Chapter 9 Linear transformations
... with ad − bc = 0 but a, b, c, d not all zero? Suppose for example that none of a, b, c, d is zero. Then ad − bc = 0 implies that a/c = b/d, so the second column of A is a scalar multiple of the first column. Writing u for first column of A and λu for the second column of A we see that ...
... with ad − bc = 0 but a, b, c, d not all zero? Suppose for example that none of a, b, c, d is zero. Then ad − bc = 0 implies that a/c = b/d, so the second column of A is a scalar multiple of the first column. Writing u for first column of A and λu for the second column of A we see that ...
Linear Algebra 1 Exam 2 Solutions 7/14/3
... We insert the formulas for x, y and z for the line L into the equation of the plane and solve for t: 5(2 + 5t) − (−4 − t) + 7 + t = 12, ...
... We insert the formulas for x, y and z for the line L into the equation of the plane and solve for t: 5(2 + 5t) − (−4 − t) + 7 + t = 12, ...
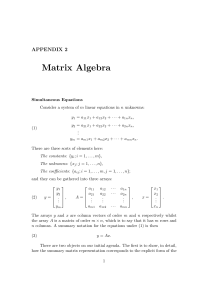
matrix
... • A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. • A matrix with m rows and n columns is called an m × n matrix. • The plural of matrix is matrices. A matrix with the same number of rows as columns is called square. • Two matrices are equal if they have the same number of rows and the same number of co ...
... • A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. • A matrix with m rows and n columns is called an m × n matrix. • The plural of matrix is matrices. A matrix with the same number of rows as columns is called square. • Two matrices are equal if they have the same number of rows and the same number of co ...
0.1 Linear Transformations
... TB ◦ TA = TBA Remark: This equation points out an important interpretation of the matrix product. Composition of two linear transformations is equivalent to the multiplication of two matrices. Example 10 In general: Composition is not commutative. T1 :reflection about y = x, and T2 orthogonal projec ...
... TB ◦ TA = TBA Remark: This equation points out an important interpretation of the matrix product. Composition of two linear transformations is equivalent to the multiplication of two matrices. Example 10 In general: Composition is not commutative. T1 :reflection about y = x, and T2 orthogonal projec ...
(1) as fiber bundles
... If X is a complex manifold, then (T∗ )R X comes with an action J (corresponding to multiplication by i) on each fiber. For (T∗ ) ⊗ C, J acts (functorially) and T∗ ⊗ C ∼ = T1,0 ⊕ T0,1 , where T1,0 is the i eigenspace, and T0,1 is the −i eigenspace for J. Sections of T1,0 are (1, 0)P ∂ vector fields, ...
... If X is a complex manifold, then (T∗ )R X comes with an action J (corresponding to multiplication by i) on each fiber. For (T∗ ) ⊗ C, J acts (functorially) and T∗ ⊗ C ∼ = T1,0 ⊕ T0,1 , where T1,0 is the i eigenspace, and T0,1 is the −i eigenspace for J. Sections of T1,0 are (1, 0)P ∂ vector fields, ...
Physics Practice Exam Solutions
... hr. So the average velocity is (1 km)/( 2.16667 hr) = 0.46 km/hr 6. [E] If we have v(t), we can find a(t) just by taking a derivative, so a(t)= 3at² + 4at³ = 3t² + 8t³, so a(3)= 3(3)² + 8(3)³ = 243 7. [D] If you draw a straight line from City A to City B, this will be the sum of your two vectors, th ...
... hr. So the average velocity is (1 km)/( 2.16667 hr) = 0.46 km/hr 6. [E] If we have v(t), we can find a(t) just by taking a derivative, so a(t)= 3at² + 4at³ = 3t² + 8t³, so a(3)= 3(3)² + 8(3)³ = 243 7. [D] If you draw a straight line from City A to City B, this will be the sum of your two vectors, th ...