Water Cycle
... body of water and travels into the air. Condensation: Water vapor in the air becomes cold and changes back into a liquid. When this happens, clouds are formed. Precipitation: Occurs when so much water has condensed that the air can no longer hold it. Clouds get heavy and the water falls back to the ...
... body of water and travels into the air. Condensation: Water vapor in the air becomes cold and changes back into a liquid. When this happens, clouds are formed. Precipitation: Occurs when so much water has condensed that the air can no longer hold it. Clouds get heavy and the water falls back to the ...
Earth Science Weather Variable Review Sheet Topics: Air
... How do winds move (High- to Low-Pressure or from Low- to High-Pressure)? What causes winds on the surface of Earth? Understand the convection currents for land and sea breezes between day and night. Cloud Formation Understand the conditions for the formation of a cloud (air rises and cools, ...
... How do winds move (High- to Low-Pressure or from Low- to High-Pressure)? What causes winds on the surface of Earth? Understand the convection currents for land and sea breezes between day and night. Cloud Formation Understand the conditions for the formation of a cloud (air rises and cools, ...
Hydrologic Cycle Note
... leaves behind salts and other impurities as it evaporates. As the evaporated moisture rises, it declines in temperature at the average rate of 1°C/100m. Moving air masses carry the vapour over the land. Condensation: Water vapour is changed to a liquid (or solid). A critical temperature called “dewp ...
... leaves behind salts and other impurities as it evaporates. As the evaporated moisture rises, it declines in temperature at the average rate of 1°C/100m. Moving air masses carry the vapour over the land. Condensation: Water vapour is changed to a liquid (or solid). A critical temperature called “dewp ...
The Water Cycle
... Condensation: water changing from a gas to a liquid. Just as evaporation requires warmer temperatures, condensation occurs when air that is holding water vapor cools. If this happens in the atmosphere, a cloud forms (clouds are a bunch of water droplets or ice crystals). If it happens on the surface ...
... Condensation: water changing from a gas to a liquid. Just as evaporation requires warmer temperatures, condensation occurs when air that is holding water vapor cools. If this happens in the atmosphere, a cloud forms (clouds are a bunch of water droplets or ice crystals). If it happens on the surface ...
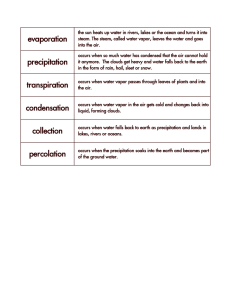
evaporation precipitation transpiration condensation collection
... occurs when so much water has condensed that the air cannot hold it anymore. The clouds get heavy and water falls back to the earth in the form of rain, hail, sleet or snow. ...
... occurs when so much water has condensed that the air cannot hold it anymore. The clouds get heavy and water falls back to the earth in the form of rain, hail, sleet or snow. ...
Unit 8 Vocabulary - Part 1 Atmosphere
... caused by temperature changes in liquid or gas. Oceans, storm clouds and the earth’s crust are all affected by convection currents. ...
... caused by temperature changes in liquid or gas. Oceans, storm clouds and the earth’s crust are all affected by convection currents. ...
DoubleJeopardy2
... The topsoil of a mature prairie has more of what material than The layers below? ...
... The topsoil of a mature prairie has more of what material than The layers below? ...
Water Cycle and Weather Vocabulary
... Earth to the air and back again Evaporation the process by which liquid water changes into water vapor ...
... Earth to the air and back again Evaporation the process by which liquid water changes into water vapor ...
Radiation
... • All 3 phases exist naturally in normal atmospheric temperature ranges • All 3 phases can and do exist at the same temperature ...
... • All 3 phases exist naturally in normal atmospheric temperature ranges • All 3 phases can and do exist at the same temperature ...
Ch 11 Vocabulary
... local winds (p. 395). Movements of air that result from local changes in temperatures (p. 401). prevailing winds (p. 395). Global winds that blow constantly from the same direction (p. 402). water cycle (p. 405). The process in which water continuously moves from Earth’s surface into the atmosphere ...
... local winds (p. 395). Movements of air that result from local changes in temperatures (p. 401). prevailing winds (p. 395). Global winds that blow constantly from the same direction (p. 402). water cycle (p. 405). The process in which water continuously moves from Earth’s surface into the atmosphere ...
air temperature
... Due to the heat air absorbs from or gives off to the environment. SPECIFIC HEAT – amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a substance. Thermometer ...
... Due to the heat air absorbs from or gives off to the environment. SPECIFIC HEAT – amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a substance. Thermometer ...
Weather and Water Cycle Notes
... Humidity: Amount of water vapor or moisture in the air Relative Humidity (%) the amount of moisture the air contains compared to the amount it can hold Evaporation: Liquid changing into water vapor (gas) rising into the Atmosphere Transpiration: the process where plants release water vapor into the ...
... Humidity: Amount of water vapor or moisture in the air Relative Humidity (%) the amount of moisture the air contains compared to the amount it can hold Evaporation: Liquid changing into water vapor (gas) rising into the Atmosphere Transpiration: the process where plants release water vapor into the ...
Air well (condenser)

An air well or aerial well is a structure or device that collects water by promoting the condensation of moisture from air. Designs for air wells are many and varied, but the simplest designs are completely passive, require no external energy source and have few, if any, moving parts.Three principal designs are used for air wells, designated as high mass, radiative, and active: High-mass air wells were used in the early 20th century, but the approach failed. From the late 20th century onwards, low-mass, radiative collectors proved to be much more successful. Active collectors collect water in the same way as a dehumidifier; although the designs work well, they require an energy source, making them uneconomical except in special circumstances. New, innovative designs seek to minimise the energy requirements of active condensers or make use of renewable energy resources.↑ ↑ ↑ 3.0 3.1