35°C, gross CV of fuel and after deduction of the parasitic losses). This means the A-Cubed achieves the efficiency level of A+++ under the EuP Directive at these operating temperatures. Using A-Cubed as either the sole heat generating applianc ...
... offers efficiency figures of up to 144% (Air 7°C, Water 35°C, gross CV of fuel and after deduction of the parasitic losses). This means the A-Cubed achieves the efficiency level of A+++ under the EuP Directive at these operating temperatures. Using A-Cubed as either the sole heat generating applianc ...
Name
... 11. What process causes cloud formation? Condensation or deposition of water above the Earth's surface creates clouds. In general, clouds develop in any air mass that becomes saturated (relative humidity becomes 100 %). Saturation can occur by way of atmospheric mechanisms that cause the temperature ...
... 11. What process causes cloud formation? Condensation or deposition of water above the Earth's surface creates clouds. In general, clouds develop in any air mass that becomes saturated (relative humidity becomes 100 %). Saturation can occur by way of atmospheric mechanisms that cause the temperature ...
Chapter 9 Surface Water
... condensation powered by the sun. The pathway may spend time within a living organism or as part of a glacier, lake, ocean, etc. ...
... condensation powered by the sun. The pathway may spend time within a living organism or as part of a glacier, lake, ocean, etc. ...
Grade 8 Quiz Review #2 – Water Systems
... Long walls of earth, are built parallel to a river. They are designed to keep the river contained during flooding. Landslide – a massive movement of soil and water, often after heavy rain Water Tables Two forces appear to act on water: gravity and its attraction to other materials ...
... Long walls of earth, are built parallel to a river. They are designed to keep the river contained during flooding. Landslide – a massive movement of soil and water, often after heavy rain Water Tables Two forces appear to act on water: gravity and its attraction to other materials ...
Heat overhead notes - SD43 Teacher Sites
... e.g. sun’s light energy is absorbed by Earth’s water, rocks, and soil, which changes to heat >> it warms the layer of air closest to Earth’s surface >> reason why the temperature is warmer closer to Earth than at the top of a mountain Convection Movement of thermal energy from one area to another th ...
... e.g. sun’s light energy is absorbed by Earth’s water, rocks, and soil, which changes to heat >> it warms the layer of air closest to Earth’s surface >> reason why the temperature is warmer closer to Earth than at the top of a mountain Convection Movement of thermal energy from one area to another th ...
20130926123994
... These plates are still moving. Who knows…. In thousands of years California may be located off the coast of Canada! ...
... These plates are still moving. Who knows…. In thousands of years California may be located off the coast of Canada! ...
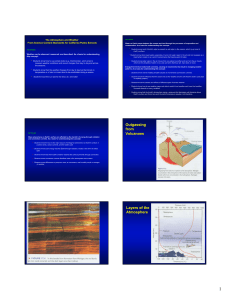
Outgassing from Volcanoes Layers of the Atmosphere
... measure weather conditions and record changes from day to day and across the seasons. ...
... measure weather conditions and record changes from day to day and across the seasons. ...
Air well (condenser)

An air well or aerial well is a structure or device that collects water by promoting the condensation of moisture from air. Designs for air wells are many and varied, but the simplest designs are completely passive, require no external energy source and have few, if any, moving parts.Three principal designs are used for air wells, designated as high mass, radiative, and active: High-mass air wells were used in the early 20th century, but the approach failed. From the late 20th century onwards, low-mass, radiative collectors proved to be much more successful. Active collectors collect water in the same way as a dehumidifier; although the designs work well, they require an energy source, making them uneconomical except in special circumstances. New, innovative designs seek to minimise the energy requirements of active condensers or make use of renewable energy resources.↑ ↑ ↑ 3.0 3.1